 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | a" bir a' ter one |
| Trade names | Zytiga, Yonsa, others |
| Other names | CB-7630; JNJ-212082; 17-(3-Pyridinyl)androsta-5,16-dien-3β-ol acetate, abiraterone (BAN UK), abiraterone acetate (JAN JP), abiraterone acetate (USAN US) |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a611046 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth [2] [3] |
| Drug class | Antineoplastic |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown, but may be 50% at most on empty stomach [7] |
| Protein binding | Abiraterone: ~99.8% (to albumin and α1-AGp ) [7] [2] [8] |
| Metabolism | Esterases, CYP3A4, SULT2A1 [8] |
| Metabolites | Abiraterone, others [2] [7] |
| Elimination half-life | Abiraterone: 12–24 hours [2] [7] [3] |
| Excretion | Feces: 88% [2] [8] Urine: 5% [2] [8] [3] |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.149.063 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
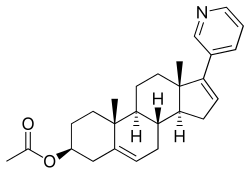
| Formula | C26H33NO2 |
| Molar mass | 391.555 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 144 to 145 °C (291 to 293 °F) [9] |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Abiraterone acetate, sold under the brand name Zytiga among others, is a medication used to treat prostate cancer. [10] Specifically it is used together with a corticosteroid for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) and metastatic high-risk castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCSPC). [2] [3] It should either be used following removal of the testicles or along with a gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) analog. [2] It is taken by mouth. [10]
Contents
- Medical uses
- Contraindications
- Side effects
- Overdose
- Interactions
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacodynamics
- Pharmacokinetics
- Chemistry
- History
- Society and culture
- Names
- Brand names
- Economics
- Research
- Prostate cancer
- References
Common side effects include tiredness, vomiting, headache, joint pain, high blood pressure, swelling, low blood potassium, high blood sugar, hot flashes, diarrhea, and cough. [10] [2] Other severe side effects may include liver failure and adrenocortical insufficiency. [2] In males whose partners can become pregnant, birth control is recommended. [2] Supplied as abiraterone acetate it is converted in the body to abiraterone. [2] Abiraterone acetate works by suppressing the production of androgens – specifically it inhibits CYP17A1 – and thereby decreases the production of testosterone. [10] In doing so, it prevents the effects of these hormones in prostate cancer. [10]
Abiraterone acetate was described in 1995, and approved for medical use in the United States and the European Union in 2011. [11] [2] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [12] It is available as a generic medication. [13]

