
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, and enable mobility. Bones come in a variety of shapes and sizes and have complex internal and external structures. They are lightweight yet strong and hard and serve multiple functions.

Bone healing, or fracture healing, is a proliferative physiological process in which the body facilitates the repair of a bone fracture.

A callus is an area of thickened and sometimes hardened skin that forms as a response to repeated friction, pressure, or other irritation. Since repeated contact is required, calluses are most often found on the feet and hands, but they may occur anywhere on the skin. Some degree of callus, such as on the bottom of the foot, is normal.

A bone fracture is a medical condition in which there is a partial or complete break in the continuity of any bone in the body. In more severe cases, the bone may be broken into several fragments, known as a comminuted fracture. A bone fracture may be the result of high force impact or stress, or a minimal trauma injury as a result of certain medical conditions that weaken the bones, such as osteoporosis, osteopenia, bone cancer, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where the fracture is then properly termed a pathologic fracture.
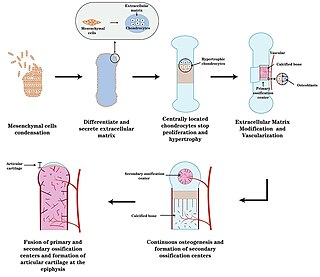
Endochondral ossification is one of the two essential pathways by which bone tissue is produced during fetal development of the mammalian skeletal system, the other pathway being intramembranous ossification. Both endochondral and intramembranous processes initiate from a precursor mesenchymal tissue, but their transformations into bone are different. In intramembranous ossification, mesenchymal tissue is directly converted into bone. On the other hand, endochondral ossification starts with mesenchymal tissue turning into an intermediate cartilage stage, which is eventually substituted by bone.

Intramembranous ossification is one of the two essential processes during fetal development of the gnathostome skeletal system by which rudimentary bone tissue is created. Intramembranous ossification is also an essential process during the natural healing of bone fractures and the rudimentary formation of bones of the head.
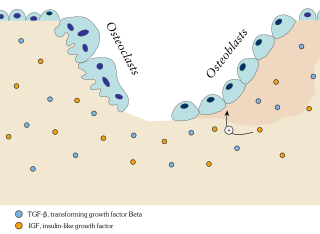
Ossification in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor.
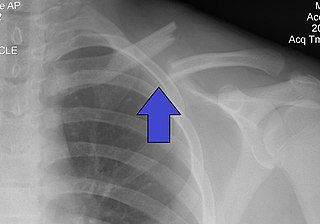
A clavicle fracture, also known as a broken collarbone, is a bone fracture of the clavicle. Symptoms typically include pain at the site of the break and a decreased ability to move the affected arm. Complications can include a collection of air in the pleural space surrounding the lung (pneumothorax), injury to the nerves or blood vessels in the area, and an unpleasant appearance.
Jebel Sahaba is a prehistoric cemetery site in the Nile Valley, near the northern border of Sudan with Egypt in Northeast Africa. It is associated with the Qadan culture. It was discovered in 1964 by a team led by Fred Wendorf.
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) are a group of growth factors also known as cytokines and as metabologens. Professor Marshall Urist and Professor Hari Reddi discovered their ability to induce the formation of bone and cartilage, BMPs are now considered to constitute a group of pivotal morphogenetic signals, orchestrating tissue architecture throughout the body. The important functioning of BMP signals in physiology is emphasized by the multitude of roles for dysregulated BMP signalling in pathological processes. Cancerous disease often involves misregulation of the BMP signalling system. Absence of BMP signalling is, for instance, an important factor in the progression of colon cancer, and conversely, overactivation of BMP signalling following reflux-induced esophagitis provokes Barrett's esophagus and is thus instrumental in the development of esophageal adenocarcinoma.

In medicine, the Ilizarov apparatus is a type of external fixation apparatus used in orthopedic surgery to lengthen or to reshape the damaged bones of an arm or a leg; used as a limb-sparing technique for treating complex fractures and open bone fractures; and used to treat an infected non-union of bones, which cannot be surgically resolved. The Ilizarov apparatus corrects angular deformity in a leg, corrects differences in the lengths of the legs of the patient, and resolves osteopathic non-unions; further developments of the Ilizarov apparatus progressed to the development of the Taylor Spatial Frame.

Paleopathology, also spelled palaeopathology, is the study of ancient diseases and injuries in organisms through the examination of fossils, mummified tissue, skeletal remains, and analysis of coprolites. Specific sources in the study of ancient human diseases may include early documents, illustrations from early books, painting and sculpture from the past. All these objects provide information on the evolution of diseases as well as how past civilizations treated conditions. Studies have historically focused on humans, although there is no evidence that humans are more prone to pathologies than any other animal.

Nonunion is permanent failure of healing following a broken bone unless intervention is performed. A fracture with nonunion generally forms a structural resemblance to a fibrous joint, and is therefore often called a "false joint" or pseudoarthrosis. The diagnosis is generally made when there is no healing between two sets of medical imaging, such as X-ray or CT scan. This is generally after 6–8 months.

Distraction osteogenesis (DO), also called callus distraction, callotasis and osteodistraction, is a process used in orthopedic surgery, podiatric surgery, and oral and maxillofacial surgery to repair skeletal deformities and in reconstructive surgery. The procedure involves cutting and slowly separating bone, allowing the bone healing process to fill in the gap.

Osteochondritis dissecans is a joint disorder primarily of the subchondral bone in which cracks form in the articular cartilage and the underlying subchondral bone. OCD usually causes pain during and after sports. In later stages of the disorder there will be swelling of the affected joint that catches and locks during movement. Physical examination in the early stages does only show pain as symptom, in later stages there could be an effusion, tenderness, and a crackling sound with joint movement.

Short bones are designated as those bones that are more or less equal in length, width, and thickness. They include the tarsals in the ankle and the carpals in the wrist. They are one of five types of bones: short, long, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Most short bones are named according to their shape as they exhibit a variety of complex morphological features
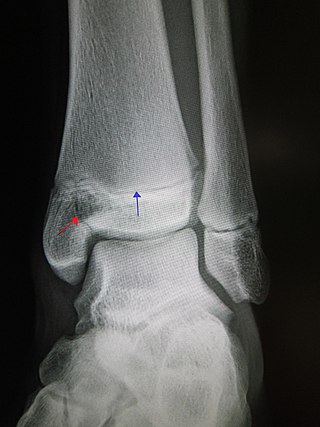
A Salter–Harris fracture is a fracture that involves the epiphyseal plate of a bone, specifically the zone of provisional calcification. It is thus a form of child bone fracture. It is a common injury found in children, occurring in 15% of childhood long bone fractures. This type of fracture and its classification system is named for Robert B. Salter and William H. Harris who created and published this classification system in the Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery in 1963.

Transcription factor Sp7, also called osterix (Osx), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SP7 gene. It is a member of the Sp family of zinc-finger transcription factors It is highly conserved among bone-forming vertebrate species It plays a major role, along with Runx2 and Dlx5 in driving the differentiation of mesenchymal precursor cells into osteoblasts and eventually osteocytes. Sp7 also plays a regulatory role by inhibiting chondrocyte differentiation maintaining the balance between differentiation of mesenchymal precursor cells into ossified bone or cartilage. Mutations of this gene have been associated with multiple dysfunctional bone phenotypes in vertebrates. During development, a mouse embryo model with Sp7 expression knocked out had no formation of bone tissue. Through the use of GWAS studies, the Sp7 locus in humans has been strongly associated with bone mass density. In addition there is significant genetic evidence for its role in diseases such as Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI).

Ossinodus is an extinct genus of stem tetrapod. Fossils have been found from the Ducabrook Formation in Queensland, Australia dating back to the middle Visean stage of the Early Carboniferous (Mississippian). It was originally placed within the family Whatcheeriidae, but the absence of an intertemporal bone as suggested by a recent reconstruction of the skull based on fragmentary material may prove it to be stemward of all whatcheeriids.
Craniofacial regeneration refers to the biological process by which the skull and face regrow to heal an injury. This page covers birth defects and injuries related to the craniofacial region, the mechanisms behind the regeneration, the medical application of these processes, and the scientific research conducted on this specific regeneration. This regeneration is not to be confused with tooth regeneration. Craniofacial regrowth is broadly related to the mechanisms of general bone healing.


















