
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Substances that increase or decrease the overall activity of the cholinergic system are called cholinergics and anticholinergics, respectively.

The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies smooth muscle and glands, and thus influences the function of internal organs. The autonomic nervous system is a control system that acts largely unconsciously and regulates bodily functions, such as the heart rate, digestion, respiratory rate, pupillary response, urination, and sexual arousal. This system is the primary mechanism in control of the fight-or-flight response.

The parasympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the sympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.

The sympathetic nervous system is one of the three divisions of the autonomic nervous system, the others being the parasympathetic nervous system and the enteric nervous system. The enteric nervous system is sometimes considered part of the autonomic nervous system, and sometimes considered an independent system.
Anticholinergics are substances that block the action of the neurotransmitter called acetylcholine (ACh) at synapses in the central and peripheral nervous system.
A parasympathomimetic drug, sometimes called a cholinomimetic drug or cholinergic receptor stimulating agent, is a substance that stimulates the parasympathetic nervous system (PSNS). These chemicals are also called cholinergic drugs because acetylcholine (ACh) is the neurotransmitter used by the PSNS. Chemicals in this family can act either directly by stimulating the nicotinic or muscarinic receptors, or indirectly by inhibiting cholinesterase, promoting acetylcholine release, or other mechanisms. Common uses of parasympathomimetics include glaucoma, sjögren syndrome and underactive bladder.

Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral nervous system, muscle, and many other tissues of many organisms. At the neuromuscular junction they are the primary receptor in muscle for motor nerve-muscle communication that controls muscle contraction. In the peripheral nervous system: (1) they transmit outgoing signals from the presynaptic to the postsynaptic cells within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system, and (2) they are the receptors found on skeletal muscle that receive acetylcholine released to signal for muscular contraction. In the immune system, nAChRs regulate inflammatory processes and signal through distinct intracellular pathways. In insects, the cholinergic system is limited to the central nervous system.

Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, or mAChRs, are acetylcholine receptors that form G protein-coupled receptor complexes in the cell membranes of certain neurons and other cells. They play several roles, including acting as the main end-receptor stimulated by acetylcholine released from postganglionic fibers in the parasympathetic nervous system.

Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors.
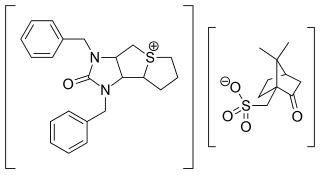
Trimetaphan camsilate (INN) or trimethaphan camsylate (USAN), trade name Arfonad, is a drug that counteracts cholinergic transmission at the ganglion type of nicotinic receptors of the autonomic ganglia and therefore blocks both the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. It acts as a non-depolarizing competitive antagonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, is short-acting, and is given intravenously.
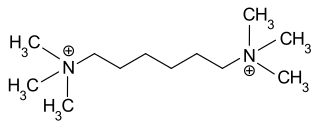
Hexamethonium is a non-depolarising ganglionic blocker, a nicotinic (nAChR) receptor antagonist that acts in autonomic ganglia by binding mostly in or on the nAChR receptor, and not the acetylcholine binding site itself. It does not have any effect on the muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (mAChR) located on target organs of the parasympathetic nervous system but acts as antagonist at the nicotinic acetylcholine receptors located in sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia (nAChR).

In the autonomic nervous system, fibers from the ganglion to the effector organ are called postganglionic fibers.
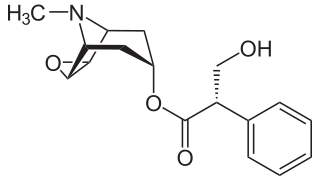
A muscarinic receptor antagonist (MRA) is a type of anticholinergic agent that blocks the activity of the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. The muscarinic receptor is a protein involved in the transmission of signals through certain parts of the nervous system, and muscarinic receptor antagonists work to prevent this transmission from occurring. Notably, muscarinic antagonists reduce the activation of the parasympathetic nervous system. The normal function of the parasympathetic system is often summarised as "rest-and-digest", and includes slowing of the heart, an increased rate of digestion, narrowing of the airways, promotion of urination, and sexual arousal. Muscarinic antagonists counter this parasympathetic "rest-and-digest" response, and also work elsewhere in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
A sympatholytic drug is a medication that opposes the downstream effects of postganglionic nerve firing in effector organs innervated by the sympathetic nervous system (SNS). They are indicated for various functions; for example, they may be used as antihypertensives. They are also used to treat anxiety, such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder and PTSD. In some cases, such as with Guanfacine, they have also shown to be beneficial in the treatment of ADHD.
Pentolinium is a ganglionic blocking agent which acts as a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist. Formulated as the pentolinium tartrate salt, it is also known as Ansolysen. It can be used as an antihypertensive drug during surgery or to control hypertensive crises. It works by binding to the acetylcholine receptor of adrenergic nerves and thereby inhibiting the release of noradrenaline and adrenaline. Blocking this receptor leads to smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation.

Surugatoxin (SGTX) is a type of venom found in the mid-gut digestive gland of the Japanese ivory mollusk Babyloniajaponica, a carnivorous gastropod. It functions as a ganglionic blocker of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The structurally and functionally related neosurugatoxin, also derived from Babylonia japonica, is an even more potent nAChR antagonist than SGTX.
The alpha-3 beta-4 nicotinic receptor, also known as the α3β4 receptor and the ganglion-type nicotinic receptor, is a type of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor, consisting of α3 and β4 subunits. It is located in the autonomic ganglia and adrenal medulla, where activation yields post- and/or presynaptic excitation, mainly by increased Na+ and K+ permeability.

Phantasmidine is a toxic substance derived from the Ecuadorian poisonous frog Anthony's poison arrow frog, more commonly known as the “phantasmal poison frog”. It is a nicotinic agonist, meaning it binds to nicotinic receptors in the body and mimics the effects of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. This causes the stimulation of the body's parasympathetic nervous system, which induces many inhibitory behaviors in the body such as decreased heart rate.
Autonomic drugs can either inhibit or enhance the functions of the parasympathetic and sympathetic nervous systems. This type of drug can be used to treat a wide range of diseases, such as glaucoma, asthma, urinary, gastrointestinal and cardiopulmonary disorders.

Cholinergic blocking drugs are a group of drugs that block the action of acetylcholine (ACh), a neurotransmitter, in synapses of the cholinergic nervous system. They block acetylcholine from binding to cholinergic receptors, namely the nicotinic and muscarinic receptors.












