Related Research Articles

Progesterone (P4) is an endogenous steroid and progestogen sex hormone involved in the menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and embryogenesis of humans and other species. It belongs to a group of steroid hormones called the progestogens and is the major progestogen in the body. Progesterone has a variety of important functions in the body. It is also a crucial metabolic intermediate in the production of other endogenous steroids, including the sex hormones and the corticosteroids, and plays an important role in brain function as a neurosteroid.

A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into two classes: corticosteroids and sex steroids. Within those two classes are five types according to the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids and androgens, estrogens, and progestogens. Vitamin D derivatives are a sixth closely related hormone system with homologous receptors. They have some of the characteristics of true steroids as receptor ligands.

Glucocorticoids are a class of corticosteroids, which are a class of steroid hormones. Glucocorticoids are corticosteroids that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor that is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell. The name "glucocorticoid" is a portmanteau and is composed from its role in regulation of glucose metabolism, synthesis in the adrenal cortex, and its steroidal structure.
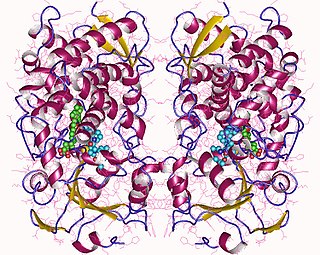
Cytochrome P450 3A4 is an important enzyme in the body, mainly found in the liver and in the intestine, which in humans is encoded by CYP3A4 gene. It oxidizes small foreign organic molecules (xenobiotics), such as toxins or drugs, so that they can be removed from the body. It is highly homologous to CYP3A5, another important CYP3A enzyme.
Steroid hormone receptors are found in the nucleus, cytosol, and also on the plasma membrane of target cells. They are generally intracellular receptors and initiate signal transduction for steroid hormones which lead to changes in gene expression over a time period of hours to days. The best studied steroid hormone receptors are members of the nuclear receptor subfamily 3 (NR3) that include receptors for estrogen and 3-ketosteroids. In addition to nuclear receptors, several G protein-coupled receptors and ion channels act as cell surface receptors for certain steroid hormones.
Drug metabolism is the metabolic breakdown of drugs by living organisms, usually through specialized enzymatic systems. More generally, xenobiotic metabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that modify the chemical structure of xenobiotics, which are compounds foreign to an organism's normal biochemistry, such as any drug or poison. These pathways are a form of biotransformation present in all major groups of organisms and are considered to be of ancient origin. These reactions often act to detoxify poisonous compounds. The study of drug metabolism is the object of pharmacokinetics. Metabolism is one of the stages of the drug's transit through the body that involves the breakdown of the drug so that it can be excreted by the body.
In humans and other animals, the adrenocortical hormones are hormones produced by the adrenal cortex, the outer region of the adrenal gland. These polycyclic steroid hormones have a variety of roles that are crucial for the body's response to stress, and they also regulate other functions in the body. Threats to homeostasis, such as injury, chemical imbalances, infection, or psychological stress, can initiate a stress response. Examples of adrenocortical hormones that are involved in the stress response are aldosterone and cortisol. These hormones also function in regulating the conservation of water by the kidneys and glucose metabolism, respectively.

Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) are transcription factors that bind to the sterol regulatory element DNA sequence TCACNCCAC. Mammalian SREBPs are encoded by the genes SREBF1 and SREBF2. SREBPs belong to the basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper class of transcription factors. Unactivated SREBPs are attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum membranes. In cells with low levels of sterols, SREBPs are cleaved to a water-soluble N-terminal domain that is translocated to the nucleus. These activated SREBPs then bind to specific sterol regulatory element DNA sequences, thus upregulating the synthesis of enzymes involved in sterol biosynthesis. Sterols in turn inhibit the cleavage of SREBPs and therefore synthesis of additional sterols is reduced through a negative feed back loop.

The liver X receptor (LXR) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors and is closely related to nuclear receptors such as the PPARs, FXR and RXR. Liver X receptors (LXRs) are important regulators of cholesterol, fatty acid, and glucose homeostasis. LXRs were earlier classified as orphan nuclear receptors, however, upon discovery of endogenous oxysterols as ligands they were subsequently deorphanized.

In the field of molecular biology, the pregnane X receptor (PXR), also known as the steroid and xenobiotic sensing nuclear receptor (SXR) or nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (NR1I2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I2 gene.
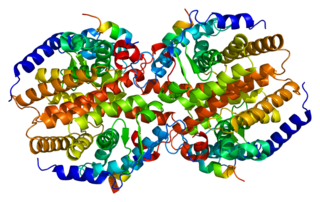
The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I3 gene. CAR is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and along with pregnane X receptor (PXR) functions as a sensor of endobiotic and xenobiotic substances. In response, expression of proteins responsible for the metabolism and excretion of these substances is upregulated. Hence, CAR and PXR play a major role in the detoxification of foreign substances such as drugs.

Guggulsterone is a phytosteroid found in the resin of the guggul plant, Commiphora mukul. Guggulsterone can exist as either of two stereoisomers, E-guggulsterone and Z-guggulsterone. In humans, it acts as an antagonist of the farnesoid X receptor, which was once believed to result in decreased cholesterol synthesis in the liver. Several studies have been published that indicate no overall reduction in total cholesterol occurs using various dosages of guggulsterone, and levels of low-density lipoprotein increased in many people. Nevertheless, guggulsterone is an ingredient in many nutritional supplements. Guggulsterone was also found to have interactions with the viral ADP ribose phosphatase enzyme of SARS-CoV-2 and has been proposed as a potential candidate for the development of therapeutics for the treatment of COVID-19.

Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase also known as cholesterol 7-alpha-monooxygenase or cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CYP7A1 gene which has an important role in cholesterol metabolism. It is a cytochrome P450 enzyme, which belongs to the oxidoreductase class, and converts cholesterol to 7-alpha-hydroxycholesterol, the first and rate limiting step in bile acid synthesis.

Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2), also known as nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-like 2, is a transcription factor that in humans is encoded by the NFE2L2 gene. NRF2 is a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) protein that may regulate the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidative damage triggered by injury and inflammation, according to preliminary research. In vitro, NRF2 binds to antioxidant response elements (AREs) in the promoter regions of genes encoding cytoprotective proteins. NRF2 induces the expression of heme oxygenase 1 in vitro leading to an increase in phase II enzymes. NRF2 also inhibits the NLRP3 inflammasome.

Estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα), also known as NR3B1, is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the ESRRA gene. ERRα was originally cloned by DNA sequence homology to the estrogen receptor alpha, but subsequent ligand binding and reporter-gene transfection experiments demonstrated that estrogens did not regulate ERRα. Currently, ERRα is considered an orphan nuclear receptor.

Cytochrome P450 3A5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CYP3A5 gene.

5α-Dihydroprogesterone is an endogenous progestogen and neurosteroid that is synthesized from progesterone. It is also an intermediate in the synthesis of allopregnanolone and isopregnanolone from progesterone.
Glyceroneogenesis is a metabolic pathway which synthesizes glycerol 3-phosphate from precursors other than glucose. Usually, glycerol 3-phosphate is generated from glucose by glycolysis, in the liquid of the cell's cytoplasm. Glyceroneogenesis is used when the concentrations of glucose in the cytosol are low, and typically uses pyruvate as the precursor, but can also use alanine, glutamine, or any substances from the TCA cycle. The main regulator enzyme for this pathway is an enzyme called phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPC-K), which catalyzes the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate to phosphoenolpyruvate. Glyceroneogenesis is observed mainly in adipose tissue, and in the liver. A significant biochemical pathway regulates cytosolic lipid levels. Intense suppression of glyceroneogenesis may lead to metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes.

5β-Dihydroprogesterone is an endogenous neurosteroid and an intermediate in the biosynthesis of pregnanolone and epipregnanolone from progesterone. It is synthesized from progesterone by the enzyme 5β-reductase.

The hydroxylation of estradiol is one of the major routes of metabolism of the estrogen steroid hormone estradiol. It is hydroxylated into the catechol estrogens 2-hydroxyestradiol and 4-hydroxyestradiol and into estriol (16α-hydroxyestradiol), reactions which are catalyzed by cytochrome P450 enzymes predominantly in the liver, but also in various other tissues.
References
- 1 2 Timsit YE, Negishi M (March 2007). "CAR and PXR: the xenobiotic-sensing receptors". Steroids. 72 (3): 231–46. doi:10.1016/j.steroids.2006.12.006. PMC 1950246 . PMID 17284330.
- 1 2 Klaassen C, Lu H (2010). "Xenobiotic Receptors CAR and PXR". Nuclear Receptors. Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands. pp. 287–305. doi:10.1007/978-90-481-3303-1_11. ISBN 978-90-481-3302-4.
- ↑ Erickson SL, Alston L, Nieves K, Chang TK, Mani S, Flannigan KL, Hirota SA (February 2020). "The xenobiotic sensing pregnane X receptor regulates tissue damage and inflammation triggered by C difficile toxins". FASEB Journal. 34 (2): 2198–2212. doi: 10.1096/fj.201902083rr . PMC 7027580 . PMID 31907988.