
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) are a class of drugs that inhibit the activity of one or both monoamine oxidase enzymes: monoamine oxidase A (MAO-A) and monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B). They are best known as effective antidepressants, especially for treatment-resistant depression and atypical depression. They are also used to treat panic disorder, social anxiety disorder, Parkinson's disease, and several other disorders.

Phenelzine, sold under the brand name Nardil, among others, is a non-selective and irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class which is primarily used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic. Along with tranylcypromine and isocarboxazid, phenelzine is one of the few non-selective and irreversible MAOIs still in widespread clinical use.

Tranylcypromine, sold under the brand name Parnate among others, is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). More specifically, tranylcypromine acts as nonselective and irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme monoamine oxidase (MAO). It is used as an antidepressant and anxiolytic agent in the clinical treatment of mood and anxiety disorders, respectively. It is also effective in the treatment of ADHD.

Mirtazapine, sold under the brand name Remeron among others, is an atypical tetracyclic antidepressant, and as such is used primarily to treat depression. Its effects may take up to four weeks but can also manifest as early as one to two weeks. It is often used in cases of depression complicated by anxiety or insomnia. The effectiveness of mirtazapine is comparable to other commonly prescribed antidepressants. It is taken by mouth.

Isocarboxazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class used as an antidepressant. Along with phenelzine and tranylcypromine, it is one of only three classical MAOIs still available for clinical use in the treatment of psychiatric disorders in the United States, though it is not as commonly employed in comparison to the others.

Nialamide is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was used as an antidepressant. It was withdrawn by Pfizer several decades ago due to the risk of hepatotoxicity.

Iproniazid is a non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It is a xenobiotic that was originally designed to treat tuberculosis, but was later most prominently used as an antidepressant drug. However, it was withdrawn from the market because of its hepatotoxicity. The medical use of iproniazid was discontinued in most of the world in the 1960s, but remained in use in France until its discontinuation in 2015.
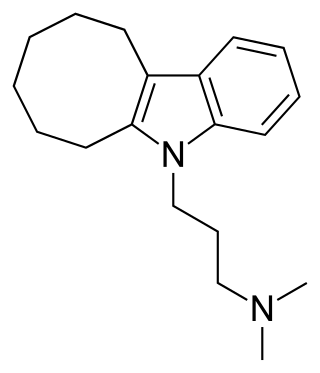
Iprindole, sold under the brand names Prondol, Galatur, and Tertran, is an atypical tricyclic antidepressant (TCA) that has been used in the United Kingdom and Ireland for the treatment of depression but appears to no longer be marketed. It was developed by Wyeth and was marketed in 1967. The drug has been described by some as the first "second-generation" antidepressant to be introduced. However, it was very little-used compared to other TCAs, with the number of prescriptions dispensed only in the thousands.

Iproclozide is an irreversible and selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was used as an antidepressant, but has since been discontinued. It has been known to cause fulminant hepatitis and there have been at least three reported fatalities due to administration of the drug.

Brasofensine is a phenyltropane dopamine reuptake inhibitor that had been under development by Bristol-Myers Squibb and defunct company NeuroSearch for the treatment of Parkinson's and Alzheimer's diseases.

Seproxetine, also known as (S)-norfluoxetine, is a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI). It is the S enantiomer of norfluoxetine, the main active metabolite of the widely used antidepressant fluoxetine; it is nearly 4 times more selective for stimulating neurosteroid synthesis relative to serotonin reuptake inhibition than fluoxetine. It is formed through the demethylation, or removal of a methyl group, of norfluoxetine. Seproxetine is both an inhibitor of serotonin and dopamine transporters, 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. It was being investigated by Eli Lilly and Company as an antidepressant; however, it inhibited the KvLQT1 protein, which is responsible for the management of the QT interval. This is the time it takes for the heart to contract and recover. Due to the inhibition, the QT interval was prolonged, which could lead to significant cardiac side complications. Due to this, development of the medication was discontinued. Tests on its efficacy found that it was equivalent to fluoxetine, but sixteen times more powerful than the R enantiomer of norfluoxetine.
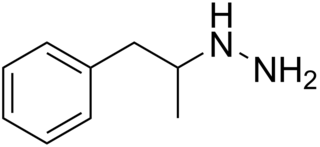
Pheniprazine is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was used as an antidepressant in the 1960s. It was also used in the treatment of angina pectoris and schizophrenia. Pheniprazine has been largely discontinued due to toxicity concerns such as jaundice, amblyopia, and optic neuritis.

Mebanazine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine chemical class that was previously used as an antidepressant in the 1960s, but has since been withdrawn due to hepatotoxicity.

Phenoxypropazine is an irreversible and non-selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine family. It was introduced as an antidepressant in 1961, but was subsequently withdrawn in 1966 due to hepatotoxicity concerns.

Benmoxin, also known as mebamoxine, is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class. It was synthesized in 1967 and was subsequently used as an antidepressant in Europe, but is now no longer marketed.

Binedaline (also called binodaline or binedaline hydrochloride;) is a drug that was investigated as an antidepressant in the 1980s but was never marketed. It acts as a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (Ki = 25 nM), with relatively insignificant influence on the serotonin (Ki = 847 nM) and dopamine (Ki >= 2 μM) transporters. It has negligible affinity for the α-adrenergic, mACh, H1, or 5-HT2 receptors.

The hydrazine antidepressants are a group of non-selective, irreversible monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) which were discovered and initially marketed in the 1950s and 1960s. Most have been withdrawn due to toxicity, namely hepatotoxicity, but a few still remain in clinical use.

Octamoxin, also known as 2-octylhydrazine, is an irreversible and nonselective monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) of the hydrazine class that was used as an antidepressant in the 1960s but is now no longer marketed.
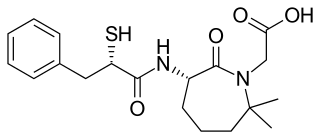
Gemopatrilat (INN) is an experimental drug that was never marketed. It acts as a vasopeptidase inhibitor. It inhibits both angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and neutral endopeptidase (neprilysin).

Fluperlapine, also known as fluoroperlapine, is a morphanthridine (11H-dibenzo[b,e]azepine) atypical antipsychotic with additional antidepressant and sedative effects. It was first synthesized in 1979, and then subsequently studied in animals and humans in 1984 and beyond, but despite demonstrating efficacy in the treatment of a variety of medical conditions including schizophrenia, psychosis associated with Parkinson's disease, depressive symptoms, and dystonia, it was never marketed. This was perhaps due to its capacity for producing potentially life-threatening agranulocytosis, similarly to clozapine, which it closely resembles both structurally and pharmacologically.



















