
Estriol (E3), also spelled oestriol, is a steroid, a weak estrogen, and a minor female sex hormone. It is one of three major endogenous estrogens, the others being estradiol and estrone. Levels of estriol in women who are not pregnant are almost undetectable. However, during pregnancy, estriol is synthesized in very high quantities by the placenta and is the most produced estrogen in the body by far, although circulating levels of estriol are similar to those of other estrogens due to a relatively high rate of metabolism and excretion. Relative to estradiol, both estriol and estrone have far weaker activity as estrogens.
17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases, also 17-ketosteroid reductases (17-KSR), are a group of alcohol oxidoreductases which catalyze the reduction of 17-ketosteroids and the dehydrogenation of 17β-hydroxysteroids in steroidogenesis and steroid metabolism. This includes interconversion of DHEA and androstenediol, androstenedione and testosterone, and estrone and estradiol.

Estrone sulfate, also known as E1S, E1SO4 and estrone 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester and conjugate.
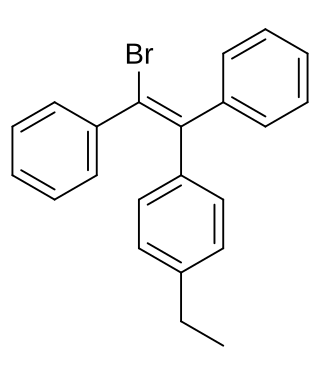
Broparestrol, also known as α-bromo-α,β-diphenyl-β-p-ethylphenylethylene (BDPE), is a synthetic, nonsteroidal selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group that has been used in Europe as a dermatological agent and for the treatment of breast cancer. The drug is described as slightly estrogenic and potently antiestrogenic, and inhibits mammary gland development and suppresses prolactin levels in animals. It is structurally related to clomifene and diethylstilbestrol. Broparestrol is a mixture of E- and Z- isomers, both of which are active, and are similarly antiestrogenic but, unlike broparestrol, were never marketed.

Estradiol sulfate (E2S), or 17β-estradiol 3-sulfate, is a natural, endogenous steroid and an estrogen ester. E2S itself is biologically inactive, but it can be converted by steroid sulfatase into estradiol, which is a potent estrogen. Simultaneously, estrogen sulfotransferases convert estradiol to E2S, resulting in an equilibrium between the two steroids in various tissues. Estrone and E2S are the two immediate metabolic sources of estradiol. E2S can also be metabolized into estrone sulfate (E1S), which in turn can be converted into estrone and estradiol. Circulating concentrations of E2S are much lower than those of E1S. High concentrations of E2S are present in breast tissue, and E2S has been implicated in the biology of breast cancer via serving as an active reservoir of estradiol.

8,9-Dehydroestrone, or Δ8-estrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10),8-tetraen-3-ol-17-one, is a naturally occurring estrogen found in horses which is closely related to equilin, equilenin, and estrone, and, as the 3-sulfate ester sodium salt, is a minor constituent (3.5%) of conjugated estrogens (Premarin). It produces 8,9-dehydro-17β-estradiol as an important active metabolite, analogously to conversion of estrone or estrone sulfate into estradiol. The compound was first described in 1997. In addition to 8,9-dehydroestrone and 8,9-dehydro-17β-estradiol, 8,9-dehydro-17α-estradiol is likely also to be present in conjugated estrogens, but has not been identified at this time.

2-Hydroxyestradiol (2-OHE2), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-2,3,17β-triol, is an endogenous steroid, catechol estrogen, and metabolite of estradiol, as well as a positional isomer of estriol.

16α-Hydroxyestrone (16α-OH-E1), or hydroxyestrone, also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,16α-diol-17-one, is an endogenous steroidal estrogen and a major metabolite of estrone, as well as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of estriol. It is a potent estrogen similarly to estrone, and it has been suggested that the ratio of 16α-hydroxyestrone to 2-hydroxyestrone, the latter being much less estrogenic in comparison and even antiestrogenic in the presence of more potent estrogens like estradiol, may be involved in the pathophysiology of breast cancer. Conversely, 16α-hydroxyestrone may help to protect against osteoporosis.

A catechol estrogen is a steroidal estrogen that contains catechol (1,2-dihydroxybenzene) within its structure. The catechol estrogens are endogenous metabolites of estradiol and estrone and include the following compounds:
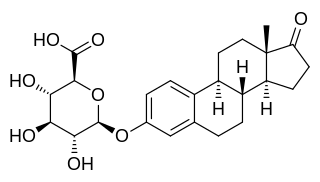
Estrone glucuronide, or estrone-3-D-glucuronide, is a conjugated metabolite of estrone. It is formed from estrone in the liver by UDP-glucuronyltransferase via attachment of glucuronic acid and is eventually excreted in the urine by the kidneys. It has much higher water solubility than does estrone. Glucuronides are the most abundant estrogen conjugates and estrone glucuronide is the dominant metabolite of estradiol.

4-Hydroxyestradiol (4-OHE2), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4,17β-triol, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen and a minor metabolite of estradiol. It is estrogenic, similarly to many other hydroxylated estrogen metabolites such as 2-hydroxyestradiol, 16α-hydroxyestrone, estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), and 4-hydroxyestrone but unlike 2-hydroxyestrone.
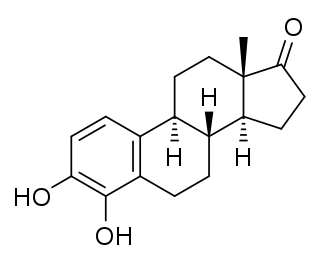
4-Hydroxyestrone (4-OHE1), also known as estra-1,3,5(10)-triene-3,4-diol-17-one, is an endogenous, naturally occurring catechol estrogen, neuroestrogen and a minor metabolite of estrone and estradiol. It is estrogenic, similarly to many other hydroxylated estrogen metabolites such as 2-hydroxyestradiol, 16α-hydroxyestrone, estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), and 4-hydroxyestradiol but unlike 2-hydroxyestrone. 4-OHE1 is also categorized as a carcinogen.
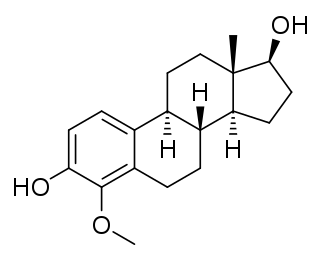
4-Methoxyestradiol (4-ME2) is an endogenous, naturally occurring methoxylated catechol estrogen and metabolite of estradiol that is formed by catechol O-methyltransferase via the intermediate 4-hydroxyestradiol. It has estrogenic activity similarly to estrone and 4-hydroxyestrone.

The hydroxylation of estradiol is one of the major routes of metabolism of the estrogen steroid hormone estradiol. It is hydroxylated into the catechol estrogens 2-hydroxyestradiol and 4-hydroxyestradiol and into estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), reactions which are catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes predominantly in the liver, but also in various other tissues.

Estriol 3-glucuronide, or oestriol 3-glucuronide, also known as estriol 3-β-D-glucosiduronic acid, is a natural, steroidal estrogen and a glucuronic acid conjugate of estriol. It is found in the urine of women as a reversibly formed metabolite of estriol. The positional isomer of estriol 3-glucuronide, estriol 16α-glucuronide, also occurs as an endogenous metabolite of estriol, but to a much greater extent in comparison.

RU-16117 is an estrogen medication which was investigated for the potential treatment of symptoms of estrogen deficiency such as hot flashes and osteoporosis in women but was never marketed. It was developed for use by mouth.

Estrone sulfate (E1S) is an estrogen medication and naturally occurring steroid hormone. It is used in menopausal hormone therapy among other indications. As the sodium salt, it is the major estrogen component of conjugated estrogens (Premarin) and esterified estrogens. In addition, E1S is used on its own as the piperazine salt estropipate. The compound also occurs as a major and important metabolite of estradiol and estrone. E1S is most commonly taken by mouth, but in the form of Premarin can also be taken by parenteral routes such as transdermal, vaginal, and injection.

16β-Hydroxyestrone (16β-OH-E1) is an endogenous estrogen which serves as a metabolite of estrone as well as a metabolic intermediate in the transformation of estrone into epiestriol (16β-hydroxyestradiol). 16β-Hydroxyestrone has similar estrogenic activity to that of 16α-hydroxyestrone. It is less potent than estradiol or estrone but can produce similar maximal uterotrophy at sufficiently high doses, suggesting a fully estrogenic profile.
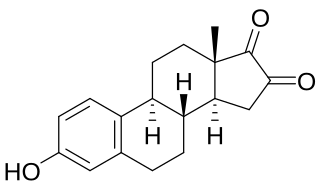
16-Ketoestrone is an endogenous estrogen related to 16α-hydroxyestrone and 16β-hydroxyestrone. In contrast to 16α-hydroxyestrone and 16β-hydroxyestrone, but similarly to 16-ketoestradiol, 16-ketoestrone is a very weak estrogen with less than 1/1000 the estrogenic potency of estrone in the uterus. 16-Ketoestrone has been reported to act as an inhibitor of 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. 16-Ketoestrone can be converted by 16α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase into estriol in the body.

The estrogen provocation test, also known as the estrogen stimulation test or estrogen challenge test, is a diagnostic procedure used to evaluate the function of the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal axis. It involves the administration of a large amount of estrogen, resulting in estrogenic exposure similar to or greater than normal preovulatory estradiol levels, in an attempt to induce a positive feedback surge in levels of the gonadotropins, luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Estrogens that have been used in the estrogen provocation test include estradiol benzoate, estradiol valerate, ethinylestradiol, and high-dose transdermal estradiol patches. The test involves sustained estrogenic exposure equivalent to estradiol levels of 200 to 300 pg/mL or more for at least 50 hours and results in a surge in gonadotropin levels about 32 to 72 hours following initiation of estrogenic exposure. Levels of LH and FSH increase during the gonadotropin surge by about 10-fold and 4-fold, respectively.

















