Related Research Articles

Histone acetyltransferases (HATs) are enzymes that acetylate conserved lysine amino acids on histone proteins by transferring an acetyl group from acetyl-CoA to form ε-N-acetyllysine. DNA is wrapped around histones, and, by transferring an acetyl group to the histones, genes can be turned on and off. In general, histone acetylation increases gene expression.

MyoD, also known as myoblast determination protein 1, is a protein in animals that plays a major role in regulating muscle differentiation. MyoD, which was discovered in the laboratory of Harold M. Weintraub, belongs to a family of proteins known as myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs). These bHLH transcription factors act sequentially in myogenic differentiation. Vertebrate MRF family members include MyoD1, Myf5, myogenin, and MRF4 (Myf6). In non-vertebrate animals, a single MyoD protein is typically found.

Histone deacetylases (EC 3.5.1.98, HDAC) are a class of enzymes that remove acetyl groups (O=C-CH3) from an ε-N-acetyl lysine amino acid on a histone, allowing the histones to wrap the DNA more tightly. This is important because DNA is wrapped around histones, and DNA expression is regulated by acetylation and de-acetylation. Its action is opposite to that of histone acetyltransferase. HDAC proteins are now also called lysine deacetylases (KDAC), to describe their function rather than their target, which also includes non-histone proteins.

Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is a multifunctional cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor superfamily that includes three different mammalian isoforms and many other signaling proteins. TGFB proteins are produced by all white blood cell lineages.

Histone acetyltransferase p300 also known as p300 HAT or E1A-associated protein p300 also known as EP300 or p300 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the EP300 gene. It functions as histone acetyltransferase that regulates transcription of genes via chromatin remodeling by allowing histone proteins to wrap DNA less tightly. This enzyme plays an essential role in regulating cell growth and division, prompting cells to mature and assume specialized functions (differentiate), and preventing the growth of cancerous tumors. The p300 protein appears to be critical for normal development before and after birth.
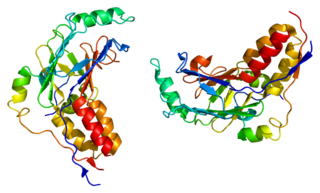
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 2 also known as SMAD family member 2 or SMAD2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD2 gene. MAD homolog 2 belongs to the SMAD, a family of proteins similar to the gene products of the Drosophila gene 'mothers against decapentaplegic' (Mad) and the C. elegans gene Sma. SMAD proteins are signal transducers and transcriptional modulators that mediate multiple signaling pathways.
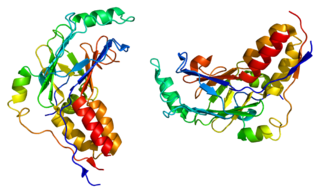
Mothers against decapentaplegic homolog 3 also known as SMAD family member 3 or SMAD3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SMAD3 gene.
Smads comprise a family of structurally similar proteins that are the main signal transducers for receptors of the transforming growth factor beta (TGF-B) superfamily, which are critically important for regulating cell development and growth. The abbreviation refers to the homologies to the Caenorhabditis elegans SMA and MAD family of genes in Drosophila.
The transforming growth factor beta (TGFB) signaling pathway is involved in many cellular processes in both the adult organism and the developing embryo including cell growth, cell differentiation, apoptosis, cellular homeostasis and other cellular functions. In spite of the wide range of cellular processes that the TGFβ signaling pathway regulates, the process is relatively simple. TGFβ superfamily ligands bind to a type II receptor, which recruits and phosphorylates a type I receptor. The type I receptor then phosphorylates receptor-regulated SMADs (R-SMADs) which can now bind the coSMAD SMAD4. R-SMAD/coSMAD complexes accumulate in the nucleus where they act as transcription factors and participate in the regulation of target gene expression.

CREB-binding protein, also known as CREBBP or CBP, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREBBP gene. The CREB protein carries out its function by activating transcription, where interaction with transcription factors is managed by one or more CREB domains: the nuclear receptor interaction domain (RID), the KIX domain, the cysteine/histidine regions and the interferon response binding domain (IBiD). The CREB protein domains, KIX, TAZ1 and TAZ2, each bind tightly to a sequence spanning both transactivation domains 9aaTADs of transcription factor p53.

Histone acetylation and deacetylation are the processes by which the lysine residues within the N-terminal tail protruding from the histone core of the nucleosome are acetylated and deacetylated as part of gene regulation.

Jun dimerization protein 2 (JUNDM2) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the JDP2 gene. The Jun dimerization protein is a member of the AP-1 family of transcription factors.

Histone deacetylase 1 (HDAC1) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the HDAC1 gene.

Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2A gene. MEF2A is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. In humans it is located on chromosome 15q26. Certain mutations in MEF2A cause an autosomal dominant form of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.

MDS1 and EVI1 complex locus protein EVI1 (MECOM) also known as ecotropic virus integration site 1 protein homolog (EVI-1) or positive regulatory domain zinc finger protein 3 (PRDM3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MECOM gene. EVI1 was first identified as a common retroviral integration site in AKXD murine myeloid tumors. It has since been identified in a plethora of other organisms, and seems to play a relatively conserved developmental role in embryogenesis. EVI1 is a nuclear transcription factor involved in many signaling pathways for both coexpression and coactivation of cell cycle genes.

Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFYC gene.

Interferon-related developmental regulator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IFRD1 gene. The gene is expressed mostly in neutrophils, skeletal and cardiac muscle, brain, pancreas. The rat and the mouse homolog genes of interferon-related developmental regulator 1 gene are also known with the name PC4 and Tis21, respectively. IFRD1 is member of a gene family that comprises a second gene, IFRD2, also known as SKmc15.
Neurogenins are a family of bHLH transcription factors involved in specifying neuronal differentiation. It is one of many gene families related to the atonal gene in Drosophila. Other positive regulators of neuronal differentiation also expressed during early neural development include NeuroD and ASCL1.

EP300-interacting inhibitor of differentiation 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EID1 gene.

In Xenopus laevis, the specification of the three germ layers occurs at the blastula stage. Great efforts have been made to determine the factors that specify the endoderm and mesoderm. On the other hand, only a few examples of genes that are required for ectoderm specification have been described in the last decade. The first molecule identified to be required for the specification of ectoderm was the ubiquitin ligase Ectodermin ; later, it was found that the deubiquitinating enzyme, FAM/USP9x, is able to overcome the effects of ubiquitination made by Ectodermin in Smad4. Two transcription factors have been proposed to control gene expression of ectodermal specific genes: POU91/Oct3/4 and FoxIe1/Xema. A new factor specific for the ectoderm, XFDL156, has shown to be essential for suppression of mesoderm differentiation from pluripotent cells.
References
- ↑ Ji A, Dao D, Chen J, MacLellan WR (October 2003). "EID-2, a novel member of the EID family of p300-binding proteins inhibits transactivation by MyoD". Gene. 318: 35–43. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2003.06.001. PMID 14585496.
| This article on a gene on human chromosome 19 is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |