
Vasodilation is the widening of blood vessels. It results from relaxation of smooth muscle cells within the vessel walls, in particular in the large veins, large arteries, and smaller arterioles. The process is the opposite of vasoconstriction, which is the narrowing of blood vessels.
ATC code C02Antihypertensives is a therapeutic subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System, a system of alphanumeric codes developed by the World Health Organization (WHO) for the classification of drugs and other medical products. Subgroup C02 is part of the anatomical group C Cardiovascular system.
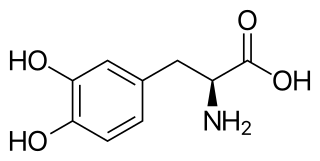
l-DOPA, also known as levodopa and l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, is an amino acid that is made and used as part of the normal biology of humans, as well as some animals and plants. Humans, as well as a portion of the other animals that utilize l-DOPA in their biology, make it via biosynthesis from the amino acid l-tyrosine. l-DOPA is the precursor to the neurotransmitters dopamine, norepinephrine (noradrenaline), and epinephrine (adrenaline), which are collectively known as catecholamines. Furthermore, l-DOPA itself mediates neurotrophic factor release by the brain and CNS. l-DOPA can be manufactured and in its pure form is sold as a psychoactive drug with the INN levodopa; trade names include Sinemet, Pharmacopa, Atamet, and Stalevo. As a drug, it is used in the clinical treatment of Parkinson's disease and dopamine-responsive dystonia.

Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes on physical examination.
Carbidopa (Lodosyn) is a drug given to people with Parkinson's disease in order to inhibit peripheral metabolism of levodopa. This property is significant in that it allows a greater proportion of peripheral levodopa to cross the blood–brain barrier for central nervous system effect.

Methyldopa, sold under the brand name Aldomet among others, is a medication used for high blood pressure. It is one of the preferred treatments for high blood pressure in pregnancy. For other types of high blood pressure including very high blood pressure resulting in symptoms other medications are typically preferred. It can be given by mouth or injection into a vein. Onset of effects is around 5 hours and they last about a day.
Breast pain is the symptom of discomfort in the breast. Pain that involves both breasts and which occurs repeatedly before the menstrual period is generally not serious. Pain that involves only one part of a breast is more concerning. It is particularly concerning if a hard mass or nipple discharge is also present.

Tizanidine, sold under the brand name Zanaflex among others, is a medication that is used to treat muscle spasticity due to spinal cord injury or multiple sclerosis. Effectiveness appears similar to baclofen or diazepam. It is taken by mouth.

d-DOPA is similar to l-DOPA (levodopa), but with opposite chirality. Levo- and dextro- rotation refer to a molecule's ability to rotate planes of polarized light in either direction. Whereas l-DOPA is moderately effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) and Dopamine-responsive dystonia (DRD) by stimulating the production of dopamine in the brain, d-DOPA is biologically inactive.

Rilmenidine is a prescription medication for the treatment of hypertension. It is marketed under the brand names Albarel, Hyperium, Iterium and Tenaxum.

Corbadrine, also known as levonordefrin (USAN) and α-methylnorepinephrine, is a catecholamine sympathomimetic used as a topical nasal decongestant and vasoconstrictor in dentistry in the United States,.

A catechol-O-methyltransferase(COMT) inhibitor is a drug that inhibits the enzyme catechol-O-methyltransferase. This enzyme methylates catecholamines such as dopamine, norepinephrine and epinephrine. It also methylates levodopa. COMT inhibitors are indicated for the treatment of Parkinson's disease in combination with levodopa and an aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor. The therapeutic benefit of using a COMT inhibitor is based on its ability to prevent the methylation of levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa, thus increasing the bioavailability of levodopa. COMT inhibitors significantly decrease off time in people with Parkinson's disease also taking carbidopa/levodopa.
Hematologic diseases are disorders which primarily affect the blood & blood-forming organs. Hematologic diseases include rare genetic disorders, anemia, HIV, sickle cell disease & complications from chemotherapy or transfusions.

Bethanidine is a sympatholytic drug.

An aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase inhibitor is a medication of type enzyme inhibitor which inhibits the synthesis of dopamine by the enzyme aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase. It is used to inhibit the decarboxylation of L-DOPA to Dopamine outside the brain, i.e. in the blood. This is primarily co-administered with L-DOPA to combat Parkinson's disease. Administration can prevent common side-effects, such as nausea and vomiting, as a result of interaction with D2 receptors in the vomiting center located outside the blood–brain barrier.

α-Difluoromethyl-DOPA is a DOPA decarboxylase inhibitor.
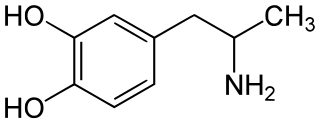
α-Methyldopamine (α-Me-DA), also known as 3,4-dihydroxyamphetamine, is a research chemical of the catecholamine and amphetamine chemical classes. Its bis-glutathionyl metabolite is slightly neurotoxic when directly injected into the brain's ventricles.
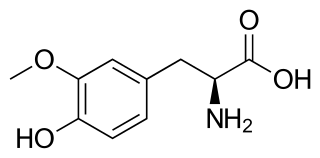
3-O-Methyldopa (3-OMD) is one of the most important metabolites of L-DOPA, a drug used in the treatment of the Parkinson's disease.














