Related Research Articles

A homeobox is a DNA sequence, around 180 base pairs long, that regulates large-scale anatomical features in the early stages of embryonic development. Mutations in a homeobox may change large-scale anatomical features of the full-grown organism.
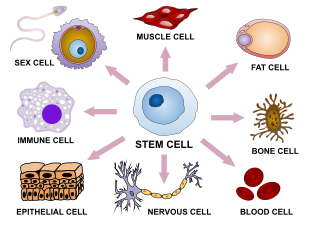
Cellular differentiation is the process in which a stem cell changes from one type to a differentiated one. Usually, the cell changes to a more specialized type. Differentiation happens multiple times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. However, metabolic composition does get altered quite dramatically where stem cells are characterized by abundant metabolites with highly unsaturated structures whose levels decrease upon differentiation. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.

Oct-4, also known as POU5F1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU5F1 gene. Oct-4 is a homeodomain transcription factor of the POU family. It is critically involved in the self-renewal of undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. As such, it is frequently used as a marker for undifferentiated cells. Oct-4 expression must be closely regulated; too much or too little will cause differentiation of the cells.

Homeobox protein NANOG(hNanog) is a transcriptional factor that helps embryonic stem cells (ESCs) maintain pluripotency by suppressing cell determination factors. hNanog is encoded in humans by the NANOG gene. Several types of cancer are associated with NANOG.
Oct-2 also known as POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU2F2 gene.
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) also known as acute myeloid leukemia 1 protein (AML1) or core-binding factor subunit alpha-2 (CBFA2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RUNX1 gene.

High-mobility group protein HMG-I/HMG-Y is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HMGA1 gene.

POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU2F1 gene.

Non-POU domain-containing octamer-binding protein (NonO) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NONO gene.

SRY -box 2, also known as SOX2, is a transcription factor that is essential for maintaining self-renewal, or pluripotency, of undifferentiated embryonic stem cells. Sox2 has a critical role in maintenance of embryonic and neural stem cells.
POU is a family of eukaryotic transcription factors that have well-conserved homeodomains. The Pou domain is a bipartite DNA binding domain found in these proteins.

POU domain class 2-associating factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU2AF1 gene. The protein is also termed Oct coactivator from B cells, Oct binding factor 1, and, as commonly found in the literature, BOB1. BOB1 is a transcriptional coactivator which is expressed principally by B-cell lymphocytes and controls immunoglobulin and other genes critical for these cells expression of CD20, CRISP-3, and CD36. The expression of BOB1 has proven useful for identifying certain lymphomas as being B-cell lymphomas, as exemplified in studies which use BOB1 expression to help identify lymphomas as being diffuse large B-cell lymphomas, not otherwise specified.

POU domain, class 3, transcription factor 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU3F2 gene.

POU domain, class 4, transcription factor 1 (POU4F1) also known as brain-specific homeobox/POU domain protein 3A (BRN3A), homeobox/POU domain protein RDC-1 or Oct-T1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU4F1 gene.

Sal-like protein 4(SALL4) is a transcription factor encoded by a member of the Spalt-like (SALL) gene family, SALL4. The SALL genes were identified based on their sequence homology to Spalt, which is a homeotic gene originally cloned in Drosophila melanogaster that is important for terminal trunk structure formation in embryogenesis and imaginal disc development in the larval stages. There are four human SALL proteins with structural homology and playing diverse roles in embryonic development, kidney function, and cancer. The SALL4 gene encodes at least three isoforms, termed A, B, and C, through alternative splicing, with the A and B forms being the most studied. SALL4 can alter gene expression changes through its interaction with many co-factors and epigenetic complexes. It is also known as a key embryonic stem cell (ESC) factor.

ID4 is a protein coding gene. In humans, it encodes for the protein known as DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-4. This protein is known to be involved in the regulation of many cellular processes during both prenatal development and tumorigenesis. This is inclusive of embryonic cellular growth, senescence, cellular differentiation, apoptosis, and as an oncogene in angiogenesis.

POU domain, class 3, transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU3F1 gene.

POU domain, class 2, transcription factor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the POU2F3 gene.
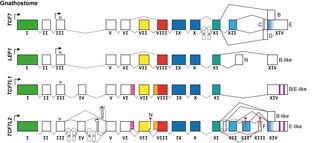
The TCF/LEF family is a group of genes that encode transcription factors which bind to DNA through a SOX-like high mobility group domain. They are involved in the Wnt signaling pathway, particularly during embryonic and stem-cell development, but also had been found to play a role in cancer and diabetes. TCF/LEF factors recruit the coactivator beta-catenin to enhancer elements of genes they target. They can also recruit members of the Groucho family of corepressors.
References
- ↑ Petryniak B, Staudt LM, Postema CE, McCormack WT, Thompson CB (1990). "Characterization of chicken octamer-binding proteins demonstrates that POU domain-containing homeobox transcription factors have been highly conserved during vertebrate evolution". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87 (3): 1099–103. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.1099P. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1099 . PMC 53418 . PMID 1967834.
- ↑ Oct-5 and Oct-10 are not found in humans, while Oct-3 and Oct-4 were identified as the same protein.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Zhao, FQ (1 June 2013). "Octamer-binding transcription factors: genomics and functions". Frontiers in Bioscience (Landmark Edition). 18 (3): 1051–71. doi:10.2741/4162. PMC 4349413 . PMID 23747866.