
Weissenbacher–Zweymuller syndrome (WZS), also called Pierre-Robin syndrome with fetal chondrodysplasia, is an autosomal recessive congenital disorder, linked to mutations in the COL11A2 gene, which codes for the α2 strand of collagen type XI. It is a collagenopathy, types II and XI disorder. The condition was first characterized in 1964 by G. Weissenbacher and Ernst Zweymüller.
Diastrophic dysplasia is an autosomal recessive dysplasia which affects cartilage and bone development. Diastrophic dysplasia is due to mutations in the SLC26A2 gene.

Atelosteogenesis, type II is a severe disorder of cartilage and bone development. It is rare, and infants with the disorder are usually stillborn; those who survive birth die soon after.

Stickler syndrome is a group of rare genetic disorders affecting connective tissue, specifically collagen. Stickler syndrome is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI. Stickler syndrome is characterized by distinctive facial abnormalities, ocular problems, hearing loss, and joint and skeletal problems. It was first studied and characterized by Gunnar B. Stickler in 1965.

Spondyloperipheral dysplasia is an autosomal dominant disorder of bone growth. The condition is characterized by flattened bones of the spine (platyspondyly) and unusually short fingers and toes (brachydactyly). Some affected individuals also have other skeletal abnormalities, short stature, nearsightedness (myopia), hearing loss, and mental retardation. Spondyloperipheral dysplasia is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI.
The type II and XI collagenopathies are a group of disorders that affect connective tissue, the tissue that supports the body's joints and organs. These disorders are caused by defects in type II or type XI collagen. Collagens are complex molecules that provide structure, strength, and elasticity to connective tissue. Type II and type XI collagen disorders are grouped together because both types of collagen are components of the cartilage found in joints and the spinal column, the inner ear, and the jelly-like substance that fills the eyeball. The type II and XI collagenopathies result in similar clinical features.
Hypochondrogenesis is a severe genetic disorder causing malformations of bone growth. The condition is characterized by a short body and limbs and abnormal bone formation in the spine and pelvis.
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita is a rare disorder of bone growth that results in dwarfism, characteristic skeletal abnormalities, and occasionally problems with vision and hearing. The name of the condition indicates that it affects the bones of the spine (spondylo-) and the ends of bones (epiphyses), and that it is present from birth (congenital). The signs and symptoms of spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita are similar to, but milder than, the related skeletal disorders achondrogenesis type 2 and hypochondrogenesis. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita is a subtype of collagenopathy, types II and XI.

Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Strudwick type is an inherited disorder of bone growth that results in dwarfism, characteristic skeletal abnormalities, and problems with vision. The name of the condition indicates that it affects the bones of the spine (spondylo-) and two regions near the ends of bones. This type was named after the first reported patient with the disorder. Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia, Strudwick type is a subtype of type II collagenopathies.

Collagen alpha-2(XI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL11A2 gene.

Autosomal recessive multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (ARMED), also called epiphyseal dysplasia, multiple, 4 (EDM4), multiple epiphyseal dysplasia with clubfoot or –with bilayered patellae, is an autosomal recessive congenital disorder affecting cartilage and bone development. The disorder has relatively mild signs and symptoms, including joint pain, scoliosis, and malformations of the hands, feet, and knees.
An osteochondrodysplasia, or skeletal dysplasia, is a disorder of the development of bone and cartilage. Osteochondrodysplasias are rare diseases. About 1 in 5,000 babies are born with some type of skeletal dysplasia. Nonetheless, if taken collectively, genetic skeletal dysplasias or osteochondrodysplasias comprise a recognizable group of genetically determined disorders with generalized skeletal affection. These disorders lead to disproportionate short stature and bone abnormalities, particularly in the arms, legs, and spine. Skeletal dysplasia can result in marked functional limitation and even mortality.

Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED), also known as Fairbank's disease, is a rare genetic disorder that affects the growing ends of bones. Long bones normally elongate by expansion of cartilage in the growth plate near their ends. As it expands outward from the growth plate, the cartilage mineralizes and hardens to become bone (ossification). In MED, this process is defective.
Vici syndrome, also called immunodeficiency with cleft lip/palate, cataract, hypopigmentation and absent corpus callosum, is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by albinism, agenesis of the corpus callosum, cataracts, cardiomyopathy, severe psychomotor retardation, seizures, immunodeficiency and recurrent severe infections. To date, about 50 cases have been reported.

Collagen alpha-1(XI) chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the COL11A1 gene.

Frontonasal dysplasia (FND) is a congenital malformation of the midface. For the diagnosis of FND, a patient should present at least two of the following characteristics: hypertelorism, a wide nasal root, vertical midline cleft of the nose and/or upper lip, cleft of the wings of the nose, malformed nasal tip, encephalocele or V-shaped hair pattern on the forehead. The cause of FND remains unknown. FND seems to be sporadic (random) and multiple environmental factors are suggested as possible causes for the syndrome. However, in some families multiple cases of FND were reported, which suggests a genetic cause of FND.

Marshall syndrome is a genetic disorder of the connective tissue that can cause hearing loss. The three most common areas to be affected are the eyes, which are uncommonly large, joints and the mouth and facial structures. Marshall syndrome and Stickler syndrome closely resemble each other; in fact they are so similar, some say they are the same. The condition is named for D. Weber.
Malpuech facial clefting syndrome, also called Malpuech syndrome or Gypsy type facial clefting syndrome, is a rare congenital syndrome. It is characterized by facial clefting, a caudal appendage, growth deficiency, intellectual and developmental disability, and abnormalities of the renal system (kidneys) and the male genitalia. Abnormalities of the heart, and other skeletal malformations may also be present. The syndrome was initially described by Georges Malpuech and associates in 1983. It is thought to be genetically related to Juberg-Hayward syndrome. Malpuech syndrome has also been considered as part of a spectrum of congenital genetic disorders associated with similar facial, urogenital and skeletal anomalies. Termed "3MC syndrome", this proposed spectrum includes Malpuech, Michels and Mingarelli-Carnevale (OSA) syndromes. Mutations in the COLLEC11 and MASP1 genes are believed to be a cause of these syndromes. The incidence of Malpuech syndrome is unknown. The pattern of inheritance is autosomal recessive, which means a defective (mutated) gene associated with the syndrome is located on an autosome, and the syndrome occurs when two copies of this defective gene are inherited.
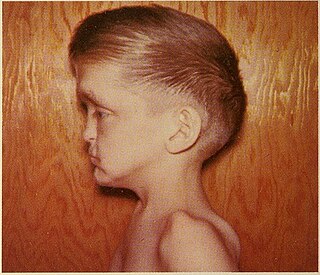
Oto-palato-digital syndrome is the generalised term for two conditions, oto-palato-digital syndrome type I (OPD1) and oto-palato-digital syndrome type II (OPD2), that are both X-linked recessive genetic disorders with overlapping phenotypes. The most severe phenotypes of each syndrome occur only in males, with females generally having attenuated forms of the condition, although this does not apply to all individual cases. Some writers conceptualise oto-palato-digital syndrome as a spectrum disorder including two similarly-presenting genetic syndromes, frontometaphyseal dysplasia and Melnick-Needles syndrome.








