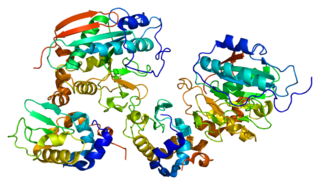Isoaspartic acid is an aspartic acid residue isomeric to the typical α peptide linkage. It is a β-amino acid, with the side chain carboxyl moved to the backbone. Such a change is caused by a chemical reaction in which the nitrogen atom on the N+1 following peptide bond nucleophilically attacks the γ-carbon of the side chain of an asparagine or aspartic acid residue, forming a succinimide intermediate. Hydrolysis of the intermediate results in two products, either aspartic acid or isoaspartic acid, which is a β-amino acid. The reaction also results in the deamidation of the asparagine residue. Racemization may occur leading to the formation of D-aminoacids.

Aldolase B also known as fructose-bisphosphate aldolase B or liver-type aldolase is one of three isoenzymes of the class I fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase enzyme, and plays a key role in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. The generic fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase enzyme catalyzes the reversible cleavage of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) into glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) as well as the reversible cleavage of fructose 1-phosphate (F1P) into glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate. In mammals, aldolase B is preferentially expressed in the liver, while aldolase A is expressed in muscle and erythrocytes and aldolase C is expressed in the brain. Slight differences in isozyme structure result in different activities for the two substrate molecules: FBP and fructose 1-phosphate. Aldolase B exhibits no preference and thus catalyzes both reactions, while aldolases A and C prefer FBP.

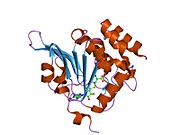
Cathepsin A is an enzyme that is classified both as a cathepsin and a carboxypeptidase. In humans, it is encoded by the CTSA gene.

Prosaposin, also known as PSAP, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the PSAP gene.

Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5(IBF-5) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the IGFBP5 gene. An IGFBP5 gene was recently identified as being important for adaptation to varying water salinity in fish.
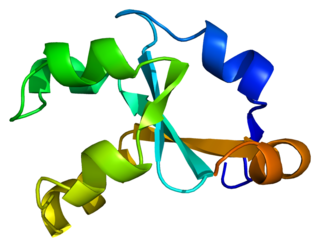
Cytochrome b5, form A, is a human microsomal cytochrome b5.

Calpastatin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAST gene.
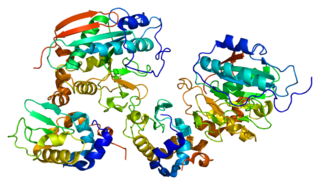
Beta-1,4-galactosyltransferase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the B4GALT1 gene.

Ran-binding protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RANBP9 gene.

Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADAM9 gene.
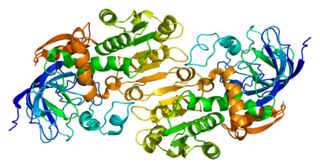
Alcohol dehydrogenase class-3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ADH5 gene.

Sterile alpha motif and leucine zipper containing kinase AZK, also known as ZAK, is a human gene.

Phosphofructokinase, platelet, also known as PFKP is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the PFKP gene.

Tropomodulin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TMOD1 gene.

Aspartyl-tRNA synthetase, cytoplasmic is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DARS gene.

Triadin, also known as TRDN, is a human gene associated with the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum triggering muscular contraction through calcium-induced calcium release. Triadin is a multiprotein family, arising from different processing of the TRDN gene on chromosome 6. It is a transmembrane protein on the sarcoplasmic reticulum due to a well defined hydrophobic section and it forms a quaternary complex with the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RYR2), calsequestrin (CASQ2) and junctin proteins. The luminal (inner compartment of the sarcoplasmic reticulum) section of Triadin has areas of highly charged amino acid residues that act as luminal Ca2+ receptors. Triadin is also able to sense luminal Ca2+ concentrations by mediating interactions between RYR2 and CASQ2. Triadin has several different forms; Trisk 95 and Trisk 51, which are expressed in skeletal muscle, and Trisk 32 (CT1), which is mainly expressed in cardiac muscle.

Aspartate aminotransferase, cytoplasmic is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GOT1 gene.

Protein-S-isoprenylcysteine O-methyltransferase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ICMT gene.
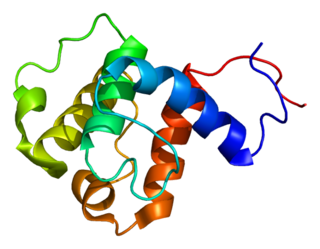
NEDD9-interacting protein with calponin homology and LIM domains is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MICAL1 gene.

Solute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC2A12 gene.