The molecular formula C19H26N4O2 may refer to:
- BIMU8, a drug which acts as a 5-HT4 receptor selective agonist
- Sucrononic acid, a guanidino derivative artificial sweetener
The molecular formula C19H26N4O2 may refer to:
A chemical formula is a way of presenting information about the chemical proportions of atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound or molecule, using chemical element symbols, numbers, and sometimes also other symbols, such as parentheses, dashes, brackets, commas and plus (+) and minus (−) signs. These are limited to a single typographic line of symbols, which may include subscripts and superscripts. A chemical formula is not a chemical name, and it contains no words. Although a chemical formula may imply certain simple chemical structures, it is not the same as a full chemical structural formula. Chemical formulae can fully specify the structure of only the simplest of molecules and chemical substances, and are generally more limited in power than chemical names and structural formulae.
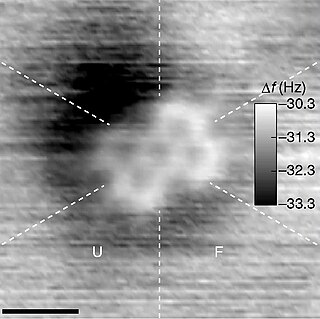
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and molecule is often used when referring to polyatomic ions.
Benzol may refer to:
The molecular formula C8H10N4O2 may refer to:
The molecular formula BaSO4 (molar mass: 233.39 g/mol, exact mass: 233.8570 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula CH4N2O (molar mass: 60.06 g/mol, exact mass: 60.03236 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H10O may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H10N2 may refer to:
The molecular formula C4H4O4 (molar mass: 116.07 g/mol) may refer to:
The molecular formula C5H12O (molar mass: 88.15 g/mol, exact mass: 88.088815) may refer to:
Dihydroxybenzoic acids (DHBA) are a type of phenolic acids.
Dioxin may refer to:
The molecular formula C19H28O3 may refer to:
The molecular formula C16H12O4 (molar mass: 268.26 g/mol, exact mass: 268.073559 u) may refer to:
The molecular formula C11H17BrNO2 (molar mass: 258.11 g/mol) may refer to:
Dihydroxycinnamic acid may refer to several molecules with the molecular formula C9H8O4 including:
Octynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C8H14.
Nonynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C9H16.
Decynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C10H18.
Heptynes are alkynes with one triple bond and the molecular formula C7H12.