Related Research Articles

A condominium is an ownership regime in which a building is divided into multiple units that are either each separately owned, or owned in common with exclusive rights of occupation by individual owners. These individual units are surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned and managed by the owners of the units. The term can be applied to the building or complex itself, and is sometimes applied to individual units. The term "condominium" is mostly used in the US and Canada, but similar arrangements are used in many other countries under different names.

In legal usage in the English-speaking world, an act of God, act of nature, or damnum fatale is an event caused by no direct human action for which individual persons are not responsible and cannot be held legally liable for loss of life, injury, or property damage. An act of God may amount to an exception to liability in contracts, or it may be an "insured peril" in an insurance policy. In Scots law, the equivalent term is damnum fatale, while most Common law proper legal systems use the term act of God.
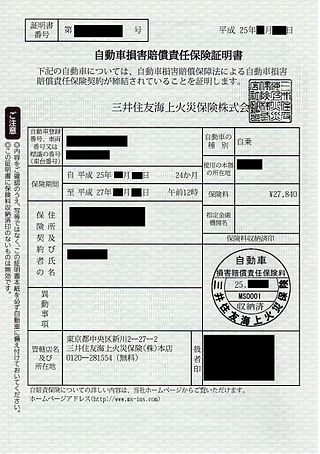
Vehicle insurance is insurance for cars, trucks, motorcycles, and other road vehicles. Its primary use is to provide financial protection against physical damage or bodily injury resulting from traffic collisions and against liability that could also arise from incidents in a vehicle. Vehicle insurance may additionally offer financial protection against theft of the vehicle, and against damage to the vehicle sustained from events other than traffic collisions, such as vandalism, weather or natural disasters, and damage sustained by colliding with stationary objects. The specific terms of vehicle insurance vary with legal regulations in each region.

A private limited company is any type of business entity in "private" ownership used in many jurisdictions, in contrast to a publicly listed company, with some differences from country to country. Examples include the LLC in the United States, private company limited by shares in the United Kingdom, GmbH in Germany and Austria, Besloten vennootschap (BV) in The Netherlands and Belgium, société à responsabilité limitée (SARL) in France, and sociedad de responsabilidad limitada (SRL) in the Spanish-speaking world. The benefit of having a private limited company is that there is limited liability.
A waiver is the voluntary relinquishment or surrender of some known right or privilege.
In its broadest sense, no-fault insurance is any type of insurance contract under which the insured party is indemnified by their own insurance company for losses, regardless of the source of the cause of loss. In this sense, it is similar to first-party coverage. The term "no-fault" is most commonly used in the United States, Australia, and Canada when referring to state or provincial automobile insurance laws where a policyholder and their passengers are reimbursed by the policyholder's own insurance company without proof of fault, and are restricted in their right to seek recovery through the civil-justice system for losses caused by other parties. No-fault insurance has the goal of lowering premium costs by avoiding expensive litigation over the causes of the collision, while providing quick payments for injuries or loss of property.
Liability insurance is a part of the general insurance system of risk financing to protect the purchaser from the risks of liabilities imposed by lawsuits and similar claims and protects the insured if the purchaser is sued for claims that come within the coverage of the insurance policy.

A garde champêtre is the combination of a forest ranger, game warden and code enforcement officer in certain rural communes in France.

The French national identity card is an official identity document consisting of an electronic ID-1 card bearing a photograph, name and address. While the identity card is non-compulsory, all persons must possess some form of valid government-issued identity documentation.
The French Institut de radioprotection et de sûreté nucléaire (IRSN) located in Fontenay-aux-Roses is a public official establishment with an industrial and commercial aspect (EPIC) created by the AFSSE Act and by February 22, 2002 decreed n°2002-254. The IRSN is placed under the conjoint authority of the Defence minister, the Environmental minister, the Industry minister and the Health and Research minister.
A car rental, hire car or car hire agency is a company that rents automobiles for short periods of time to the public, generally ranging from a few hours to a few weeks. It is often organized with numerous local branches, and primarily located near airports or busy city areas and often complemented by a website allowing online reservations.

DZI, an acronym for State Insurance Institute is a Bulgarian company primarily engaged in various forms of insurance.

The Occupiers' Liability Act 1957 is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom that covers occupiers' liability. The result of the Third Report of the Law Reform Committee, the act was introduced to Parliament as the Occupiers' Liability Bill and granted royal assent on 6 June 1957, coming into force on 1 January 1958.

Civil conscription is the obligation of civilians to perform mandatory labour for the government. This kind of work has to correspond with the exceptions in international agreements, otherwise it could fall under the category of unfree labour. There are two basic kinds of civil conscriptions. On the one hand, a compulsory service can be ordered on a temporary basis during wartimes and other times of emergency, like severe economic crisis or extraordinary natural events to provide basic services to the population. These include, but are not limited to, medical care, food supplies, defense industry supplies or cleanup efforts, following a severe weather or environmental disaster for the duration of the emergency. Therefore, it generally makes striking illegal for the duration of the civil mobilization. On the other hand, a revolving mandatory service may be required for a longer period of time, for example, to ensure community fire protection or to carry out infrastructure work at a local or community level.
Vehicle insurance in the United States is designed to cover the risk of financial liability or the loss of a motor vehicle that the owner may face if their vehicle is involved in a collision that results in property or physical damage. Most states require a motor vehicle owner to carry some minimum level of liability insurance. States that do not require the vehicle owner to carry car insurance include Virginia, where an uninsured motor vehicle fee may be paid to the state, New Hampshire, and Mississippi, which offers vehicle owners the option to post cash bonds. The privileges and immunities clause of Article IV of the U.S. Constitution protects the rights of citizens in each respective state when traveling to another. A motor vehicle owner typically pays insurers a monthly or yearly fee, often called an insurance premium. The insurance premium a motor vehicle owner pays is usually determined by a variety of factors including the type of covered vehicle, marital status, credit score, whether the driver rents or owns a home, the age and gender of any covered drivers, their driving history, and the location where the vehicle is primarily driven and stored. Most insurance companies will increase insurance premium rates based on these factors and offer discounts less frequently.
Increases in the use of autonomous car technologies are causing incremental shifts in the responsibility of driving, with the primary motivation of reducing the frequency of traffic collisions. Liability for incidents involving self-driving cars is a developing area of law and policy that will determine who is liable when a car causes physical damage to persons or property. As autonomous cars shift the responsibility of driving from humans to autonomous car technology, there is a need for existing liability laws to evolve to reasonably identify the appropriate remedies for damage and injury. As higher levels of autonomy are commercially introduced, the insurance industry stands to see higher proportions of commercial and product liability lines of business, while the personal automobile insurance line of business shrinks.
Workers' compensation in the United States is a primarily state-based system of workers' compensation.
The French code of criminal procedure is the codification of French criminal procedure, "the set of legal rules in France that govern the State's response to offenses and offenders". It guides the behavior of police, prosecutors, and judges in dealing with a possible crime. The current code was established in 1958 and replaced the code of 1808 created under Napoleon.

Vehicle insurance in France is an compensation-based insurance policy for terrestrial motor vehicles that are insured in France and circulate on French territory, as well as in the European Economic Area and the Green Card zone.
The anti-money laundering framework for financial institutions in France encompasses the key components of the country's regulations aimed at combating money laundering and terrorist financing. This framework includes the laws and regulations established for responsible parties, ensuring compliance with international initiatives.
References
- ↑ "Chapitre II : L'obligation d'assurer. Le bureau central de tarification. (Articles L252-1 à L252-2) - Légifrance". www.legifrance.gouv.fr. Retrieved 2024-03-25.
- ↑ "Le Bureau Central de Tarification". Association Léo Lagrange pour la défense des consommateurs (in French). 2024-03-15. Retrieved 2024-03-25.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Acedo, Sébastien (June 11, 2015). Réglementation : le Bureau central de tarification retrouve une stabilité. L'Argus de l'assurance.
- ↑ Qu'est ce que le BCT Quel est son rôle ?