Vitex agnus-castus is a plant native of the Mediterranean region. It is one of the few temperate-zone species of Vitex, which is on the whole a genus of tropical and subtropical flowering plants. Theophrastus mentioned the shrub several times, as agnos (άγνος) in Enquiry into Plants. It has been long believed to be an anaphrodisiac – leading to its name as chaste tree – but its effectiveness for such action remains unproven.

Parabens are chemicals that are commonly used as preservatives in cosmetic and pharmaceutical products. Chemically, they are a series of parahydroxybenzoates or esters of parahydroxybenzoic acid. Research is being conducted to evaluate the potential negative health implications of paraben usage. Certain parabens have been linked to cancer.
The Kolbe–Schmitt reaction or Kolbe process is a carboxylation chemical reaction that proceeds by treating phenol with sodium hydroxide to form sodium phenoxide, then heating sodium phenoxide with carbon dioxide under pressure, then treating the product with sulfuric acid. The final product is an aromatic hydroxy acid which is also known as salicylic acid.

Methylparaben, also methyl paraben, one of the parabens, is a preservative with the chemical formula CH3(C6H4(OH)COO). It is the methyl ester of p-hydroxybenzoic acid.

The mitomycins are a family of aziridine-containing natural products isolated from Streptomyces caespitosus or Streptomyces lavendulae. They include mitomycin A, mitomycin B, and mitomycin C. When the name mitomycin occurs alone, it usually refers to mitomycin C, its international nonproprietary name. Mitomycin C is used as a medicine for treating various disorders associated with the growth and spread of cells.
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid, also known as p-hydroxybenzoic acid (PHBA), is a monohydroxybenzoic acid, a phenolic derivative of benzoic acid. It is a white crystalline solid that is slightly soluble in water and chloroform but more soluble in polar organic solvents such as alcohols and acetone. 4-Hydroxybenzoic acid is primarily known as the basis for the preparation of its esters, known as parabens, which are used as preservatives in cosmetics and some ophthalmic solutions. It is isomeric with 2-hydroxybenzoic acid, known as salicylic acid, a precursor to aspirin, and with 3-hydroxybenzoic acid.
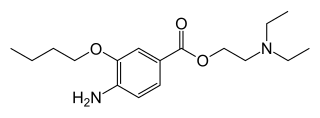
Oxybuprocaine (INN), also known as benoxinate or BNX, is an ester-type local anesthetic, which is used especially in ophthalmology and otolaryngology. Oxybuprocaine is sold by Novartis under the brand names Novesine or Novesin.
Monohydroxybenzoic acid may refer to any of three isomeric phenolic acids:
In enzymology, a 4-hydroxybenzoate polyprenyltransferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

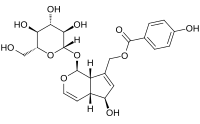
Aucubin is an iridoid glycoside. Iridoids are commonly found in plants and function as defensive compounds. Iridoids decrease the growth rates of many generalist herbivores.

Phenolic acids or phenolcarboxylic acids are types of aromatic acid compounds. Included in that class are substances containing a phenolic ring and an organic carboxylic acid function. Two important naturally occurring types of phenolic acids are hydroxybenzoic acids and hydroxycinnamic acids, which are derived from non-phenolic molecules of benzoic and cinnamic acid, respectively.

The phenolic content in tea refers to the phenols and polyphenols, natural plant compounds which are found in tea. These chemical compounds affect the flavor and mouthfeel of tea. Polyphenols in tea include catechins, theaflavins, tannins, and flavonoids.

3-Hydroxybenzoic acid is a monohydroxybenzoic acid.
Hydroxybenzoic acid may refer to several related chemical compounds:
2-Hydroxymuconate-6-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.85, xylG [gene], praB [gene] ) is an enzyme with systematic name (2E,4Z)-2-hydroxy-6-oxohexa-2,4-dienoate:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Casticin is a methoxylated flavonol, meaning the core flavonoid structure has methyl groups attached. Found in Artemisia annua, the flavonoid has been shown to enhance the antimalarial activity of artemisinin though casticin itself has no direct antimalarial effects. It has been shown to have anti-mitotic activity. It is also found in Vitex agnus-castus.
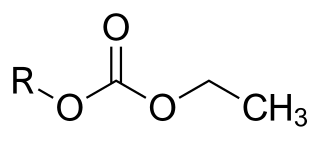
Etabonate or ethyl carbonate is the chemical group with formula –CO
3–C
2H
5, or H
3C–CH
2–O–C(=O)–O–. The names are also used for esters R–OCO
2C
2H
5, for the anion [C
2H
5OCO−
2], and for salts of the latter.

4-Hydroxybenzoic acid 4-O-glucoside is a glucoside of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. It can be found in mycorrhizal and non-mycorrhizal roots of Norway spruces.

Paroxypropione, also known as paraoxypropiophenone, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen which has been used medically as an antigonadotropin in Spain and Italy but appears to no longer be marketed. It was first synthesized in 1902. The antigonadotropic properties of the drug were discovered in 1951 and it entered clinical use shortly thereafter.