
Ethers are a class of organic compounds that contain an ether group—an oxygen atom connected to two alkyl or aryl groups. They have the general formula R–O–R′, where R and R′ represent the alkyl or aryl groups. Ethers can again be classified into two varieties: if the alkyl groups are the same on both sides of the oxygen atom, then it is a simple or symmetrical ether, whereas if they are different, the ethers are called mixed or unsymmetrical ethers. A typical example of the first group is the solvent and anesthetic diethyl ether, commonly referred to simply as "ether" (CH3–CH2–O–CH2–CH3). Ethers are common in organic chemistry and even more prevalent in biochemistry, as they are common linkages in carbohydrates and lignin.
In chemical nomenclature, the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is a method of naming organic chemical compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). It is published in the Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which an unambiguous structural formula can be created. There is also an IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry.

Fenobucarb is a carbamate insecticide. A pale yellow or pale red liquid, insoluble in water; used as an agricultural insecticide on rice and cotton and moderately toxic for humans.

A methoxy group is the functional group consisting of a methyl group bound to oxygen. This alkoxy group has the formula O–CH3. On a benzene ring, the Hammett equation classifies a methoxy substituent at the para position as an electron-donating group, but as an electron-withdrawing group if at the meta position. At the ortho position, steric effects are likely to cause a significant alteration in the Hammett equation prediction which otherwise follows the same trend as that of the para position.
Demeton-S-methyl is an organic compound with the molecular formula C6H15O3PS2. It was used as an organothiophosphate acaricide and organothiophosphate insecticide. It is flammable. With prolonged storage, Demeton-S-methyl becomes more toxic due to formation of a sulfonium derivative which has greater affinity to the human form of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, and this may present a hazard in agricultural use.

Dimethyl terephthalate (DMT) is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(COOCH3)2. It is the diester formed from terephthalic acid and methanol. It is a white solid that melts to give a distillable colourless liquid.
The Controlled Drugs and Substances Act is Canada's federal drug control statute. Passed in 1996 under Prime Minister Jean Chrétien's government, it repeals the Narcotic Control Act and Parts III and IV of the Food and Drugs Act, and establishes eight Schedules of controlled substances and two Classes of precursors. It provides that "The Governor in Council may, by order, amend any of Schedules I to VIII by adding to them or deleting from them any item or portion of an item, where the Governor in Council deems the amendment to be necessary in the public interest."

A sulfoxide is a chemical compound containing a sulfinyl (SO) functional group attached to two carbon atoms. It is a polar functional group. Sulfoxides are the oxidized derivatives of sulfides. Examples of important sulfoxides are alliin, a precursor to the compound that gives freshly crushed garlic its aroma, and dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), a common solvent.
Pyrylium is a cation with formula C
5H
5O+
, consisting of a six-membered ring of five carbon atoms, each with one hydrogen atom, and one positively charged oxygen atom. The bonds in the ring are conjugated as in benzene, giving it an aromatic character. In particular, because of the positive charge, the oxygen atom is trivalent. Pyrilium is a mono-cyclic and heterocyclic compound, one of the oxonium ions.

Methyl carbamate (also called methylurethane, or urethylane) is an organic compound and the simplest ester of carbamic acid (H2NCO2H). It is a colourless solid.
This is the list of extremely hazardous substances defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act. The list can be found as an appendix to 40 C.F.R. 355. Updates as of 2006 can be seen on the Federal Register, 71 FR 47121.

Organothiophosphates or organophosphorothioates are a subclass of organophosphorus compounds. Many of these compounds are used as pesticides, some have medical applications, and some are used as oil additives. They generally have the chemical formula (RO)3PS, [(RO)2P(S)O]−, R(RO)2PS, etc.

Dimethyl carbonate (DMC) is an organic compound with the formula OC(OCH3)2. It is a colourless, flammable liquid. It is classified as a carbonate ester. This compound has found use as a methylating agent and more recently as a solvent that is exempt from the restrictions placed on most volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in the US. Dimethyl carbonate is often considered to be a green reagent.

Dimethyl malonate is a diester derivative of malonic acid. It is a common reagent for organic synthesis used, for example, as a precursor for barbituric acid. It is also used in the malonic ester synthesis. It can be synthesized from dimethoxymethane and carbon monoxide.
4-Pyrone (γ-pyrone or pyran-4-one) is an unsaturated cyclic chemical compound with the molecular formula C5H4O2. It is isomeric with 2-pyrone.

Pirimiphos-methyl, marketed as Actellic, and Sybol is a phosphorothioate used as an insecticide. It was originally developed by Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd., now Syngenta, at their Jealott's Hill site and first marketed in 1977, ten years after its discovery.

Hagemann's ester, ethyl 2-methyl-4-oxo-2-cyclohexenecarboxylate, is an organic compound that was first prepared and described in 1893 by German chemist Carl Hagemann. The compound is used in organic chemistry as a reagent in the synthesis of many natural products including sterols, trisporic acids, and terpenoids.
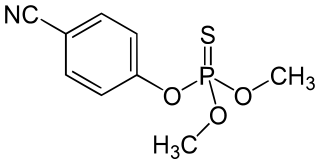
Cyanophos is a cholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide and avicide; for example, against rice stem borers and house flies. It is part of the chemical class of organophosphorus compounds, and is a yellow to reddish-yellow transparent liquid.

To combat the illicit synthetic cannabinoid industry many jurisdictions have created a system to control these cannabinoids through their general structure as opposed to their specific identity. In this way new analogs are already controlled before they are even created. A large number of cannabinoids have been grouped into classes based on similarities in their chemical structure, and these classes have been widely adopted across a variety of jurisdictions.














