
Diethylstilbestrol (DES), also known as stilbestrol or stilboestrol, is a nonsteroidal estrogen medication, which is presently rarely used. In the past, it was widely used for a variety of indications, including pregnancy support for those with a history of recurrent miscarriage, hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and estrogen deficiency, treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer, and other uses. By 2007, it was only used in the treatment of prostate cancer and breast cancer. In 2011, Hoover and colleagues reported on adverse health outcomes linked to DES including infertility, miscarriage, ectopic pregnancy, preeclampsia, preterm birth, stillbirth, infant death, menopause prior to age 45, breast cancer, cervical cancer, and vaginal cancer. While most commonly taken by mouth, DES was available for use by other routes as well, for instance, vaginal, topical, and by injection.
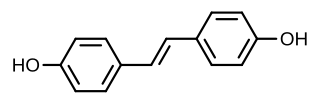
Stilbestrol, or stilboestrol, also known as 4,4'-dihydroxystilbene or 4,4'-stilbenediol, is a stilbenoid nonsteroidal estrogen and the parent compound of a group of more potent nonsteroidal estrogen derivatives that includes, most notably, diethylstilbestrol (DES). The term "stilbestrol" is often used incorrectly to refer to DES, but they are not the same compound.

Polyestradiol phosphate (PEP), sold under the brand name Estradurin, is an estrogen medication which is used primarily in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. It is also used in women to treat breast cancer, as a component of hormone therapy to treat low estrogen levels and menopausal symptoms, and as a component of feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women. It is given by injection into muscle once every four weeks.

Estradiol benzoate (EB), sold under the brand name Progynon-B among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women, in hormone therapy for transgender women, and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It is also used in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. Estradiol benzoate is used in veterinary medicine as well. When used clinically, the medication is given by injection into muscle usually two to three times per week.

Estradiol cypionate (EC), sold under the brand name Depo-Estradiol among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in cis women, in hormone therapy for trans women, and in hormonal birth control for cis women. It is given by injection into muscle once every 1 to 4 weeks.

Estriol succinate, sold under the brand name Synapause among others, is an estrogen medication which is used in the treatment of menopausal symptoms. It is taken by mouth, in through the vagina, and by injection.

Methallenestril (INN), also known as methallenoestril (BAN) and as methallenestrol, as well as Horeau's acid, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen and a derivative of allenolic acid and allenestrol that was formerly used to treat menstrual issues but is now no longer marketed. It is a seco-analogue of bisdehydrodoisynolic acid, and although methallenestril is potently estrogenic in rats, in humans it is only weakly so in comparison. Vallestril was a brand of methallenestril issued by G. D. Searle & Company in the 1950s. Methallenestril is taken by mouth. By the oral route, a dose of 25 mg methallenestril is approximately equivalent to 1 mg diethylstilbestrol, 4 mg dienestrol, 20 mg hexestrol, 25 mg estrone, 2.5 mg conjugated estrogens, and 0.05 mg ethinylestradiol.
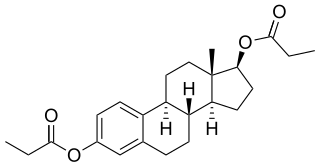
Estradiol dipropionate (EDP), sold under the brand names Agofollin, Di-Ovocylin, and Progynon DP among others, is an estrogen medication which has been used in hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms and low estrogen levels in women and in the treatment of gynecological disorders. It has also been used in feminizing hormone therapy for transgender women and in the treatment of prostate cancer in men. Although widely used in the past, estradiol dipropionate has largely been discontinued and is mostly no longer available today. It appears to remain in use only in Japan, Macedonia, and Australia. Estradiol dipropionate is given by injection into muscle at intervals ranging from once or twice a week to once every week and a half to two weeks.
An estrogen ester is an ester of an estrogen, most typically of estradiol but also of other estrogens such as estrone, estriol, and even nonsteroidal estrogens like diethylstilbestrol. Esterification renders estradiol into a prodrug of estradiol with increased resistance to first-pass metabolism, slightly improving its oral bioavailability. In addition, estrogen esters have increased lipophilicity, which results in a longer duration when given by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection due to the formation of a long-lasting local depot in muscle and fat. Conversely, this is not the case with intravenous injection or oral administration. Estrogen esters are rapidly hydrolyzed into their parent estrogen by esterases once they have been released from the depot. Because estradiol esters are prodrugs of estradiol, they are considered to be natural and bioidentical forms of estrogen.

Anol, also known as para-hydroxypropenylbenzene, is a simple phenol that was derived via demethylation from anethole, an estrogenic constituent of anise and fennel, by Sir Charles Dodds in 1937. It was reported to possess extremely potent estrogenic activity on par with that of steroidal estrogens like estrone, with a dose of 1 μg inducing estrus in rats. However, subsequent studies with different preparations of anol failed to confirm these findings, and it was found that dimerization of anol into dianol and hexestrol can rapidly occur and that the latter impurity was responsible for the highly potent estrogenic effects. Dodds later synthesized the structurally related and extremely potent estrogen diethylstilbestrol in 1938.

Methestrol or methoestrol, also known as promethestrol or promethoestrol (BAN) or as dimethylhexestrol, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol which is no longer marketed.

Estradiol hexahydrobenzoate (EHHB), sold under a number of brand names including Benzo-Ginoestril A.P., BenzoGynoestryl Retard, Ginestryl-15-Depot, Menodin, and Tardoginestryl, is an estrogen medication which was previously used for indications such as menopausal hormone therapy and gynecological disorders. EHHB is given by injection into muscle at regular intervals, for instance once every few weeks.

Dienestrol diacetate is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of dienestrol.

Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate (DESDP), or diethylstilbestrol dipropanoate, also known as stilboestrol dipropionate (BANM), is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group that was formerly marketed widely throughout Europe. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol with propionic acid, and is more slowly absorbed in the body than diethylstilbestrol. The medication has been said to be one of the most potent estrogens known.

Hexestrol diacetate (JAN) is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and was discovered in 1939.

Hexestrol dipropionate, or hexestrol dipropanoate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol. It is an ester of hexestrol, and has been known since at least 1931. The drug has been used in the past to inhibit lactation in women.
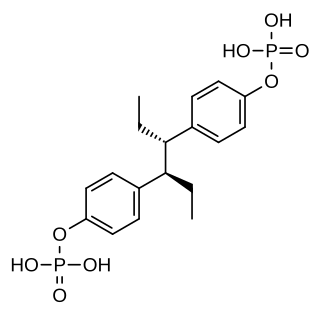
Hexestrol diphosphate is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol and used as an estrogen and antineoplastic agent in the treatment of prostate cancer. It is a water-soluble ester of hexestrol. The medication has been known since at least 1956.

Dianol is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen that was never marketed. It is a dimer and impurity of anol, and was, along with hexestrol, involved in erroneous findings of highly potent estrogenic activity with anol. Although a potent estrogen, it requires a dose of 100 μg to show activity, whereas hexestrol shows activity with a mere dose of 0.2 μg.
Hexestrol dicaprylate, or dioctanoylhexestrol, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol that is no longer marketed. It is a long-acting ester of hexestrol.


















