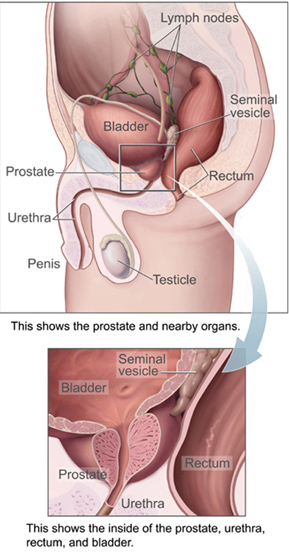
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found in all male mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physiologically. Anatomically, the prostate is found below the bladder, with the urethra passing through it. It is described in gross anatomy as consisting of lobes and in microanatomy by zone. It is surrounded by an elastic, fibromuscular capsule and contains glandular tissue, as well as connective tissue.

Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), also called prostate enlargement, is a noncancerous increase in size of the prostate gland. Symptoms may include frequent urination, trouble starting to urinate, weak stream, inability to urinate, or loss of bladder control. Complications can include urinary tract infections, bladder stones, and chronic kidney problems.
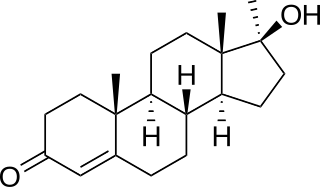
Methyltestosterone, sold under the brand names Android, Metandren, and Testred among others, is an androgen and anabolic steroid (AAS) medication which is used in the treatment of low testosterone levels in men, delayed puberty in boys, at low doses as a component of menopausal hormone therapy for menopausal symptoms like hot flashes, osteoporosis, and low sexual desire in women, and to treat breast cancer in women. It is taken by mouth or held in the cheek or under the tongue.

Finasteride, sold under the brand names Proscar and Propecia among others, is a medication used to treat pattern hair loss and benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men. It can also be used to treat excessive hair growth in women. It is usually taken orally but there are topical formulations for patients with hair loss, designed to minimize systemic exposure by acting specifically on hair follicles.

5α-Reductases, also known as 3-oxo-5α-steroid 4-dehydrogenases, are enzymes involved in steroid metabolism. They participate in three metabolic pathways: bile acid biosynthesis, androgen and estrogen metabolism. There are three isozymes of 5α-reductase encoded by the genes SRD5A1, SRD5A2, and SRD5A3.
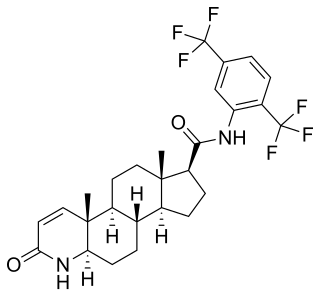
5α-Reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs), also known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT) blockers, are a class of medications with antiandrogenic effects which are used primarily in the treatment of enlarged prostate and scalp hair loss. They are also sometimes used to treat excess hair growth in women and as a component of hormone therapy for transgender women.
Paraldehyde is the cyclic trimer of acetaldehyde molecules. Formally, it is a derivative of 1,3,5-trioxane, with a methyl group substituted for a hydrogen atom at each carbon. The corresponding tetramer is metaldehyde. A colourless liquid, it is sparingly soluble in water and highly soluble in ethanol. Paraldehyde slowly oxidizes in air, turning brown and producing an odour of acetic acid. It attacks most plastics and rubbers and should be kept in glass bottles.
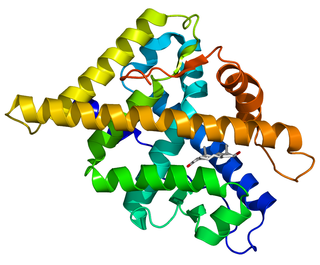
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone, in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.
Alpha-1 blockers constitute a variety of drugs that block the effect of catecholamines on alpha-1-adrenergic receptors. They are mainly used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), hypertension and post-traumatic stress disorder. Alpha-1-adrenergic receptors are present in vascular smooth muscle, the central nervous system, and other tissues. When alpha blockers bind to these receptors in vascular smooth muscle, they cause vasodilation.
Matthew Moncrieff Pattison Muir, FRSE, FCS (1848–1931) was a British chemist and author. He taught chemistry at Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge and was head of the Caius Laboratory there. Although he published some research on bismuth compounds, he became known through his textbooks and history of science works.

Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is a rare neuromuscular disorder that results in the loss of motor neurons and progressive muscle wasting. It is usually diagnosed in infancy or early childhood and if left untreated it is the most common genetic cause of infant death. It may also appear later in life and then have a milder course of the disease. The common feature is progressive weakness of voluntary muscles, with arm, leg and respiratory muscles being affected first. Associated problems may include poor head control, difficulties swallowing, scoliosis, and joint contractures.

Gestonorone caproate, also known as gestronol hexanoate or norhydroxyprogesterone caproate and sold under the brand names Depostat and Primostat, is a progestin medication which is used in the treatment of enlarged prostate and cancer of the endometrium. It is given by injection into muscle typically once a week.
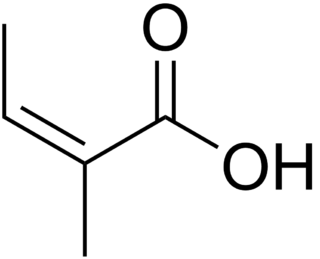
Angelic acid is a monocarboxylic unsaturated organic acid, mostly found in the plants of the family Apiaceae. It is a volatile solid with a biting taste and pungent sour odor. It is the cis isomer of 2-methyl-2-butenoic acid, which easily converts to the trans isomer, tiglic acid, upon heating or reaction with inorganic acids. The reverse transformation occurs much less readily. The salts and esters of angelic acid are called angelates. Angelic acid esters are the active components of herbal medicine used against a wide range of various health disturbances including pains, fever, gout, heartburn, etc.
An androgen-dependent condition, disease, disorder, or syndrome, is a medical condition that is, in part or full, dependent on, or is sensitive to, the presence of androgenic activity in the body.
Henry Watts (1815–1884) was an English chemist.
The first antiandrogen was discovered in the 1960s. Antiandrogens antagonise the androgen receptor (AR) and thereby block the biological effects of testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT). Antiandrogens are important for men with hormonally responsive diseases like prostate cancer, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BHP), acne, seborrhea, hirsutism and androgen alopecia. Antiandrogens are mainly used for the treatment of prostate diseases. Research from 2010 suggests that ARs could be linked to the disease progression of triple-negative breast cancer and salivary duct carcinoma and that antiandrogens can potentially be used to treat it.
Antiandrogens in the environment have become a topic of concern. Many industrial chemicals, including phthalates and pesticides, exhibit antiandrogen activity in animal experiments. Certain plant species have also been found to produce antiandrogens. In animal studies, environmental antiandrogens can harm reproductive organ development in fetuses exposed in utero as well as their offspring.
This article is about the discovery and development of 5α-reductase inhibitors (5-ARIs), also known as dihydrotestosterone (DHT) blockers.










