
The enzyme cholinesterase (EC 3.1.1.8, choline esterase; systematic name acylcholine acylhydrolase) catalyses the hydrolysis of choline-based esters:

A carbamate is a category of organic compounds that is formally derived from carbamic acid (NH2COOH). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion H
2NCOO−
(e.g. ammonium carbamate).

Galantamine is used for the treatment of cognitive decline in mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease and various other memory impairments. It is an alkaloid that has been isolated from the bulbs and flowers of Galanthus nivalis, Galanthus caucasicus, Galanthus woronowii, and some other members of the family Amaryllidaceae, such as Narcissus (daffodil), Leucojum aestivum (snowflake), and Lycoris including Lycoris radiata. It can also be produced synthetically.
Butyrylcholine is a choline-based ester that can function as a neurotransmitter. It is similar to acetylcholine, with activation of some of the same receptors as acetylcholine. Butyrylcholine is a synthetic compound and does not occur in the body naturally. It is used as a clinical laboratory tool to distinguish between the cholinesterases; acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase preferentially lyse acetylcholine and butyrylcholine, respectively. It is also known as pseudocholinesterase.

Huperzine A is a naturally occurring sesquiterpene alkaloid compound found in the firmoss Huperzia serrata and in varying quantities in other food Huperzia species, including H. elmeri, H. carinat, and H. aqualupian. Huperzine A has been investigated as a treatment for neurological conditions such as Alzheimer's disease, but a meta-analysis of those studies concluded that they were of poor methodological quality and the findings should be interpreted with caution. Huperzine A inhibits the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. It is commonly available over the counter as a nutrient supplement, and is marketed as a cognitive enhancer for improving memory and concentration.

Pralidoxime or 2-PAM, usually as the chloride or iodide salts, belongs to a family of compounds called oximes that bind to organophosphate-inactivated acetylcholinesterase. It is used to treat organophosphate poisoning in conjunction with atropine and either diazepam or midazolam. It is a white solid.
Ambenonium is a cholinesterase inhibitor used in the management of myasthenia gravis.

Acetylcholinesterase (HGNC symbol ACHE; EC 3.1.1.7; systematic name acetylcholine acetylhydrolase), also known as AChE, AChase or acetylhydrolase, is the primary cholinesterase in the body. It is an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine and some other choline esters that function as neurotransmitters:

Minaprine is a monoamine oxidase inhibitor antidepressant drug that was used in France for the treatment of depression until it was withdrawn from the market in 1996 because it caused convulsions.

Onchidal is a naturally occurring neurotoxin produced as a defensive secretion by the mollusc Onchidella binneyi and several other related species in Onchidella, a genus of small, air-breathing sea slugs. It acts as an irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, the same mechanism of action as that of the deadly nerve agents, however onchidal is not an organophosphorus or carbamate compound and bears little resemblance to other compounds of this nature.

Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (AChEIs) also often called cholinesterase inhibitors, inhibit the enzyme acetylcholinesterase from breaking down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine into choline and acetate, thereby increasing both the level and duration of action of acetylcholine in the central nervous system, autonomic ganglia and neuromuscular junctions, which are rich in acetylcholine receptors. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are one of two types of cholinesterase inhibitors; the other being butyryl-cholinesterase inhibitors. Acetylcholinesterase is the primary member of the cholinesterase enzyme family.

Corynoline is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Corydalis incisa.
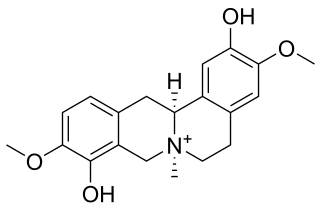
Cyclanoline is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Stephania venosa tuber.

Ungiminorine is an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Narcissus.

Arisugacin A is an orally-active acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.

Fasciculins are a class of toxic proteins found in certain snake venoms, notably some species of mamba. Investigations have revealed distinct forms in some green mamba venoms, in particular FAS1 and FAS2 Fasciculins are so called because they cause intense fasciculation in muscle fascicles of susceptible organisms, such as the preferred prey of the snakes. This effect helps to incapacitate the muscles, either killing the prey, or paralysing it so that the snake can swallow it.

Mipafox is a highly toxic organophosphate insecticide that can cause delayed neurotoxicity and paralysis. It is an irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor that is resistant to oxime reactivators.

Methylfluorophosphonylcholine (MFPCh) is an extremely toxic chemical compound related to the G-series nerve agents. It is an extremely potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which is around 100 times more potent than sarin at inhibiting acetylcholinesterase in vitro, and around 10 times more potent in vivo, depending on route of administration and animal species tested. MFPCh is resistant to oxime reactivators, meaning the acetylcholinesterase inhibited by MFPCh can't be reactivated by oxime reactivators. MFPCh also acts directly on the acetylcholine receptors. However, despite its high toxicity, methylfluorophosphonylcholine is a relatively unstable compound and degrades rapidly in storage, so it was not deemed suitable to be weaponised for military use.
BW284C51 is a selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is also a nicotinic antagonist.

TMTFA is an extremely potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. As a transition state analog of acetylcholinesterase, TMTFA is able to inhibit the acetylcholinesterase at extremely low concentrations, making it one of the most potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitors known.

















