 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
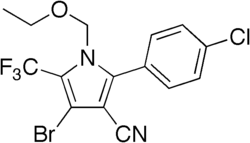
| Preferred IUPAC name 4-Bromo-2-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(ethoxymethyl)-5-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-pyrrole-3-carbonitrile | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.116.332 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H11BrClF3N2O | |
| Molar mass | 407.62 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.543 g/ml tapped bulk density |
| Melting point | 100 to 101 °C (212 to 214 °F; 373 to 374 K) |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
    | |
| Danger | |
| H302, H320, H331, H371, H373, H410 | |
| P260, P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P301+P312, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P309+P311, P311, P314, P321, P330, P337+P313, P391, P403+P233, P405, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Chlorfenapyr is an insecticide, and specifically a pro-insecticide (meaning it is metabolized into an active insecticide after entering the host). [1] It is derived from a class of microbially produced compounds known as halogenated pyrroles.