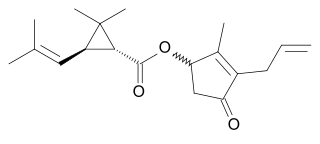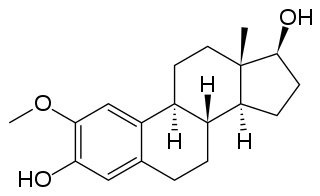
2-Methoxyestradiol (2-ME2) is a natural metabolite of estradiol. As an experimental drug candidate, it is being developed under the tradename of Panzem. It prevents the formation of new blood vessels that tumors need in order to grow (angiogenesis), hence it is an angiogenesis inhibitor.

Oxabolone cipionate, or oxabolone cypionate, also known as 4-hydroxy-19-nortestosterone 17β-cypionate or estr-4-en-4,17β-diol-3-one 17β-cypionate, is synthetic and injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) which has been marketed in Europe. It is the C17β cypionate ester and a prodrug of oxabolone (4-hydroxy-19-nortestosterone).

Adrenosterone, also known as Reichstein's substance G , as well as 11-ketoandrostenedione (11-KA4), 11-oxoandrostenedione (11-OXO), and androst-4-ene-3,11,17-trione, is a steroid hormone with a weak androgenic effect, and an intermediate/prohormone of 11-ketotestosterone. It was first isolated in 1936 from the adrenal cortex by Tadeus Reichstein at the Pharmaceutical Institute in the University of Basel. Originally, adrenosterone was called Reichstein's substance G. Adrenosterone occurs in trace amounts in humans as well as most mammals and in larger amounts in fish, where it is a precursor to the primary androgen, 11-ketotestosterone.
Methoxyestradiol may refer to:

16α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone is an endogenous metabolite of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). Both 16α-OH-DHEA and its 3β-sulfate ester, 16α-OH-DHEA-S, are intermediates in the biosynthesis of estriol from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). 16α-OH-DHEA has estrogenic activity.

11-Ketotestosterone (11-KT) is an oxidized form of testosterone that contains a keto group at the C11 position. It is related to adrenosterone, an androgen found in trace quantities in humans. In fish, 11-ketotestosterone functions as the endogenous androgenic sex hormone. In midshipman fish, 11-ketotestosterone is not present in females or Type II Males — Type II Males reach sexual maturation later, are less territorial, and have higher testosterone than Type I Males.

2-Hydroxyestradiol (2-OHE2), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,17β-triol, is an endogenous steroid, catechol estrogen, and metabolite of estradiol, as well as a positional isomer of estriol.

16α-Hydroxyestrone (16α-OH-E1), or hydroxyestrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α-diol-17-one, is an endogenous steroidal estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone, as well as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of estriol. It is a potent estrogen similarly to estrone, and it has been suggested that the ratio of 16α-hydroxyestrone to 2-hydroxyestrone, the latter being much less estrogenic in comparison and even antiestrogenic in the presence of more potent estrogens like estradiol, may be involved in the pathophysiology of breast cancer. Conversely, 16α-hydroxyestrone may help to protect against osteoporosis. In contrast to estradiol, the binding of 16α-hydroxyestrone to the estrogen receptor is, uniquely, covalent and irreversible, and genotoxicity and aberrant hyperproliferations may result. A diacetate ester of 16α-hydroxyestrone, hydroxyestrone diacetate, has been marketed and is used medically as an estrogen in Europe.

MP-2001, also known as 2,3,4-trimethoxyestra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17β-ol or 2,4-dimethoxyestradiol 3-methyl ether, is a steroid and derivative of estradiol that was described in 1966 and is devoid of estrogenic activity but produces potent analgesic effects in animals. It was never marketed.

16α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (16α-OH-DHEA-S), also known as 16α-hydroxy-17-oxoandrost-5-en-3β-yl sulfate, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and a metabolic intermediate in the production of estriol from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) during pregnancy. It is the C3β sulfate ester of 16α-hydroxy-DHEA.

11β-Hydroxyandrostenedione (11β-OHA4), also known as 11β-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and androgen prohormone that is produced primarily, if not exclusively, in the adrenal glands. It is closely related to adrenosterone, 11-ketotestosterone (11-KT), and 11-ketodihydrotestosterone (11-KDHT), which are also produced in the adrenal glands.

11-Ketodihydrotestosterone (11-KDHT), also known as 5α-androstan-17β-ol-3,11-dione, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and androgen prohormone that is produced primarily, if not exclusively, in the adrenal glands. It is closely related to 11β-hydroxyandrostenedione (11β-KA4), adrenosterone, and 11-ketotestosterone (11-KT), which are also produced in the adrenal glands.

16α-Hydroxyandrostenedione (16α-OH-A4), also known as 16α-hydroxyandrost-4-ene-3,17-dione, is an endogenous and naturally occurring steroid and metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of estriol during pregnancy. It is produced from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), which is converted into 16α-hydroxy-DHEA sulfate, then desulfated and aromatized into 16α-hydroxyestrone, and finally converted into estriol by 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
Hydroxyandrostenedione may refer to:

2-Hydroxyestrone (2-OHE1), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-2,3-diol-17-one, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone and estradiol. It is formed irreversibly from estrone in the liver and to a lesser extent in other tissues via 2-hydroxylation mediated by cytochrome P450 enzymes, mainly the CYP3A and CYP1A subfamilies. 2-OHE1 is the most abundant catechol estrogen in the body. It is not significantly uterotrophic in bioassays, whereas other hydroxylated estrogen metabolites including 2-hydroxyestradiol, 16α-hydroxyestrone, estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), 4-hydroxyestradiol, and 4-hydroxyestrone all are.

2-Methoxyestrone (2-ME1) is an endogenous, naturally occurring methoxylated catechol estrogen and metabolite of estrone that is formed by catechol O-methyltransferase via the intermediate 2-hydroxyestrone. Unlike estrone but similarly to 2-hydroxyestrone and 2-methoxyestradiol, 2-methoxyestrone has very low affinity for the estrogen receptor and lacks significant estrogenic activity.
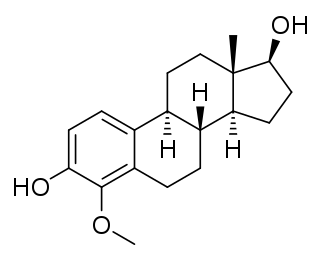
4-Methoxyestradiol (4-ME2) is an endogenous, naturally occurring methoxylated catechol estrogen and metabolite of estradiol that is formed by catechol O-methyltransferase via the intermediate 4-hydroxyestradiol. It has estrogenic activity similarly to estrone and 4-hydroxyestrone.

4-Methoxyestrone (4-ME1) is an endogenous, naturally occurring methoxylated catechol estrogen and metabolite of estrone that is formed by catechol O-methyltransferase via the intermediate 4-hydroxyestrone. It has estrogenic activity similarly to estrone and 4-hydroxyestrone.

15α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone, abbreviated as 15α-hydroxy-DHEA or 15α-OH-DHEA, is an endogenous metabolite of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA). Both 15α-OH-DHEA and its 3β-sulfate ester, 15α-OH-DHEA-S, are intermediates in the biosynthesis of estetrol from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA).

15α-Hydroxydehydroepiandrosterone sulfate, abbreviated as 15α-hydroxy-DHEA sulfate or 15α-OH-DHEA-S, also known as 15α-hydroxy-17-oxoandrost-5-en-3β-yl sulfate, is an endogenous, naturally occurring steroid and a metabolic intermediate in the production of estetrol from dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) during pregnancy. It is the C3β sulfate ester of 15α-hydroxy-DHEA.