Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB7A gene. [5] [6] [7]
Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB7A gene. [5] [6] [7]
Zbtb7, whose protein product is also known as Pokemon, is a gene that functions as a regulator of cellular growth and a proto oncogene.
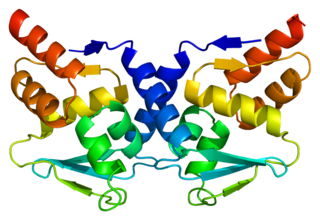
Bcl-6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL6 gene. BCL6 is a master transcription factor for regulation of T follicular helper cells proliferation. BCL6 has three evolutionary conserved structural domains. The interaction of these domains with corepressors allows for germinal center development and leads to B cell proliferation.

Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 16 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB16 gene.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF1 gene.

Y box binding protein 1 also known as Y-box transcription factor or nuclease-sensitive element-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YBX1 gene.

C-terminal-binding protein 1 also known as CtBP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CTBP1 gene. CtBP1 is one of two CtBP proteins, the other protein being CtBP2.

Tristetraprolin (TTP), also known as zinc finger protein 36 homolog (ZFP36), is a protein that in humans, mice and rats is encoded by the ZFP36 gene. It is a member of the TIS11 family, along with butyrate response factors 1 and 2.

Tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 or A20 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFAIP3 gene.
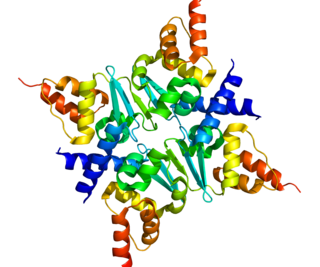
Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 17 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB17 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) also known as transcriptional intermediary factor 1α (TIF1α) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TRIM24 gene.

Zinc finger protein RFP is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM27 gene.

Transcriptional regulator Kaiso is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB33 gene. This gene encodes a transcriptional regulator with bimodal DNA-binding specificity, which binds to methylated CGCG and also to the non-methylated consensus KAISO-binding site TCCTGCNA. The protein contains an N-terminal POZ/BTB domain and 3 C-terminal zinc finger motifs. It recruits the N-CoR repressor complex to promote histone deacetylation and the formation of repressive chromatin structures in target gene promoters. It may contribute to the repression of target genes of the Wnt signaling pathway, and may also activate transcription of a subset of target genes by the recruitment of catenin delta-2 (CTNND2). Its interaction with catenin delta-1 (CTNND1) inhibits binding to both methylated and non-methylated DNA. It also interacts directly with the nuclear import receptor Importin-α2, which may mediate nuclear import of this protein. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified.

Krueppel-like factor 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF10 gene.

Early growth response protein 3 is a protein in humans, encoded by the EGR3 gene.

POZ-, AT hook-, and zinc finger-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PATZ1 gene.

Zinc finger protein 143 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF143 gene.

Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 32 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the 1960 bp ZBTB32 gene. The 52 kDa protein is a transcriptional repressor and the gene is expressed in T and B cells upon activation, but also significantly in testis cells. It is a member of the Poxviruses and Zinc-finger (POZ) and Krüppel (POK) family of proteins, and was identified in multiple screens involving either immune cell tumorigenesis or immune cell development.

Zinc finger and BTB domain-containing protein 7B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZBTB7B gene. ZFP67 is an early growth response gene that encodes a zinc finger-containing transcription factor that binds to the promoter regions of type I collagen genes and has a role in development.[supplied by OMIM]

Zinc finger protein 224 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ZNF224 gene.

The BTB/POZ domain is a common structural domain contained within some proteins. It is present near the N-terminus of a fraction of zinc finger proteins and in proteins that contain the Kelch motif and a family of pox virus proteins. The BTB/POZ domain mediates homomeric dimerisation and in some instances heteromeric dimerisation. The structure of the dimerised PLZF BTB/POZ domain has been solved and consists of a tightly intertwined homodimer. The central scaffolding of the protein is made up of a cluster of alpha-helices flanked by short beta-sheets at both the top and bottom of the molecule. BTB/POZ domains from several zinc finger proteins have been shown to mediate transcriptional repression and to interact with components of histone deacetylase co-repressor complexes including N-CoR and SMRT. The POZ or BTB domain is also known as BR-C/Ttk or ZiN.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.