 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Sterane, others |
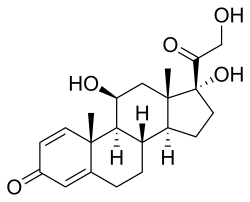
| Other names | 11,17-Dihydroxy-17-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-10,13-dimethyl-6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17-dodecahydrocyclopenta[a]phenanthren-3-one |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a615042 |
| License data |
|
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth, intravenous, topical, ophthalmic |
| Drug class | Glucocorticoid |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 2–3.5 hours [2] [3] [4] |
| Excretion | urine |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.020 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H28O5 |
| Molar mass | 360.450 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Prednisolone is a corticosteroid, a steroid hormone used to treat certain types of allergies, inflammatory conditions, autoimmune disorders, and cancers, electrolyte imbalances, and skin conditions. [5] [6] Some of these conditions include adrenocortical insufficiency, high blood calcium, rheumatoid arthritis, dermatitis, eye inflammation, asthma, multiple sclerosis, and phimosis. [6] It can be taken by mouth, injected into a vein, used topically as a skin cream, or as eye drops. [7] [8] [6]
Contents
- Medical uses
- Systemic use
- Topical use
- Adverse effects
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding
- Local adverse effects in the eye
- Pharmacology
- Pharmacodynamics
- Pharmacokinetics
- Prednisone
- Chemistry
- Interactions
- Special populations
- Children
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding 2
- Society and culture
- Dosage forms
- Athletics
- Veterinary uses
- References
- External links
Common side effects with short-term use include nausea, difficulty concentrating, insomnia, increased appetite, and fatigue. [5] More severe side effects include psychiatric problems, which may occur in about 5% of people. [9] Common side effects with long-term use include bone loss, weakness, yeast infections, and easy bruising. [6] While short-term use in the later part of pregnancy is safe, long-term use or use in early pregnancy is occasionally associated with harm to the baby. [1] It is a glucocorticoid made from hydrocortisone (cortisol). [10]
Prednisolone was discovered and approved for medical use in 1955. [10] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. [11] It is available as a generic drug. [6] In 2023, it was the 146th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 3 million prescriptions. [12] [13]

![Pred Forte Ophthalmic Suspension (Prednisolone acetate ophthalmic suspension) [second right] 001 2019 05 27 Augenpflege.jpg](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/4/47/001_2019_05_27_Augenpflege.jpg/250px-001_2019_05_27_Augenpflege.jpg)
