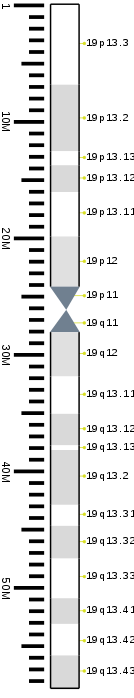
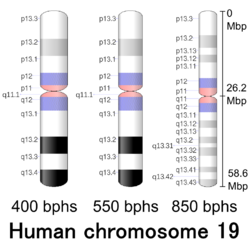
| Chromosome 19 | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 19 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 19 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 61,707,364 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 1,357 (CCDS) [1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Metacentric [2] (26.2 Mbp [3] ) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 19 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 19 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 19 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 19 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000019 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000681 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 19 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 19 spans more than 61.7 million base pairs, the building material of DNA. It is considered the most gene-rich chromosome containing roughly 1,500 genes, despite accounting for only 2 percent of the human genome. [4] [5]