A safety data sheet (SDS), material safety data sheet (MSDS), or product safety data sheet (PSDS) is a document that lists information relating to occupational safety and health for the use of various substances and products. SDSs are a widely used type of fact sheet used to catalogue information on chemical species including chemical compounds and chemical mixtures. SDS information may include instructions for the safe use and potential hazards associated with a particular material or product, along with spill-handling procedures. The older MSDS formats could vary from source to source within a country depending on national requirements; however, the newer SDS format is internationally standardized.
Registry of Toxic Effects of Chemical Substances (RTECS) is a database of toxicity information compiled from the open scientific literature without reference to the validity or usefulness of the studies reported. Until 2001 it was maintained by US National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) as a freely available publication. It is now maintained by the private company BIOVIA or from several value-added resellers and is available only for a fee or by subscription.
The Beilstein database is a database in the field of organic chemistry, in which compounds are uniquely identified by their Beilstein Registry Number. The database covers the scientific literature from 1771 to the present and contains experimentally validated information on millions of chemical reactions and substances from original scientific publications. The electronic database was created from Handbuch der Organischen Chemie, founded by Friedrich Konrad Beilstein in 1881, but has appeared online under a number of different names, including Crossfire Beilstein. Since 2009, the content has been maintained and distributed by Elsevier Information Systems in Frankfurt under the product name "Reaxys".
PubChem is a database of chemical molecules and their activities against biological assays. The system is maintained by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), a component of the National Library of Medicine, which is part of the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH). PubChem can be accessed for free through a web user interface. Millions of compound structures and descriptive datasets can be freely downloaded via FTP. PubChem contains multiple substance descriptions and small molecules with fewer than 100 atoms and 1,000 bonds. More than 80 database vendors contribute to the growing PubChem database.

Fluorometholone, also known as 6α-methyl-9α-fluoro-11β,17α-dihydroxypregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione, is a synthetic glucocorticoid which is used in the treatment of inflammatory eye diseases. The C17α acetate ester, fluorometholone acetate, is also a glucocorticoid and is used for similar indications.

The Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labelling of Chemicals (GHS) is an internationally agreed-upon standard managed by the United Nations that was set up to replace the assortment of hazardous material classification and labelling schemes previously used around the world. Core elements of the GHS include standardized hazard testing criteria, universal warning pictograms, and safety data sheets which provide users of dangerous goods relevant information with consistent organization. The system acts as a complement to the UN numbered system of regulated hazardous material transport. Implementation is managed through the UN Secretariat. Although adoption has taken time, as of 2017, the system has been enacted to significant extents in most major countries of the world. This includes the European Union, which has implemented the United Nations' GHS into EU law as the CLP Regulation, and United States Occupational Safety and Health Administration standards.
ChemSpider is a freely accessible online database of chemicals owned by the Royal Society of Chemistry. It contains information on more than 100 million molecules from over 270 data sources, each of them receiving a unique identifier called ChemSpider Identifier.
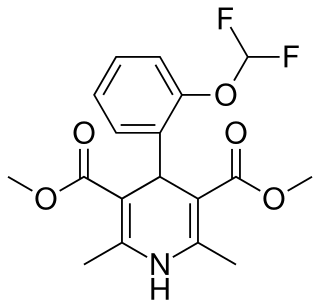
Riodipine is a calcium channel blocker.
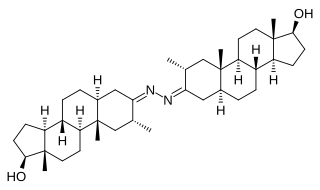
Bolazine, also known as 2α-methyl-5α-androstan-17β-ol-3-one azine, is a synthetic androgen/anabolic steroid (AAS) of the dihydrotestosterone (DHT) group which was never marketed. It is not orally active and is used as the ester prodrug bolazine capronate via depot intramuscular injection. Bolazine has a unique and unusual chemical structure, being a dimer of drostanolone linked at the C3 position of the A-ring by an azine group, and reportedly acts as a prodrug of drostanolone.

Bolenol, also known as 17α-ethyl-19-norandrost-5-en-17β-ol (ethylnorandrostenol), is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and a 17α-alkylated derivative of 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone) that was never marketed. It was described in the literature in 1969.
Molecular communications systems use the presence or absence of a selected type of molecule to digitally encode messages. The molecules are delivered into communications media such as air and water for transmission. The technique also is not subject to the requirement of using antennas that are sized to a specific ratio of the wavelength of the signal. Molecular communication signals can be made biocompatible and require very little energy.

Gestaclone, also known as 6-chloro-1α,2α:16α,17-bismethylene-4,6-pregnadiene-3,20-dione, is a steroidal progestin of unique chemical structure derived from progesterone that was first described in 1967 and was never marketed.

Leptacline is a drug described as a respiratory stimulant that was never marketed. It has a similar chemical structure to various piperidine and piperazine psychostimulants.

Penmesterol, or penmestrol, also known as 17α-methyltestosterone 3-cyclopentyl enol ether, is a synthetic, orally active anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) that was developed in the early 1960s. It is the 3-cyclopentyl enol ether of methyltestosterone.

Cloxestradiol, also known as 17-(2,2,2-trichloroethoxy)estradiol, is a synthetic, steroidal estrogen which was never marketed. It is an analogue of estradiol with a 2,2,2-trichloroethoxy substitution. The O,O-diacetate derivative, cloxestradiol acetate, has been marketed as an estrogen.

Doisynoestrol, also known as fenocycline, as well as cis-bisdehydrodoisynolic acid 7-methyl ether, is a synthetic nonsteroidal estrogen of the doisynolic acid group that is no longer marketed. It is a methyl ether of bisdehydrodoisynolic acid. Doisynoestrol was described in the literature in 1945. It has about 0.02% of the relative binding affinity of estradiol for the estrogen receptor.

Furostilbestrol (INN), also known as diethylstilbestrol di(2-furoate) or simply as diethylstilbestrol difuroate, is a synthetic, nonsteroidal estrogen of the stilbestrol group related to diethylstilbestrol, that was never marketed. It is an ester of diethylstilbestrol and was described in the literature in 1952.

Bolandiol dipropionate (USAN), or bolandiol propionate (JAN), also known as norpropandrolate or 19-nor-4-androstenediol dipropionate, as well as estr-4-ene-3β,17β-diol 3,17-dipropionate, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid (AAS) and derivative of 19-nortestosterone (nandrolone). It is an androgen ester – specifically, the 3,17-dipropionate ester of bolandiol (19-nor-4-androstenediol).

The CompTox Chemicals Dashboard is a freely accessible online database created and maintained by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The database provides access to multiple types of data including physicochemical properties, environmental fate and transport, exposure, usage, in vivo toxicity, and in vitro bioassay. EPA and other scientists use the data and models contained within the dashboard to help identify chemicals that require further testing and reduce the use of animals in chemical testing. The Dashboard is also used to provide public access to information from EPA Action Plans, e.g. around perfluorinated alkylated substances.