Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens, and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid.

A progestogen, also referred to as a progestagen, gestagen, or gestogen, is a type of medication which produces effects similar to those of the natural female sex hormone progesterone in the body. A progestin is a synthetic progestogen. Progestogens are used most commonly in hormonal birth control and menopausal hormone therapy. They can also be used in the treatment of gynecological conditions, to support fertility and pregnancy, to lower sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications. Progestogens are used alone or in combination with estrogens. They are available in a wide variety of formulations and for use by many different routes of administration. Examples of progestogens include natural or bioidentical progesterone as well as progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate and norethisterone.

Quinestrol, also known as ethinylestradiol cyclopentyl ether (EECPE), sold under the brand name Estrovis among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy, hormonal birth control, and to treat breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is taken once per week to once per month by mouth.
Dydrogesterone, sold under the brand name Duphaston, Dydroboon and Femoston, is a progestin medication which is used for a variety of indications, including threatened or recurrent miscarriage during pregnancy, dysfunctional bleeding, infertility due to luteal insufficiency, dysmenorrhea, endometriosis, secondary amenorrhea, irregular cycles, premenstrual syndrome, and as a component of menopausal hormone therapy. It is taken by mouth.

Mestranol, sold under the brand names Enovid, Norinyl, and Ortho-Novum among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and the treatment of menstrual disorders. It is formulated in combination with a progestin and is not available alone. It is taken by mouth.
Antiestrogens, also known as estrogen antagonists or estrogen blockers, are a class of drugs which prevent estrogens like estradiol from mediating their biological effects in the body. They act by blocking the estrogen receptor (ER) and/or inhibiting or suppressing estrogen production. Antiestrogens are one of three types of sex hormone antagonists, the others being antiandrogens and antiprogestogens.Antiestrogens are commonly used to stop steroid hormones, estrogen, from binding to the estrogen receptors leading to the decrease of estrogen levels. Decreased levels of estrogen can lead to complications in sexual development. Antiandrogens are sex hormone antagonists which are able to lower the production and the effects that testosterone can have on female bodies.

Cyclofenil, sold under the brand name Sexovid among others, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) medication which is used as a gonadotropin stimulant or ovulation inducer and in menopausal hormone therapy in women. It is mostly no longer available. The medication is taken by mouth.

Estriol succinate, sold under the brand name Synapause among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection.
An antigonadotropin is a drug which suppresses the activity and/or downstream effects of one or both of the gonadotropins, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). This results in an inhibition of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis, and thus a decrease in the levels of the androgen, estrogen, and progestogen sex steroids in the body. Antigonadotropins also inhibit ovulation in women and spermatogenesis in men. They are used for a variety of purposes, including for the hormonal birth control, treatment of hormonally-sensitive cancers, to delay precocious puberty and puberty in transgender youth, as a form of chemical castration to reduce the sex drives of individuals with hypersexuality or pedophilia, and to treat estrogen-associated conditions in women such as menorrhagia and endometriosis, among others. High-dose antigonadotropin therapy has been referred to as medical castration.

Conjugated estrogens (CEs), or conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs), sold under the brand name Premarin among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and for various other indications. It is a mixture of the sodium salts of estrogen conjugates found in horses, such as estrone sulfate and equilin sulfate. CEEs are available in the form of both natural preparations manufactured from the urine of pregnant mares and fully synthetic replications of the natural preparations. They are formulated both alone and in combination with progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate. CEEs are usually taken by mouth, but can also be given by application to the skin or vagina as a cream or by injection into a blood vessel or muscle.
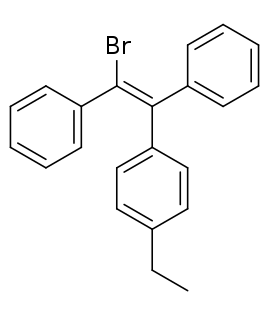
Broparestrol (INN), also known as α-bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene (BDPE), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that has been used in Europe as a dermatological agent and for the treatment of breast cancer. The drug is described as slightly estrogenic and potently antiestrogenic, and inhibits mammary gland development and suppresses prolactin levels in animals. It is structurally related to clomifene and diethylstilbestrol. Broparestrol is a mixture of E- and Z- isomers, both of which are active and are similarly antiestrogenic but, unlike broparestrol, were never marketed.

Dienestrol diacetate is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of dienestrol.

Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate (DESDP), or diethylstilbestrol dipropanoate, also known as stilboestrol dipropionate (BANM), is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group that was formerly marketed widely throughout Europe. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol with propionic acid, and is more slowly absorbed in the body than diethylstilbestrol. The medication has been said to be one of the most potent estrogens known.

Epiestriol (INN), or epioestriol (BAN), also known as 16β-epiestriol or simply 16-epiestriol as well as 16β-hydroxy-17β-estradiol, is a minor and weak endogenous estrogen, and the 16β-epimer of estriol. Epiestriol is used clinically in the treatment of acne. In addition to its estrogenic actions, epiestriol has been found to possess significant anti-inflammatory properties without glycogenic activity or immunosuppressive effects, an interesting finding that is in contrast to conventional anti-inflammatory steroids like hydrocortisone.

Bifluranol is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that has been used as an antiandrogen in the United Kingdom in the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. It is a polyfluorinated biphenyl that is related to polybrominated and polychlorinated biphenyls and diethylstilbestrol. The drug is described as a weak estrogen, and possesses about one-eighth the potency of diethylstilbestrol.

Estradiol sulfate (E2S), or 17β-estradiol 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester. E2S itself is biologically inactive, but it can be converted by steroid sulfatase into estradiol, which is a potent estrogen. Simultaneously, estrogen sulfotransferases convert estradiol to E2S, resulting in an equilibrium between the two steroids in various tissues. Estrone and E2S are the two immediate metabolic sources of estradiol. E2S can also be metabolized into estrone sulfate (E1S), which in turn can be converted into estrone and estradiol. Circulating concentrations of E2S are much lower than those of E1S. High concentrations of E2S are present in breast tissue, and E2S has been implicated in the biology of breast cancer via serving as an active reservoir of estradiol.

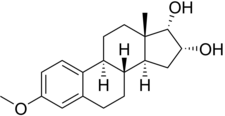
17α-Epiestriol, or simply 17-epiestriol, also known as 16α-hydroxy-17α-estradiol or estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α,17α-triol, is a minor and weak endogenous estrogen, and the 17α-epimer of estriol. It is formed from 16α-hydroxyestrone. In contrast to other endogenous estrogens like estradiol, 17α-epiestriol is a selective agonist of the ERβ. It is described as a relatively weak estrogen, which is in accordance with its relatively low affinity for the ERα. 17α-Epiestriol has been found to be approximately 400-fold more potent than estradiol in inhibiting tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα)-induced vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM-1) expression in vitro.

16β,17α-Epiestriol, or 16,17-epiestriol, also known as 16β-hydroxy-17α-estradiol, as well as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16β,17α-triol, is a minor and weak endogenous steroidal estrogen that is related to 17α-estradiol and estriol. Along with estriol, 16β,17α-epiestriol has been detected in the urine of women during the late pregnancy stage. It shows preferential affinity for the ERβ over the ERα.

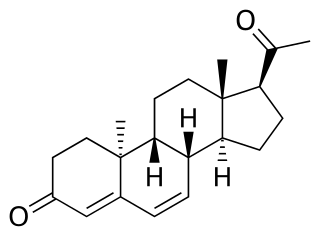
16α-Hydroxyestrone (16α-OH-E1), or hydroxyestrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α-diol-17-one, is an endogenous steroidal estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone, as well as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of estriol. It is a potent estrogen similarly to estrone, and it has been suggested that the ratio of 16α-hydroxyestrone to 2-hydroxyestrone, the latter being much less estrogenic in comparison and even antiestrogenic in the presence of more potent estrogens like estradiol, may be involved in the pathophysiology of breast cancer. Conversely, 16α-hydroxyestrone may help to protect against osteoporosis.

Lilopristone (INN) is a synthetic, steroidal antiprogestogen with additional antiglucocorticoid activity which was developed by Schering and was patented in 1985. It is described as an abortifacient and endometrial contraceptive. The drug differs from mifepristone only in the structure of its C17α side chain, and is said to have much reduced antiglucocorticoid activity in comparison.