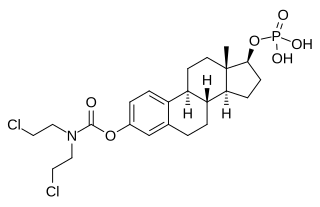
Estramustine phosphate (EMP), also known as estradiol normustine phosphate and sold under the brand names Emcyt and Estracyt, is a dual estrogen and chemotherapy medication which is used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is taken multiple times a day by mouth or by injection into a vein.

Estrone sulfate, also known as E1S, E1SO4 and estrone 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester and conjugate.
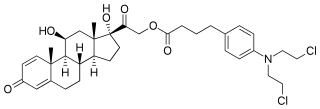
Prednimustine, sold under the brand names Mostarina and Sterecyst, is a medication which is used in chemotherapy in the treatment of leukemias and lymphomas. It is the ester formed from two other drugs, prednisolone and chlorambucil. Rarely, it has been associated with myoclonus.
An estrogen ester is an ester of an estrogen, most typically of estradiol but also of other estrogens such as estrone, estriol, and even nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Esterification renders estradiol into a prodrug of estradiol with increased resistance to first-pass metabolism, slightly improving its oral bioavailability. In addition, estrogen esters have increased lipophilicity, which results in a longer duration when given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection due to the formation of a long-lasting local depot in muscle and fat. Conversely, this is not the case with intravenous injection or oral administration. Estrogen esters are rapidly hydrolyzed into their parent estrogen by esterases once they have been released from the depot. Because estradiol esters are prodrugs of estradiol, they are considered to be natural and bioidentical forms of estrogen.

Atrimustine (INN), also known as bestrabucil or busramustine, is a cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was under development in Japan by Kureha Chemicals for the treatment of breast cancer and non-Hodgkin's lymphoma as well as for the prevention of graft-versus-host disease in bone marrow transplant recipients. It is the benzoate ester of an ester conjugate of estradiol and chlorambucil, which results in targeted/site-directed cytostatic activity toward estrogen receptor-positive tissues such as breast and bone. It reached preregistration for the treatment of cancer but was ultimately discontinued. Estrogenicic side effects of atrimustine in clinical trials included vaginal bleeding and gynecomastia. The drug was first patented in 1980.

Alestramustine (INN), also known as estradiol 3-(bis carbamate) 17β-(L-alaninate), is a cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was never marketed. It is the L-alanine ester of estramustine, which is a combination of the nitrogen mustard normustine coupled via a carbamate to the estrogen estradiol. Alestramustine acts as a prodrug to estramustine, and also forms estradiol as a byproduct. The drug, via its active metabolites, binds to microtubule-associated proteins and β-tubulin and interferes with microtubule function, thereby inhibiting cell division. Due to its estrogen moiety, alestramustine is selectively concentrated in estrogen receptor-positive cells such as prostate and breast.
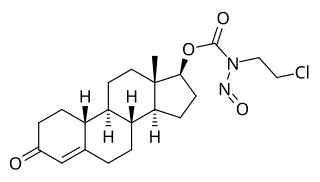
LS-1727 is a synthetic, injected anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a nitrosocarbamate ester of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) which was developed as a cytostatic antineoplastic agent but was never marketed.

ICI-85966, also known as diethylstilbestrol (DES) bis(di carbamate), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent of the stilbestrol group and a nitrogen mustard ester of diethylstilbestrol (DES) which was developed for the treatment of breast cancer and prostate cancer but was never marketed.
Phenestrol, or fenestrol, also known as hexestrol bis[4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenylacetate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard ester of hexestrol which was developed in the early 1960s for the treatment of hormone-dependent tumors but was never marketed.

Estradiol mustard, also known as chlorphenacyl estradiol diester, as well as estradiol 3,17β-bis(4- phenyl)acetate, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent and a chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard-coupled estrogen ester that was never marketed. It is selectively distributed into estrogen receptor (ER)-positive tissues such as ER-expressing tumors like those seen in breast and prostate cancers. For this reason, estradiol mustard and other cytostatic-linked estrogens like estramustine phosphate have reduced toxicity relative to non-linked nitrogen mustard cytostatic antineoplastic agents. However, they may stimulate breast tumor growth due to their inherent estrogenic activity and are said to be devoid of major therapeutic efficacy in breast cancer, although estramustine phosphate has been approved for and is used in the treatment of prostate cancer.
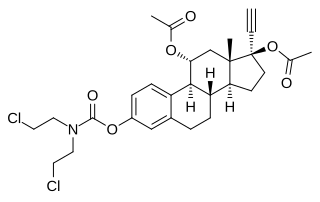
Cytestrol acetate is a steroidal antiestrogen and a cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was developed for the treatment of breast cancer but was never marketed. It is an 11α-hydroxylated derivative of ethinylestradiol in which a bis(2-chloroethyl)amine nitrogen mustard moiety has been attached as an ester at the C3 position and acetate esters have been attached at the C11α and C17β positions. The mechanism of action of cytestrol acetate in breast cancer is two-fold: (1) acting as an antiestrogen similarly to fulvestrant or ICI-164384; and (2) having cytostatic actions via the carbamate–nitrogen mustard moiety analogously to estramustine phosphate. The drug shows potent efficacy against breast cancer superior to that of tamoxifen in in vitro models.

Testifenon, also known as testiphenon, testiphenone, chlorphenacyl dihydrotestosterone ester, or dihydrotestosterone 17β-(4- phenyl)acetate, is a synthetic anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a cytostatic antineoplastic agent that was never marketed. It is an androgen ester – specifically, a chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard ester of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) – and acts as a prodrug of these two components in the body. The drug was developed in Russia as a tissue-selective cytostatic drug for the treatment of various cancers occurring in androgen receptor-expressing tissues that would have reduced side effects and toxicity relative to other chemotherapy drugs.

Estramustine is an estrogen and cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester – specifically, the C3 normustine ester of estradiol – and acts in part as a prodrug of estradiol in the body. Estramustine phosphate, the C17β phosphate ester of estramustine and a prodrug of estramustine, estromustine, estradiol, and estrone, is marketed and used in the treatment of prostate cancer.

Estrone sulfamate, or estrone-3-O-sulfamate, is a steroid sulfatase (STS) inhibitor which has not yet been marketed. It is the C3 sulfamate ester of the estrogen estrone. Unlike other estrogen esters however, EMATE is not an effective prodrug of estrogens. A closely related compound is estradiol sulfamate (E2MATE), which is extensively metabolized into EMATE and has similar properties to it.

Cortifen, also known as cortiphen or kortifen, as well as fencoron, is a synthetic glucocorticoid corticosteroid and cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was developed in Russia for potential treatment of tumors. It is a hydrophobic chlorphenacyl nitrogen mustard ester of 11-deoxycortisol (cortodoxone).
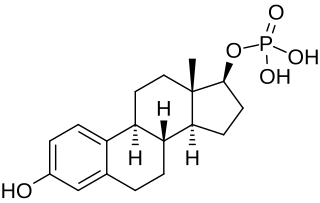
Estradiol phosphate, or estradiol 17β-phosphate, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,17β-diol 17β-(dihydrogen phosphate), is an estrogen which was never marketed. It is an estrogen ester, specifically an ester of estradiol with phosphoric acid, and acts as a prodrug of estradiol in the body. It is rapidly cleaved by phosphatase enzymes into estradiol upon administration. Estradiol phosphate is contained within the chemical structures of two other estradiol esters, polyestradiol phosphate and estramustine phosphate, both of which have been marketed for the treatment of prostate cancer.

The pharmacology of estradiol, an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone, concerns its pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and various routes of administration.















