Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, industrial buildings, for vector control, and control of insect parasites of animals and humans.
Pyrethrum was a genus of several Old World plants now classified in either Chrysanthemum or Tanacetum which are cultivated as ornamentals for their showy flower heads. Pyrethrum continues to be used as a common name for plants formerly included in the genus Pyrethrum. Pyrethrum is also the name of a natural insecticide made from the dried flower heads of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium and Chrysanthemum coccineum. The insecticidal compounds present in these species are pyrethrins.

Piperonyl butoxide (PBO) is a pale yellow to light brown liquid organic compound used as an adjuvant component of pesticide formulations for synergy. That is, despite having no pesticidal activity of its own, it enhances the potency of certain pesticides such as carbamates, pyrethrins, pyrethroids, and rotenone. It is a semisynthetic derivative of safrole and is produced from the condensation of the sodium salt of 2-(2-butoxyethoxy) ethanol and the chloromethyl derivative of hydrogenated safrole (dihydrosafrole); or through 1,2-Methylenedioxybenzene.

The pyrethrins are a class of organic compounds normally derived from Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium that have potent insecticidal activity by targeting the nervous systems of insects. Pyrethrin naturally occurs in chrysanthemum flowers and is often considered an organic insecticide when it is not combined with piperonyl butoxide or other synthetic adjuvants. Their insecticidal and insect-repellent properties have been known and used for thousands of years.

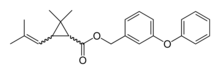
Bifenthrin is a pyrethroid insecticide. It is widely used against ant infestations.
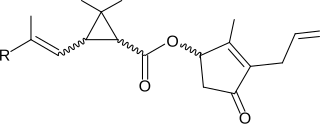
A pyrethroid is an organic compound similar to the natural pyrethrins, which are produced by the flowers of pyrethrums. Pyrethroids are used as commercial and household insecticides.

Fenvalerate is a synthetic pyrethroid insecticide. It is a mixture of four optical isomers which have different insecticidal activities. The 2-S alpha configuration, known as esfenvalerate, is the most insecticidally active isomer. Fenvalerate consists of about 23% of this isomer.

Permethrin is a medication and an insecticide. As a medication, it is used to treat scabies and lice. It is applied to the skin as a cream or lotion. As an insecticide, it can be sprayed onto outer clothing or mosquito nets to kill the insects that touch them.

An insect repellent is a substance applied to the skin, clothing, or other surfaces to discourage insects from landing or climbing on that surface. Insect repellents help prevent and control the outbreak of insect-borne diseases such as malaria, Lyme disease, dengue fever, bubonic plague, river blindness, and West Nile fever. Pest animals commonly serving as vectors for disease include insects such as flea, fly, and mosquito; and ticks (arachnids).

The allethrins are a group of related synthetic compounds used in insecticides. They are classified as pyrethroids, i.e. synthetic versions of pyrethrin, a chemical with insecticidal properties found naturally in Chrysanthemum flowers. They were first synthesized in the United States by Milton S. Schechter in 1949. Allethrin was the first pyrethroid.

Deltamethrin is a pyrethroid ester insecticide. Deltamethrin plays a key role in controlling malaria vectors, and is used in the manufacture of long-lasting insecticidal mosquito nets; however, resistance of mosquitos and bed bugs to deltamethrin has seen a widespread increase.

Methoprene is a juvenile hormone (JH) analog which acts as a growth regulator when used as an insecticide. It is an amber-colored liquid with a faint fruity odor.

Resmethrin is a pyrethroid insecticide with many uses, including control of the adult mosquito population.
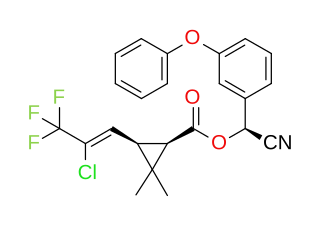
Cyhalothrin is an organic compound that, in specific isomeric forms, is used as a pesticide. It is a pyrethroid, a class of synthetic insecticides that mimic the structure and properties of the naturally occurring insecticide pyrethrin which is present in the flowers of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium. Pyrethroids, such as cyhalothrin, are often preferred as an active ingredient in agricultural insecticides because they are more cost-effective and longer acting than natural pyrethrins. λ-and γ-cyhalothrin are now used to control insects and spider mites in crops including cotton, cereals, potatoes and vegetables.
A fogger is any device that creates a fog, typically containing an insecticide for killing insects and other arthropods. Foggers are often used by consumers as a low cost alternative to professional pest control services. The number of foggers needed for pest control depends on the size of the space to be treated, as stated for safety reasons on the instructions supplied with the devices. The fog may contain flammable gases, leading to a danger of explosion if a fogger is used in a building with a pilot light or other naked flame.

Cyfluthrin is a pyrethroid insecticide and common household pesticide. It is a complex organic compound and the commercial product is sold as a mixture of isomers. Like most pyrethroids, it is highly toxic to fish and invertebrates, but it is far less toxic to humans. It is generally supplied as a 10–25% liquid concentrate for commercial use and is diluted prior to spraying onto agricultural crops and outbuildings.

Dinotefuran is an insecticide of the neonicotinoid class developed by Mitsui Chemicals for control of insect pests such as aphids, whiteflies, thrips, leafhoppers, leafminers, sawflies, mole cricket, white grubs, lacebugs, billbugs, beetles, mealybugs, and cockroaches on leafy vegetables, in residential and commercial buildings, and for professional turf management. Its mechanism of action involves disruption of the insect's nervous system by inhibiting nicotinic acetylcholine receptors.

Tefluthrin is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a pesticide. It is a pyrethroid, a class of synthetic insecticides that mimic the structure and properties of the naturally occurring insecticide pyrethrin which is present in the flowers of Chrysanthemum cinerariifolium. Pyrethroids such as tefluthrin are often preferred as active ingredients in agricultural insecticides because they are more cost-effective and longer acting than natural pyrethrins. It is effective against soil pests because it can move as a vapour without irreversibly binding to soil particles: in this respect it differs from most other pyrethroids.
Flea treatments are procedures used to treat flea infestations in human or animal populations. They may treat both the itching caused by bites and may remove or kill the fleas themselves.
Antiandrogens in the environment have become a topic of concern. Many industrial chemicals, including phthalates and pesticides, exhibit antiandrogen activity in animal experiments. Certain plant species have also been found to produce antiandrogens. In animal studies, environmental antiandrogens can harm reproductive organ development in fetuses exposed in utero as well as their offspring.