| |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lotemax |
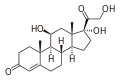
| Other names | 11β,17α,Dihydroxy-21-oxa-21-chloromethylpregna-1,4-diene-3,20-dione 17α-ethylcarbonate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Eye drops |
| Drug class | Corticosteroid; glucocorticoid |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | None |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | Ester hydrolysis |
| Metabolites | Δ1-cortienic acid and its etabonate |
| Onset of action | ≤2 hrs (allergic conjunctivitis) |
| Elimination half-life | 2.8 hrs |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H31ClO7 |
| Molar mass | 466.96 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 220.5 to 223.5 °C (428.9 to 434.3 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 0.0005 mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Loteprednol (formulated as the ester loteprednol etabonate) is a topical corticosteroid used to treat inflammations of the eye. It is marketed by Bausch and Lomb as Lotemax [2] and Loterex.
Contents
- Medical uses
- Contraindications
- Adverse effects
- Interactions
- Pharmacology
- Mechanism of action
- Pharmacokinetics
- Retrometabolic drug design
- Chemistry
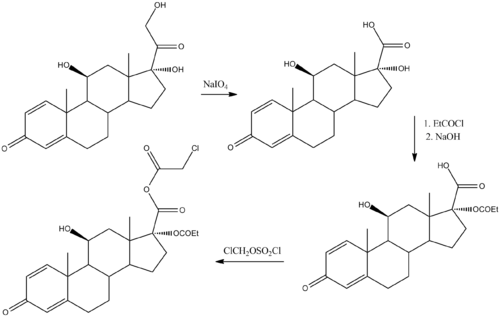
- Chemical synthesis
- References
- Further reading
It was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1998. [3] It is available as a generic medication. [4]