
In organic chemistry, hydrocarbons are divided into two classes: aromatic compounds and aliphatic compounds, also known as non-aromatic hydrocarbons. Aliphatics can be cyclic; however, hydrocarbons with conjugated pi-systems that obey Hückel's rule are instead considered to be aromatic. Aliphatic compounds can be saturated, like hexane, or unsaturated, like hexene and hexyne. Open-chain compounds contain no rings of any type, and are thus aliphatic.

Bromine is a chemical element with symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest halogen, and is a fuming red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a similarly coloured gas. Its properties are thus intermediate between those of chlorine and iodine. Isolated independently by two chemists, Carl Jacob Löwig and Antoine Jérôme Balard, its name was derived from the Ancient Greek βρῶμος ("stench"), referencing its sharp and disagreeable smell.

The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor.
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulas can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than are chemical names and structural formulas.

A heterocyclic compound or ring structure is a cyclic compound that has atoms of at least two different elements as members of its ring(s). Heterocyclic chemistry is the branch of organic chemistry dealing with the synthesis, properties, and applications of these heterocycles.
Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds, which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, as there is much overlap in the subdiscipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry, including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medications, fuels, and agriculture.

In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon. Due to carbon's ability to catenate, millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprises the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds, along with a handful of other exceptions, are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive.
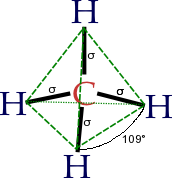
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline of chemistry that studies the structure, properties and reactions of organic compounds, which contain carbon in covalent bonding. Study of structure determines their chemical composition and formula. Study of properties includes physical and chemical properties, and evaluation of chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical study.

Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkaline, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and tin, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide, cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term "metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are representative members of this class. The field of organometallic chemistry combines aspects of traditional inorganic and organic chemistry.

Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide animals with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons. In higher organisms, the eye is a complex optical system which collects light from the surrounding environment, regulates its intensity through a diaphragm, focuses it through an adjustable assembly of lenses to form an image, converts this image into a set of electrical signals, and transmits these signals to the brain through complex neural pathways that connect the eye via the optic nerve to the visual cortex and other areas of the brain. Eyes with resolving power have come in ten fundamentally different forms, and 96% of animal species possess a complex optical system. Image-resolving eyes are present in molluscs, chordates and arthropods.

In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containing a carbonyl group is often referred to as a carbonyl compound.
An inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. However, the distinction is not clearly defined and agreed upon, and authorities have differing views on the subject.
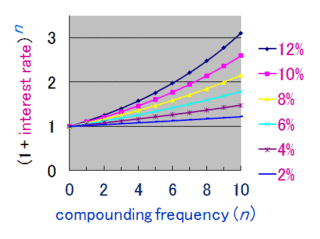
Compound interest is the addition of interest to the principal sum of a loan or deposit, or in other words, interest on interest. It is the result of reinvesting interest, rather than paying it out, so that interest in the next period is then earned on the principal sum plus previously accumulated interest. Compound interest is standard in finance and economics.
In linguistics, a compound is a lexeme that consists of more than one stem. Compounding, composition or nominal composition is the process of word formation that creates compound lexemes. That is, in familiar terms, compounding occurs when two or more words or signs are joined to make one longer word or sign. The meaning of the compound may be similar to or different from the meaning of its components in isolation. The component stems of a compound may be of the same part of speech—as in the case of the English word footpath, composed of the two nouns foot and path—or they may belong to different parts of speech, as in the case of the English word blackbird, composed of the adjective black and the noun bird. With very few exceptions, English compound words are stressed on their first component stem.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room temperature. Their high vapor pressure results from a low boiling point, which causes large numbers of molecules to evaporate or sublimate from the liquid or solid form of the compound and enter the surrounding air, a trait known as volatility. For example, formaldehyde, which evaporates from paint and releases from materials like resin, has a boiling point of only –19 °C (–2 °F).
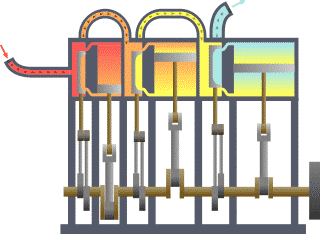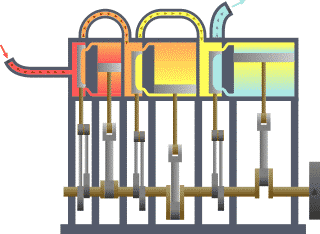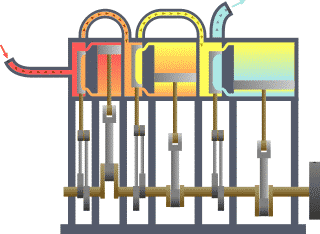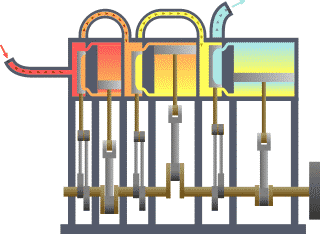
A compound steam engine unit is a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. A typical arrangement for a compound engine is that the steam is first expanded in a high-pressure (HP) cylinder, then having given up heat and losing pressure, it exhausts directly into one or more larger-volume low-pressure (LP) cylinders. Multiple-expansion engines employ additional cylinders, of progressively lower pressure, to extract further energy from the steam.
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC).

A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., without breaking chemical bonds. Chemical substances can be simple substances, chemical compounds, or alloys. Chemical elements may or may not be included in the definition, depending on expert viewpoint.
In chemical nomenclature, a preferred IUPAC name (PIN) is a unique name, assigned to a chemical substance and preferred among the possible names generated by IUPAC nomenclature. The "preferred IUPAC nomenclature" provides a set of rules for choosing between multiple possibilities in situations where it is important to decide on a unique name. It is intended for use in legal and regulatory situations.

A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules composed of atoms from more than one element held together by chemical bonds. Two atoms of the same element bonded in a molecule do not form a chemical compound, since this would require two different elements.











