
Monoamine neurotransmitters are neurotransmitters and neuromodulators that contain one amino group connected to an aromatic ring by a two-carbon chain (such as -CH2-CH2-). Examples are dopamine, norepinephrine and serotonin.

Reuptake is the reabsorption of a neurotransmitter by a neurotransmitter transporter located along the plasma membrane of an axon terminal or glial cell after it has performed its function of transmitting a neural impulse.

Monoamine transporters (MATs) are proteins that function as integral plasma-membrane transporters to regulate concentrations of extracellular monoamine neurotransmitters. The three major classes are serotonin transporters (SERTs), dopamine transporters (DATs), and norepinephrine transporters (NETs) and are responsible for the reuptake of their associated amine neurotransmitters. MATs are located just outside the synaptic cleft (peri-synaptically), transporting monoamine transmitter overflow from the synaptic cleft back to the cytoplasm of the pre-synaptic neuron. MAT regulation generally occurs through protein phosphorylation and post-translational modification. Due to their significance in neuronal signaling, MATs are commonly associated with drugs used to treat mental disorders as well as recreational drugs. Compounds targeting MATs range from medications such as the wide variety of tricyclic antidepressants, selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors such as fluoxetine (Prozac) to stimulant medications such as methylphenidate (Ritalin) and amphetamine in its many forms and derivatives methamphetamine (Desoxyn) and lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse). Furthermore, drugs such as MDMA and natural alkaloids such as cocaine exert their effects in part by their interaction with MATs, by blocking the transporters from mopping up dopamine, serotonin, and other neurotransmitters from the synapse.

Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are a class of antidepressant medications used to treat major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobia, attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), chronic neuropathic pain, fibromyalgia syndrome (FMS), and menopausal symptoms. SNRIs are monoamine reuptake inhibitors; specifically, they inhibit the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine. These neurotransmitters are thought to play an important role in mood regulation. SNRIs can be contrasted with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (NRIs), which act upon single neurotransmitters.
A dopamine reuptake inhibitor (DRI) is a class of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitter dopamine by blocking the action of the dopamine transporter (DAT). Reuptake inhibition is achieved when extracellular dopamine not absorbed by the postsynaptic neuron is blocked from re-entering the presynaptic neuron. This results in increased extracellular concentrations of dopamine and increase in dopaminergic neurotransmission.
The vesicular monoamine transporter (VMAT) is a transport protein integrated into the membranes of synaptic vesicles of presynaptic neurons. It transports monoamine neurotransmitters – such as dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and histamine – into the vesicles, which release the neurotransmitters into synapses as chemical messages to postsynaptic neurons. VMATs utilize a proton gradient generated by V-ATPases in vesicle membranes to power monoamine import.

The norepinephrine transporter (NET), also known as noradrenaline transporter (NAT), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the solute carrier family 6 member 2 (SLC6A2) gene.
Neuromodulation is the physiological process by which a given neuron uses one or more chemicals to regulate diverse populations of neurons. Neuromodulators typically bind to metabotropic, G-protein coupled receptors (GPCRs) to initiate a second messenger signaling cascade that induces a broad, long-lasting signal. This modulation can last for hundreds of milliseconds to several minutes. Some of the effects of neuromodulators include: altering intrinsic firing activity, increasing or decreasing voltage-dependent currents, altering synaptic efficacy, increasing bursting activity and reconfigurating synaptic connectivity.

The solute carrier family 18 member 2 (SLC18A2) also known as vesicular monoamine transporter 2 (VMAT2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC18A2 gene. SLC18A2 is an integral membrane protein that transports monoamines—particularly neurotransmitters such as dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and histamine—from cellular cytosol into synaptic vesicles. In nigrostriatal pathway and mesolimbic pathway dopamine-releasing neurons, SLC18A2 function is also necessary for the vesicular release of the neurotransmitter GABA.

Vesicular monoamine transporter 1 (VMAT1) also known as chromaffin granule amine transporter (CGAT) or solute carrier family 18 member 1 (SLC18A1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC18A1 gene. VMAT1 is an integral membrane protein, which is embedded in synaptic vesicles and serves to transfer monoamines, such as norepinephrine, epinephrine, dopamine, and serotonin, between the cytosol and synaptic vesicles. SLC18A1 is an isoform of the vesicular monoamine transporter.
Neurotransmitter transporters are a class of membrane transport proteins that span the cellular membranes of neurons. Their primary function is to carry neurotransmitters across these membranes and to direct their further transport to specific intracellular locations. There are more than twenty types of neurotransmitter transporters.

Benzofuranylpropylaminopentane is a drug with an unusual monoamine-release potentiating mechanism of action. It can loosely be grouped with the stimulant or antidepressant drug families, but its mechanism of action is quite different.
In pharmacology, an indirect agonist or indirect-acting agonist is a substance that enhances the release or action of an endogenous neurotransmitter but has no specific agonist activity at the neurotransmitter receptor itself. Indirect agonists work through varying mechanisms to achieve their effects, including transporter blockade, induction of transmitter release, and inhibition of transmitter breakdown.

Nisoxetine, originally synthesized in the Lilly research laboratories during the early 1970s, is a potent and selective inhibitor for the reuptake of norepinephrine (noradrenaline) into synapses. It currently has no clinical applications in humans, although it was originally researched as an antidepressant. Nisoxetine is now widely used in scientific research as a standard selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor. It has been used to research obesity and energy balance, and exerts some local analgesia effects.
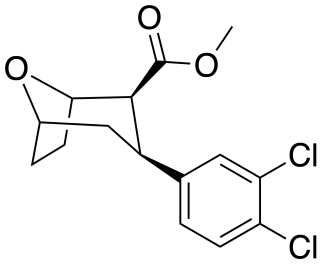
Tropoxane (O-1072) is an aryloxytropane derivative drug developed by Organix Inc., which acts as a stimulant and potent dopamine and serotonin reuptake inhibitor. It is an analogue of dichloropane where the amine nitrogen has been replaced by an oxygen ether link, demonstrating that the amine nitrogen is not required for DAT binding and reuptake inhibition.

A monoamine releasing agent (MRA), or simply monoamine releaser, is a drug that induces the release of a monoamine neurotransmitter from the presynaptic neuron into the synapse, leading to an increase in the extracellular concentrations of the neurotransmitter. Many drugs induce their effects in the body and/or brain via the release of monoamine neurotransmitters, e.g., trace amines, many substituted amphetamines, and related compounds.

Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitors (SARIs) are a class of drugs used mainly as antidepressants, but also as anxiolytics and hypnotics. They act by antagonizing serotonin receptors such as 5-HT2A and inhibiting the reuptake of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dopamine. Additionally, most also antagonize α1-adrenergic receptors. The majority of the currently marketed SARIs belong to the phenylpiperazine class of compounds.

A serotonin–dopamine reuptake inhibitor (SDRI) is a type of drug which acts as a reuptake inhibitor of the monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin and dopamine by blocking the actions of the serotonin transporter (SERT) and dopamine transporter (DAT), respectively. This in turn leads to increased extracellular concentrations of serotonin and dopamine, and, therefore, an increase in serotonergic and dopaminergic neurotransmission.
A monoamine reuptake inhibitor (MRI) is a drug that acts as a reuptake inhibitor of one or more of the three major monoamine neurotransmitters serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine by blocking the action of one or more of the respective monoamine transporters (MATs), which include the serotonin transporter (SERT), norepinephrine transporter (NET), and dopamine transporter (DAT). This in turn results in an increase in the synaptic concentrations of one or more of these neurotransmitters and therefore an increase in monoaminergic neurotransmission.
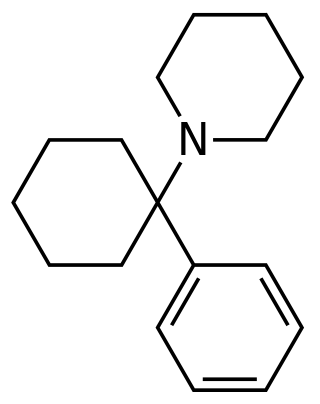
PCP site 2 is a binding site that was identified as a high-affinity target for phencyclidine (PCP), an anesthetic and dissociative hallucinogen that acts primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. The site is distinct from the PCP binding site on the NMDA receptor and the common/main sites on the monoamine transporters. It is associated with monoamine reuptake inhibition, and it has been suggested that the site may be an allosteric/regulatory site of the monoamine transporters.

















