 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
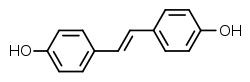
| Preferred IUPAC name 4,4′-[(E)-Ethene-1,2-diyl]diphenol | |
| Other names Dihydroxystilbene; 4,4'-Dihydroxystilbene, 4,4'-stilbenediol | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H12O2 | |
| Molar mass | 212.24388 g/mol |
| −130·10−6 cm3/mol | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Stilbestrol, or stilboestrol, also known as 4,4'-dihydroxystilbene or 4,4'-stilbenediol, is a stilbenoid nonsteroidal estrogen [1] and the parent compound of a group of more potent nonsteroidal estrogen derivatives that includes, most notably, diethylstilbestrol (DES). [1] [2] [3] The term "stilbestrol" is often used incorrectly to refer to DES, but they are not the same compound. [2]
Contents
- Stilbestrol derivatives
- Mechanism of action
- Closely related compounds
- Occupational exposure
- See also
- References
Stilbestrol itself is an active estrogen but is less potent than DES and other derivatives. [1]
