Quinestrol, also known as ethinylestradiol cyclopentyl ether (EECPE), sold under the brand name Estrovis among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in menopausal hormone therapy, hormonal birth control, and to treat breast cancer and prostate cancer. It is taken once per week to once per month by mouth.

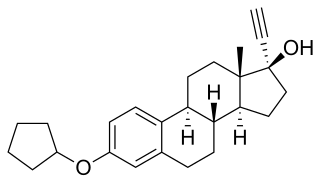
Trestolone, also known as 7α-methyl-19-nortestosterone (MENT), is an experimental androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) and progestogen medication which has been under development for potential use as a form of hormonal birth control for men and in androgen replacement therapy for low testosterone levels in men but has never been marketed for medical use. It is given as an implant that is placed into fat. As trestolone acetate, an androgen ester and prodrug of trestolone, the medication can also be given by injection into muscle.

Mestranol, sold under the brand names Enovid, Norinyl, and Ortho-Novum among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in birth control pills, menopausal hormone therapy, and the treatment of menstrual disorders. It is formulated in combination with a progestin and is not available alone. It is taken by mouth.

Zinc transporter ZIP6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC39A6 gene.

Estriol succinate, sold under the brand name Synapause among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection.

Conjugated estrogens (CEs), or conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs), sold under the brand name Premarin among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in menopausal hormone therapy and for various other indications. It is a mixture of the sodium salts of estrogen conjugates found in horses, such as estrone sulfate and equilin sulfate. CEEs are available in the form of both natural preparations manufactured from the urine of pregnant mares and fully synthetic replications of the natural preparations. They are formulated both alone and in combination with progestins such as medroxyprogesterone acetate. CEEs are usually taken by mouth, but can also be given by application to the skin or vagina as a cream or by injection into a blood vessel or muscle.

Doisynoestrol, also known as fenocycline, as well as cis-bisdehydrodoisynolic acid 7-methyl ether, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the doisynolic acid group that is no longer marketed. It is a methyl ether of bisdehydrodoisynolic acid. Doisynoestrol was described in the literature in 1945. It has about 0.02% of the relative binding affinity of estradiol for the estrogen receptor.

Dienestrol diacetate is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of dienestrol.

Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate (DESDP), or diethylstilbestrol dipropanoate, also known as stilboestrol dipropionate, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group that was formerly marketed widely throughout Europe. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol with propionic acid, and is more slowly absorbed in the body than diethylstilbestrol. The medication has been said to be one of the most potent estrogens known.

Estrofurate, also known as 17α-(3-furyl)-estra-1,3,5(10),7-tetraene-3,17-diol 3-acetate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen that was synthesized in 1967 and studied in the late 1960s and early 1970s but was never marketed. It is a relatively weak estrogen in bioassays.
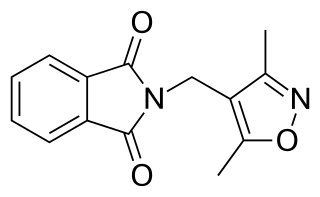
DIMP, or N-(3,5-dimethyl-4-isoxazolylmethyl)phthalimide, is a nonsteroidal antiandrogen (NSAA) structurally related to thalidomide that was first described in 1973 and was never marketed. Along with flutamide, it was one of the earliest NSAAs to be discovered, and for this reason, has been described as a "classical" NSAA. The drug is a selective, competitive, silent antagonist of the AR, although it is described as an "only relatively weak competitor". Its relative binding affinity for the androgen receptor is about 2.6% of that of metribolone. DIMP possesses no androgenic, estrogenic, progestogenic, or antigonadotropic activity, but it does reverse the antigonadotropic effects of testosterone, indicating that, like other pure AR antagonists, it is progonadotropic.
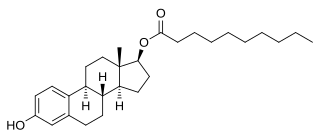
Estradiol decanoate (E2D), or estradiol decylate, also known as estradiol 17β-decanoate, is a synthetic steroidal estrogen and an estrogen ester – specifically, the 17β-decanoate (decylate) ester of estradiol – which was studied for use in hormone replacement therapy for ovariectomized women in the late 1970s but was never marketed.
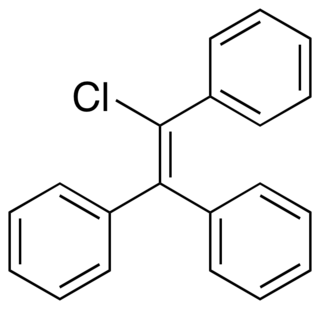
Triphenylchloroethylene, or triphenylchlorethylene, also known as chlorotriphenylethylene or as phenylstilbene chloride, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the triphenylethylene group that was marketed in the 1940s for the treatment of menopausal symptoms, vaginal atrophy, lactation suppression, and all other estrogen-indicated conditions.

Triphenylbromoethylene, also known as bromotriphenylethylene or as phenylstilbene bromide, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the triphenylethylene group that was marketed in the 1940s similarly to the closely related estrogen triphenylchloroethylene.

Dimethylstilbestrol (DMS) is a nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol which was never marketed. It is a so-called "weak", "impeded", or "short-acting" estrogen similarly to estriol and meso-butoestrol. The affinity of DMS for the ER was reported as about 10% of that of estradiol. For comparison, diethylstilbestrol had 140% of the affinity of estradiol for the ER.

Polyestriol phosphate, sold under the brand names Gynäsan, Klimadurin, and Triodurin, is an estrogen medication which was previously used in menopausal hormone therapy and is no longer available.

Polydiethylstilbestrol phosphate is an estrogen medication which has been used in scientific research and has been studied for use in veterinary medicine as a livestock growth promoter. It is a phosphate ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) in the form of a polymer and is a polymeric form of fosfestrol ; PDSP acts as a long-lasting prodrug of DES. It has similarities to polyestradiol phosphate and polyestriol phosphate.

Gestonorone acetate, or gestronol acetate, also known as norhydroxyprogesterone acetate, is a progestin of the 19-norprogesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone groups which was developed in the early 1960s but was never marketed. It is the C17α acetate ester of gestronol (17α-hydroxy-19-norprogesterone).

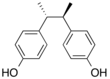
meso-Butestrol, also known as 2,3-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)butane, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen which was never marketed. It is a so-called "short-acting" or "impeded" estrogen. meso-Butestrol is structurally related to diethylstilbestrol and other stilbestrols. The fully potent counterpart to meso-butestrol is meso-hexestrol, analogously to the relationship of dimethylstilbestrol to diethylstilbestrol.

Ethinylandrostenediol, also known as 17α-ethynyl-5-androstenediol, is a synthetic estrogen, progestogen, and androgen which was never marketed. It is the C17α ethynyl derivative of the androgen precursor and prohormone 5-androstenediol.