
A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is a document that lists information relating to occupational safety and health for the use of various substances and products. SDSs are a widely used system for cataloguing information on chemicals, chemical compounds, and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product, along with spill-handling procedures. The older MSDS formats could vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements; however, the newer SDS format is internationally standardized.

VG is a "V-series" nerve agent chemically similar to the better-known VX nerve agent. Tetram is the common Russian name for the substance. Amiton was the trade name for the substance when it was marketed as an insecticide by ICI in the mid-1950s.

Aldicarb is a carbamate insecticide which is the active substance in the pesticide Temik. It is effective against thrips, aphids, spider mites, lygus, fleahoppers, and leafminers, but is primarily used as a nematicide. Aldicarb is a cholinesterase inhibitor which prevents the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synapse. In case of severe poisoning, the victim dies of respiratory failure.

The Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act of 1986 is a United States federal law passed by the 99th United States Congress located at Title 42, Chapter 116 of the U.S. Code, concerned with emergency response preparedness.

Bromadiolone is a potent anticoagulant rodenticide. It is a second-generation 4-hydroxycoumarin derivative and vitamin K antagonist, often called a "super-warfarin" for its added potency and tendency to accumulate in the liver of the poisoned organism. When first introduced to the UK market in 1980, it was effective against rodent populations that had become resistant to first generation anticoagulants.

Coumaphos is a nonvolatile, fat-soluble phosphorothioate with ectoparasiticide properties: it kills insects and mites. It is well known by a variety of brand names as a dip or wash, used on farm and domestic animals to control ticks, mites, flies and fleas.

Chlorophacinone is an anticoagulant used as a rodenticide. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
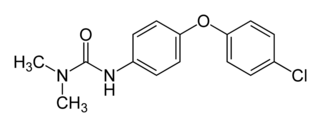
Chloroxuron is an organic compound with the chemical formula C15H15ClN2O2 used as an herbicide. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.

Isobenzan (telodrin) is a highly toxic organochloride insecticide. It was produced only in the period from 1958 to 1965 and its use has been since discontinued. It is a persistent organic pollutant that can remain in soil for 2 to 7 years, and the biological half-life of isobenzan in human blood is estimated to be about 2.8 years.

Azinphos-ethyl was a broad-spectrum organophosphate insecticide.

Methyl thiocyanate is an organic compound with the formula CH3SCN. The simplest member of the organic thiocyanates, it is a colourless liquid with an onion-like odor. It is produced by the methylation of thiocyanate salts. The compound is a precursor to the more useful isomer methyl isothiocyanate (CH3NCS).
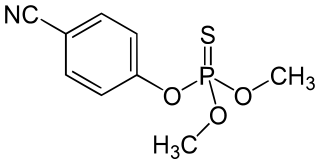
Cyanophos is a cholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide and avicide; for example, against rice stem borers and house flies. It is part of the chemical class of organophosphorus compounds, and is a yellow to reddish-yellow transparent liquid.

Oxamyl is a chemical used as a pesticide that comes in two forms: granulated and liquid. The granulated form has been banned in the United States. It is commonly sold under the trade name Vydate.

Bitoscanate is an organic chemical compound used in the treatment of hookworms. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.

Bis(chloromethyl) ketone is a chemical substance with formula C
3H
4Cl
2O. It is a solid, and is used in the making of citric acid. Exposures such as contact or inhalation of bis(chloromethyl) ketone can result in irritation or damage to skin, eyes, throat, lungs, liver and kidneys, as well as headaches and fainting.
Lactonitrile is the organic compound with the formula CH3CH(OH)CN. It is an intermediate in the industrial production of ethyl lactate and lactic acid. It is the cyanohydrin of acetaldehyde. It is a colorless liquid, although degraded samples can appear yellow.
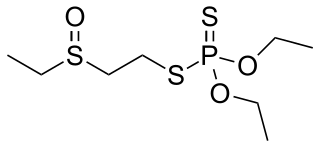
Oxydisulfoton is a chemical compound used as an acaricide and insecticide. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
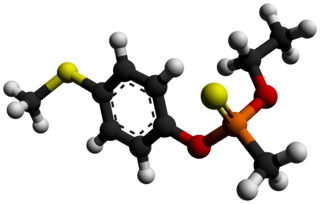
BAY-29952 is a broad spectrum insecticide. It is listed as an extremely hazardous substance according to the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.

Fluomine is a chemical compound containing a cobalt chelate. It has the ability to form a complex with molecular oxygen (O2) and then release it upon heating. Because of this ability to reversibly sorb and desorb oxygen, it has been used in high-altitude aircraft oxygen-generating systems.


















