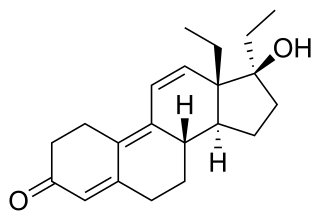
Tetrahydrogestrinone (THG), known by the nickname The Clear, is a synthetic and orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) which was never marketed for medical use. It was developed by Patrick Arnold and was used by a number of high-profile athletes such as Marion Jones, Barry Bonds, and Dwain Chambers.

Nandrolone, also known as 19-nortestosterone, is an endogenous androgen which exists in the male body at a ratio of 1:50 compared to testosterone. It is also an anabolic steroid (AAS) which is medically used in the form of esters such as nandrolone decanoate and nandrolone phenylpropionate. Nandrolone esters are used in the treatment of anemias, cachexia, osteoporosis, breast cancer, and for other indications. They are not used by mouth and instead are given by injection into muscle or fat.

The United States Anti-Doping Agency is a non-profit, non-governmental 501(c)(3) organization and the national anti-doping organization (NADO) for the United States. To protect clean competition and the integrity of sport and prevent doping in the United States with a performance-enhancing substance, the USADA provides education, leads scientific initiatives, conducts testing, and oversees the results management process. Headquartered in Colorado Springs, Colorado, USADA is a signatory to the World Anti-Doping Code, which harmonizes anti-doping practices around the world, and is widely considered the basis for the strongest and strictest anti-doping programs to prevent doping in sport.
In competitive sports, doping is the use of banned athletic performance-enhancing drugs by athletic competitors, as a way of cheating. The term doping is widely used by organizations that regulate sporting competitions. The use of drugs to enhance performance is considered unethical, and is prohibited by most international sports organizations, including the International Olympic Committee. Furthermore, athletes taking explicit measures to evade detection exacerbate the ethical violation with overt deception and cheating.
The Bay Area Laboratory Co-operative (BALCO) was an American company that operated from 1983 to 2003 led by founder and owner Victor Conte.

19-Norandrosterone, also known as 5α-estran-3α-ol-17-one, is a metabolite of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) and bolandione (19-norandrostenedione) that is formed by 5α-reductase. It is on the list of substances prohibited by the World Anti-Doping Agency since it is a detectable metabolite of nandrolone, an anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS). Consumption of androstendione products contaminated with traces of bolandione may also result in testing positive for nandrolone.
Christos Tzekos is a Greek athletics coach.
Trevor Graham is a Jamaican-born American former sprinter and athletics coach. Following the BALCO scandal, the US Olympic Committee barred him indefinitely from all its training sites.
Performance-enhancing substances, also known as performance-enhancing drugs (PEDs), are substances that are used to improve any form of activity performance in humans. A well-known example of cheating in sports involves doping in sport, where banned physical performance-enhancing drugs are used by athletes and bodybuilders. Athletic performance-enhancing substances are sometimes referred as ergogenic aids. Cognitive performance-enhancing drugs, commonly called nootropics, are sometimes used by students to improve academic performance. Performance-enhancing substances are also used by military personnel to enhance combat performance.
Patrick Arnold is an American organic chemist known for introducing androstenedione, 1-androstenediol, and methylhexanamine into the dietary supplement market, and for creating the designer steroid tetrahydrogestrinone, also known as THG and "the clear". THG, along with two other anabolic steroids that Arnold manufactured, not banned at the time of their creation, were hard-to-detect drugs at the heart of the BALCO professional sports doping scandal. BALCO distributed these worldwide to world-class athletes in a wide variety of sports ranging from track and field to professional baseball and football.

Desoxymethyltestosterone (DMT), known by the nicknames Madol and Pheraplex, is a synthetic and orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-methylated derivative of dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which was never marketed for medical use. It was one of the first designer steroids to be marketed as a performance-enhancing drug to athletes and bodybuilders.
The BALCO scandal was a scandal involving the use of banned, performance-enhancing substances by professional athletes.
The use of anabolic steroids and performance-enhancing drugs in American football is officially prohibited by virtually every sanctioning body.
Don H. Catlin is an anti-doping scientist and one of the founders of modern drug-testing in sport.
Since their discovery, anabolic steroids (AAS) have been widely used as performance-enhancing drugs to improve performance in sports, to improve one's physical appearance, as self-medication to recover from injury, and as an anti-aging aid. Use of anabolic steroids for purposes other than treating medical conditions is controversial and, in some cases, illegal. Major sports organizations have moved to ban the use of anabolic steroids. There is a wide range of health concerns for users. Legislation in many countries restricts and criminalizes AAS possession and trade.
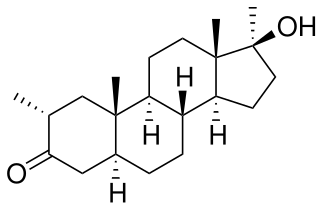
Methasterone, also known as methyldrostanolone and known by the nickname Superdrol, is a synthetic and orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) which was never marketed for medical use. It was sold legally for 9 years as a body building supplement. Because of this lengthy time being legal it has more studies and references than most other designer steroids.
Tammy Thomas is an American former sprint track cyclist, who won a silver medal at the 2001 UCI Track Cycling World Championships in the individual sprint event. However, her career was ended after she was caught using anabolic steroids.
Doping, or the use of restricted performance-enhancing drugs in the United States occurs in different sports, most notably in the sports of baseball and football.

Ligandrol is a novel nonsteroidal oral selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) for treatment of conditions such as muscle wasting and osteoporosis, discovered by Ligand Pharmaceuticals and under development by Viking Therapeutics.







