 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Simparica |
| Other names | PF-6450567 |
| ATCvet code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.234.000 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
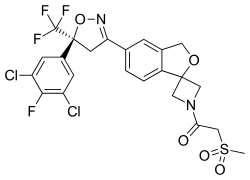
| Formula | C23H18Cl2F4N2O5S |
| Molar mass | 581.36 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Sarolaner, sold under the brand name Simparica, is an ectoparasiticide veterinary medication for the treatment of flea and tick infestations in dogs. [7] [8] It is also used off-label to control sarcoptic mange and demodectic mange. [8]
Sarolaner is also a component of the combination drug Simparica Trio, which contains sarolaner, moxidectin, and pyrantel. [9] [10] It is used for prevention of heartworm disease caused by Dirofilaria immitis ; treat and prevent flea infestations; treat and control tick infestations with the lone star tick, Gulf Coast tick, American dog tick, black-legged tick, and brown dog tick; and treat and control roundworm and adult hookworm infections. [11]
Sarolaner is also an ingredient in feline combination antiparasitic Revolution Plus (or Stronghold Plus [12] ), which contains sarolaner and selamectin and is used for prevention of sarcoptic mange, feline hookworms, feline roundworms, ear mites, and heartworms, as well as treating and preventing fleas and ticks. [13]
In November 2024, the FDA approved a supplement that provides for the addition of the indication for the treatment and control of Haemaphysalis longicornis (Asian longhorned tick) infestations for one month in dogs six months of age or older and weighing 2.8 pounds (1.3 kg) or greater. [14] [15]