Related Research Articles

Medieval music encompasses the sacred and secular music of Western Europe during the Middle Ages, from approximately the 6th to 15th centuries. It is the first and longest major era of Western classical music and followed by the Renaissance music; the two eras comprise what musicologists generally term as early music, preceding the common practice period. Following the traditional division of the Middle Ages, medieval music can be divided into Early (500–1150), High (1000–1300), and Late (1300–1400) medieval music.

Gregorian chant is the central tradition of Western plainchant, a form of monophonic, unaccompanied sacred song in Latin of the Roman Catholic Church. Gregorian chant developed mainly in western and central Europe during the 9th and 10th centuries, with later additions and redactions. Although popular legend credits Pope Gregory I with inventing Gregorian chant, scholars believe that it arose from a later Carolingian synthesis of the Old Roman chant and Gallican chant.
Organum is, in general, a plainchant melody with at least one added voice to enhance the harmony, developed in the Middle Ages. Depending on the mode and form of the chant, a supporting bass line may be sung on the same text, the melody may be followed in parallel motion, or a combination of both of these techniques may be employed. As no real independent second voice exists, this is a form of heterophony. In its earliest stages, organum involved two musical voices: a Gregorian chant melody, and the same melody transposed by a consonant interval, usually a perfect fifth or fourth. In these cases the composition often began and ended on a unison, the added voice keeping to the initial tone until the first part has reached a fifth or fourth, from where both voices proceeded in parallel harmony, with the reverse process at the end. Organum was originally improvised; while one singer performed a notated melody, another singer—singing "by ear"—provided the unnotated second melody. Over time, composers began to write added parts that were not just simple transpositions, thus creating true polyphony.
In psychometrics, item response theory (IRT) is a paradigm for the design, analysis, and scoring of tests, questionnaires, and similar instruments measuring abilities, attitudes, or other variables. It is a theory of testing based on the relationship between individuals' performances on a test item and the test takers' levels of performance on an overall measure of the ability that item was designed to measure. Several different statistical models are used to represent both item and test taker characteristics. Unlike simpler alternatives for creating scales and evaluating questionnaire responses, it does not assume that each item is equally difficult. This distinguishes IRT from, for instance, Likert scaling, in which "All items are assumed to be replications of each other or in other words items are considered to be parallel instruments". By contrast, item response theory treats the difficulty of each item as information to be incorporated in scaling items.

Cheering involves the uttering or making of sounds and may be used to encourage, excite to action, indicate approval or welcome.
Induction puzzles are logic puzzles, which are examples of multi-agent reasoning, where the solution evolves along with the principle of induction.
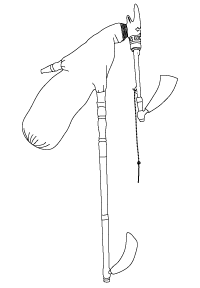
The Hungarian duda is the traditional bagpipe of Hungary. It is an example of a group of bagpipes called Medio-Carparthian bagpipes.

Buller's albatross or Buller's mollymawk, is a small mollymawk in the albatross family.

Forty Forty is a children's game combining elements of the games "It" and Hide and seek. One player is "on", or "It", and they must capture the other players by 'spying' them rather than by tagging.

The Symphony No. 5 in E-flat major, Op. 82, is a three-movement work for orchestra written from 1914 to 1915 by the Finnish composer Jean Sibelius. He revised it in 1916 and again from 1917 to 1919, at which point it reached its final form.
A skipping rhyme, is a rhyme chanted by children while skipping. Such rhymes have been recorded in all cultures where skipping is played. Examples of English-language rhymes have been found going back to at least the 17th century. Like most folklore, skipping rhymes tend to be found in many different variations. The article includes those chants used by English-speaking children.
Skedaddle is a children's game show that aired in late 1988 for six weeks as a part of The Funtastic World of Hanna-Barbera block of shows. It was hosted by guest star Ron Pearson, and created by William Hanna and Joseph Barbera. The show was executive produced by Hanna and Barbera, along with Jay Wolpert for the autumn season being aired for eight months.
Who's missing? is a game for children ages kindergarten through 6th grade, and is often played in the classroom. In this game, one student hides his or her eyes while other children trade seats and one child from the group leaves the room. Alternatively, the person who is supposed to guess leaves the room while another child hides. Once everyone else is in a seat, the leader or teacher will say, "Turn around and see who's missing." The child will then try to figure out who's missing.

The Royal Dramatic Training Academy, was the acting school of Sweden's national stage, the Royal Dramatic Theatre, and for many years (1787–1964) seen as the foremost theatre school and drama education for Swedish stage actors. It was established in 1787 by the theatre and art loving King Gustav III and was for many years under the protection of the Swedish royal family.
Traditional Filipino games or indigenous games in the Philippines are games that have been played across multiple generations, usually using native materials or instruments. In the Philippines, due to limited resources for toys, children usually invent games without needing anything but players.There are different kinds of Philippine Traditional Games that are suited for kids, and the games also stand as one of the different culture and/or traditional games of the Philippines. These games are not only fun to play, but these games are also good for you. This is because different games require different skills. These games are also an important part in Filipino culture.

Braingames is an American educational program shown on HBO in the mid-1980s. It was a half-hour program consisting of brain-teasing animated skits designed to make the viewers think. It was HBO's first attempt at a show focused on educational skits, predating Crashbox by 15 years.

A guess is a swift conclusion drawn from data directly at hand, and held as probable or tentative, while the person making the guess admittedly lacks material for a greater degree of certainty. A guess is also an unstable answer, as it is "always putative, fallible, open to further revision and interpretation, and validated against the horizon of possible meanings by showing that one interpretation is more probable than another in light of what we already know". In many of its uses, "the meaning of guessing is assumed as implicitly understood", and the term is therefore often used without being meticulously defined. Guessing may combine elements of deduction, induction, abduction, and the purely random selection of one choice from a set of given options. Guessing may also involve the intuition of the guesser, who may have a "gut feeling" about which answer is correct without necessarily being able to articulate a reason for having this feeling.

"Discovering Japan" is a song by British rock musician Graham Parker, recorded with his backing band the Rumour. The song was released on his 1979 album, Squeezing Out Sparks.
"Dragonborn" is the theme song for the soundtrack of the 2011 role-playing video game The Elder Scrolls V: Skyrim from Bethesda Softworks, composed by the American composer Jeremy Soule. The composition is Nordic-influenced classical in style and features a chorus singing lyrics in a fictional language, Dovahzul, that was created by Emil Pagliarulo for the game. The composition borrows heavily from "Nerevar Rising", the theme from The Elder Scrolls III: Morrowind, as well as elements from music in The Elder Scrolls IV: Oblivion, both of which were also composed by Soule. "Dragonborn" was lauded by critics and audiences alike. It is featured in orchestral performances and spawned numerous covers, many of which combine the song with an in-game, English-language composition "The Dragonborn Comes". One such cover, by Lindsey Stirling and Peter Hollens, holds the Guinness World Record for most viewed cover version of a video game soundtrack.
References
- ↑ Nordlander, Johan. 1886. Svenska barnvisor och barnrim, vol 1, p. 115-116.
- ↑ Widerberg, Gertrud. 1993. Bulleri bulleri bock! : ramsor om våra husdjur Stockholm: Rabén & Sjögren. ISBN 91-29-62233-6