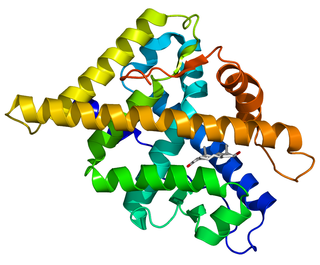
The androgen receptor (AR), also known as NR3C4, is a type of nuclear receptor that is activated by binding any of the androgenic hormones, including testosterone and dihydrotestosterone in the cytoplasm and then translocating into the nucleus. The androgen receptor is most closely related to the progesterone receptor, and progestins in higher dosages can block the androgen receptor.
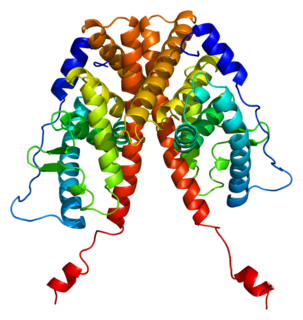
Estrogen receptor alpha (ERα), also known as NR3A1, is one of two main types of estrogen receptor, a nuclear receptor that is activated by the sex hormone estrogen. In humans, ERα is encoded by the gene ESR1.

In the field of molecular biology, the pregnane X receptor (PXR), also known as the steroid and xenobiotic sensing nuclear receptor (SXR) or nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 2 (NR1I2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I2 gene.
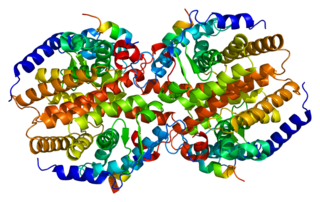
The constitutive androstane receptor (CAR) also known as nuclear receptor subfamily 1, group I, member 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR1I3 gene. CAR is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and along with pregnane X receptor (PXR) functions as a sensor of endobiotic and xenobiotic substances. In response, expression of proteins responsible for the metabolism and excretion of these substances is upregulated. Hence, CAR and PXR play a major role in the detoxification of foreign substances such as drugs.

Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC1 gene.
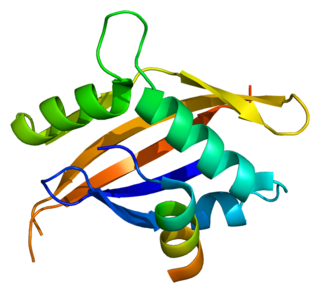
The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCOA1) is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor interacting domains and an intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. NCOA1 is recruited to DNA promotion sites by ligand-activated nuclear receptors. NCOA1, in turn, acylates histones, which makes downstream DNA more accessible to transcription. Hence, NCOA1 assists nuclear receptors in the upregulation of DNA expression.

The nuclear receptor co-repressor 2 (NCOR2) is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor-interacting domains. In addition, NCOR2 appears to recruit histone deacetylases to DNA promoter regions. Hence NCOR2 assists nuclear receptors in the down regulation of target gene expression. NCOR2 is also referred to as a silencing mediator for retinoid or thyroid-hormone receptors (SMRT) or T3 receptor-associating cofactor 1 (TRAC-1).
The testicular receptor proteins are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. There are two forms of the receptor, TR2 and TR4, each encode by a separate gene.

The nuclear receptor 4A1 also known as Nur77, TR3, and NGFI-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR4A1 gene.

The small heterodimer partner (SHP) also known as NR0B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR0B2 gene. SHP is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. SHP is unusual for a nuclear receptor in that it lacks a DNA binding domain. Therefore, it is technically neither a transcription factor nor nuclear receptor but nevertheless it is still classified as such due to relatively high sequence homology with other nuclear receptor family members.

V-erbA-related protein 2 (EAR-2) also known as NR2F6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F6 gene. V-erbA-related protein 2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. It is named after its similarity to v-erbA, a helper of an oncoprotein called v-erbB in avian erythroblastosis virus.

RAR-related orphan receptor alpha (RORα), also known as NR1F1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RORA gene. RORα participates in the transcriptional regulation of some genes involved in circadian rhythm. In mice, RORα is essential for development of cerebellum through direct regulation of genes expressed in Purkinje cells. It also plays an essential role in the development of type 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2) and mutant animals are ILC2 deficient. In addition, although present in normal numbers, the ILC3 and Th17 cells from RORα deficient mice are defective for cytokine production.
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha (HNF4A) also known as NR2A1 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the HNF4A gene.

Histone deacetylase 4, also known as HDAC4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HDAC4 gene.

TNF receptor-associated factor 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRAF5 gene.

Nuclear receptor coactivator 4, also known as Androgen Receptor Activator (ARA70), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA4 gene. It plays an important role in ferritinophagy, acting as a cargo receptor, binding to the ferritin heavy chain and latching on to ATG8 on the surface of the autophagosome.

COUP-TF1 also known as NR2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F1 gene. This protein is a member of nuclear hormone receptor family of steroid hormone receptors.

The testicular receptor 2 (TR2) also known as NR2C1 is protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2C1 gene. TR2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors.

LIGHT, also known as tumor necrosis factor superfamily member 14 (TNFSF14), is a secreted protein of the TNF superfamily. It is recognized by herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), as well as decoy receptor 3.

Herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), also known as tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 14 (TNFRSF14), is a human cell surface receptor of the TNF-receptor superfamily.





















