
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions.

The mesoderm is the middle layer of the three germ layers that develops during gastrulation in the very early development of the embryo of most animals. The outer layer is the ectoderm, and the inner layer is the endoderm.

Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. It is a semi-transparent and non-porous type of tissue. It is usually covered by a tough and fibrous membrane called perichondrium. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans and cyclostomes, it constitutes a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. It usually grows quicker than bone.

The synovial membrane is a specialized connective tissue that lines the inner surface of capsules of synovial joints, tendon sheaths, and synovial bursas. It makes direct contact with the fibrous membrane on the outside surface and with the synovial fluid lubricant on the inside surface. In contact with the synovial fluid at the tissue surface are many rounded macrophage-like synovial cells and also type B cells, which are also known as fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS). Type A cells maintain the synovial fluid by removing wear-and-tear debris. As for the FLS, they produce hyaluronan, as well as other extracellular components in the synovial fluid.

An epiphysis is one of the rounded ends or tips of a long bone that ossify from a secondary center of ossification. Between the epiphysis and diaphysis lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate. At the joint, the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage; below that covering is a zone similar to the epiphyseal plate, known as subchondral bone. In evolution, reptiles do not have epiphyses and diaphyses, being restricted to mammals.

The long bones are those that are longer than they are wide. They are one of five types of bones: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Long bones, especially the femur and tibia, are subjected to most of the load during daily activities and they are crucial for skeletal mobility. They grow primarily by elongation of the diaphysis, with an epiphysis at each end of the growing bone. The ends of epiphyses are covered with hyaline cartilage. The longitudinal growth of long bones is a result of endochondral ossification at the epiphyseal plate. Bone growth in length is stimulated by the production of growth hormone (GH), a secretion of the anterior lobe of the pituitary gland.

The diaphysis is the main or midsection (shaft) of a long bone. It is made up of cortical bone and usually contains bone marrow and adipose tissue (fat).

The nasal septum separates the left and right airways of the nasal cavity, dividing the two nostrils.
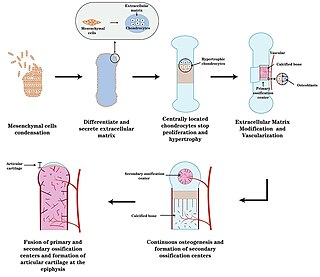
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossification. Both endochondral and intramembranous processes initiate from a precursor mesenchymal tissue, but their transformations into bone are different. In intramembranous ossification, mesenchymal tissue is directly converted into bone. On the other hand, endochondral ossification starts with mesenchymal tissue turning into an intermediate cartilage stage, which is eventually substituted by bone.
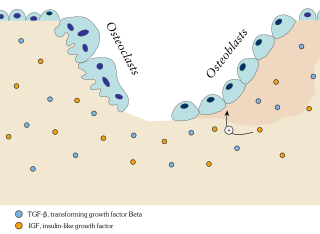
Ossification in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor.

Slipped capital femoral epiphysis is a medical term referring to a fracture through the growth plate (physis), which results in slippage of the overlying end of the femur (metaphysis).

Metachondromatosis is an autosomal dominant, incompletely penetrant genetic disease affecting the growth of bones, leading to exostoses primarily in the hands and feet as well as enchondromas of long bone metaphyses and iliac crests. This syndrome affects mainly tubular bones, though it can also involve the vertebrae, small joints, and flat bones. The disease is thought to affect exon 4 of the PTPN11 gene. Metachondromatosis is believed to be caused by an 11 base pair deletion resulting in a frameshift and nonsense mutation. The disease was discovered and named in 1971 by Pierre Maroteaux, a French physician, when he observed two families with skeletal radiologic features with exostoses and Ollier disease. The observation of one family with five affected people led to the identification of the disease as autosomal dominant. There have been less than 40 cases of the disease reported to date.
Articular cartilage, most notably that which is found in the knee joint, is generally characterized by very low friction, high wear resistance, and poor regenerative qualities. It is responsible for much of the compressive resistance and load bearing qualities of the knee joint and, without it, walking is painful to impossible. Osteoarthritis is a common condition of cartilage failure that can lead to limited range of motion, bone damage and invariably, pain. Due to a combination of acute stress and chronic fatigue, osteoarthritis directly manifests itself in a wearing away of the articular surface and, in extreme cases, bone can be exposed in the joint. Some additional examples of cartilage failure mechanisms include cellular matrix linkage rupture, chondrocyte protein synthesis inhibition, and chondrocyte apoptosis. There are several different repair options available for cartilage damage or failure.

The epiphyseal plate, epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with maintenance remodeling throughout its existing bone tissue, but the growth plate is the place where the long bone grows longer.

An ossification center is a point where ossification of the hyaline cartilage begins. The first step in ossification is that the chondrocytes at this point become hypertrophic and arrange themselves in rows.
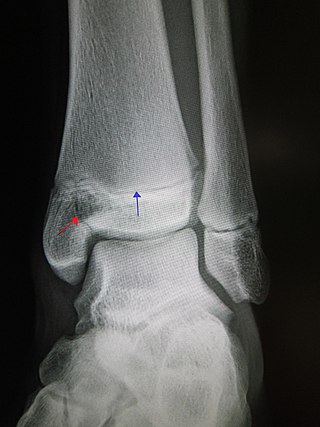
A Salter–Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. It is thus a form of child bone fracture. It is a common injury found in children, occurring in 15% of childhood long bone fractures. This type of fracture and its classification system is named for Robert B. Salter and William H. Harris who created and published this classification system in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery in 1963.

Chondroblastoma is a rare, benign, locally aggressive bone tumor that typically affects the epiphyses or apophyses of long bones. It is thought to arise from an outgrowth of immature cartilage cells (chondroblasts) from secondary ossification centers, originating from the epiphyseal plate or some remnant of it.

Fibrochondrogenesis is a rare autosomal recessive form of osteochondrodysplasia, causing abnormal fibrous development of cartilage and related tissues.
An epiphyseal line is an epiphyseal plate that has become ossified. The process of it forming from an epiphyseal plate is named epiphyseal closure. In adult humans, it marks the point of fusion between the epiphysis and the metaphysis.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to trauma and orthopaedics:

















