Blissymbols or Blissymbolics is a constructed language conceived as an ideographic writing system called Semantography consisting of several hundred basic symbols, each representing a concept, which can be composed together to generate new symbols that represent new concepts. Blissymbols differ from most of the world's major writing systems in that the characters do not correspond at all to the sounds of any spoken language.
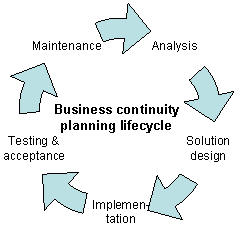
Business continuity may be defined as "the capability of an organization to continue the delivery of products or services at pre-defined acceptable levels following a disruptive incident", and business continuity planning is the process of creating systems of prevention and recovery to deal with potential threats to a company. In addition to prevention, the goal is to enable ongoing operations before and during execution of disaster recovery. Business continuity is the intended outcome of proper execution of both business continuity planning and disaster recovery.
Succession planning is a process and strategy for replacement planning or passing on leadership roles. It is used to identify and develop new, potential leaders who can move into leadership roles when they become vacant. Succession planning in dictatorships, monarchies, politics, and international relations is used to ensure continuity and prevention of power struggle. Within monarchies succession is settled by the order of succession. In business, succession planning entails developing internal people with managing or leadership potential to fill key hierarchical positions in the company. It is a process of identifying critical roles in a company and the core skills associated with those roles, and then identifying possible internal candidates to assume those roles when they become vacant. Succession planning also applies to small and family businesses where it is the process used to transition the ownership and management of a business to the next generation.

GMTV, now legally known as ITV Breakfast Broadcasting Limited, was the name of the national ITV breakfast television contractor/licensee, broadcasting in the United Kingdom from 1 January 1993 to 3 September 2010. It became a wholly owned subsidiary of ITV plc in November 2009. Shortly after, ITV plc announced the programme would end. The final edition of GMTV was broadcast on 3 September 2010.

Sir John Andrew Likierman, is the former Dean of the London Business School. In August 2017, he was succeeded by François Ortalo-Magné.
China Europe International Business School is a business school headquartered in Pudong, Shanghai, China. CEIBS has campuses in Shanghai, Beijing, Shenzhen, Accra in Ghana, and Zurich in Switzerland.

Indian Institute of Management Indore is an autonomous public business school located in Indore, Madhya Pradesh in India. Founded in 1996, IIM Indore is the sixth institute in the Indian Institute of Management (IIM) system and was named as an institute of national importance in 2017 along with the other IIMs.
Newstalk is a national independent radio station in Ireland. It is operated by News 106 Limited, a subsidiary of Bauer Media Audio Ireland, and broadcasts under a sound broadcasting contract with the Broadcasting Authority of Ireland.

Bluevale Collegiate Institute is a secondary school in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada, run by the Waterloo Region District School Board. As of the 2019–2020 school year, Bluevale has an enrollment of 1,240 students. The school opened in 1972 under the direction of principal Robert Chilton, and vice-principal Charlie Wilson, initially with grades 9 through 11, adding grades 12, and then 13 in subsequent years. Bluevale's new school boundary took in students previously registered at Cameron Heights Collegiate Institute, Kitchener–Waterloo Collegiate, and Waterloo Collegiate Institute. As of 2022, the principal is Deborah Tyrrell.

CRANN, the Centre for Research on Adaptive Nanostructures and Nanodevices, is Ireland's first purpose-built research institute whose purpose is to perform nanoscience research. It is housed in the Naughton Institute on the campus of Trinity College Dublin. Crann is the Irish word for tree.

Cranfield School of Management, established in 1967, is a business school that is part of Cranfield University in Bedfordshire, United Kingdom. Cranfield School of Management is triple accredited by the Association of MBAs (AMBA), EQUIS and AACSB.
KIMEP University is a private university founded in 1992 in Almaty, Kazakhstan.

Countess Walburga Douglas is a German-born Swedish lawyer and politician, who served as a member of the Riksdag of Sweden for the Moderate Party from 2006 to 2014. She is the vice-president of the Paneuropean Union and a board member of the Institute for Information on the Crimes of Communism.
Walker Lee Cisler was a noted American engineer, business executive, and a founding member of the National Academy of Engineering.

Bar Council of India (BCI) is a statutory body established under section 4 of the Advocates Act 1961 that regulates the legal practice and legal education in India. Its members are elected from amongst the lawyers in India and represent the Indian bar. It prescribes standards of professional conduct, etiquettes and exercises disciplinary jurisdiction over the bar. It also sets standards for legal education and grants recognition to universities whose law degrees will qualify students to enrol themselves as advocates upon graduation.
Brantford Collegiate Institute and Vocational School, also known as "Brantford Collegiate Institute" or "BCI", is a secondary school in the city of Brantford. It is a member of the Grand Erie District School Board, a medium-sized school board in the Province of Ontario. About 1350 students attend BCI. BCI has many sports teams, clubs, and an active Library Learning Commons.
Blessing the Children International (BCI) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization, founded in 2001, that engages in Christian missionary work in Ethiopia, Africa. According to the Urban Institute, BCI is classified as an "International Relief" organization.
The University of CEMA is a private university in Buenos Aires, Argentina. It was founded by Carlos Rodríguez, along with Roque Fernández and Pedro Pou, as the Center for Macro-economic Studies of Argentina (CEMA) University Institute in 1995, a pioneer in higher education programs in the areas of economics, politics, management, and finance in Argentina.
The Cambridge Institute for Sustainability Leadership (CISL), formerly the Cambridge Programme for Sustainability Leadership and the Cambridge Programme for Industry, is part of the University of Cambridge.









