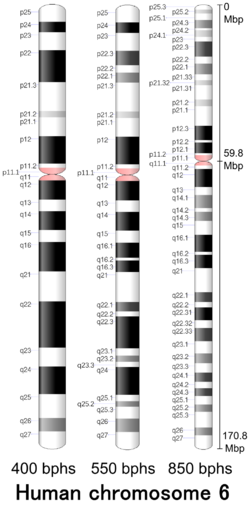
| Chromosome 6 | |
|---|---|
 Human chromosome 6 pair after G-banding. One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 6 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 172,126,628 bp (CHM13) |
| No. of genes | 996 (CCDS) [1] |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric [2] (59.8 Mbp [3] ) |
| Complete gene lists | |
| CCDS | Gene list |
| HGNC | Gene list |
| UniProt | Gene list |
| NCBI | Gene list |
| External map viewers | |
| Ensembl | Chromosome 6 |
| Entrez | Chromosome 6 |
| NCBI | Chromosome 6 |
| UCSC | Chromosome 6 |
| Full DNA sequences | |
| RefSeq | NC_000006 (FASTA) |
| GenBank | CM000668 (FASTA) |
Chromosome 6 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 6 spans nearly 171 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5.5 and 6% of the total DNA in cells. It contains the major histocompatibility complex, which contains over 132 genes related to the immune response, and plays a vital role in organ transplantation.