
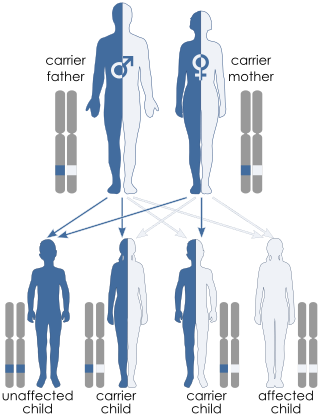
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorders are the most common, the term is mostly used when discussing disorders with a single genetic cause, either in a gene or chromosome. The mutation responsible can occur spontaneously before embryonic development, or it can be inherited from two parents who are carriers of a faulty gene or from a parent with the disorder. When the genetic disorder is inherited from one or both parents, it is also classified as a hereditary disease. Some disorders are caused by a mutation on the X chromosome and have X-linked inheritance. Very few disorders are inherited on the Y chromosome or mitochondrial DNA.

Cystinosis is a lysosomal storage disease characterized by the abnormal accumulation of cystine, the oxidized dimer of the amino acid cysteine. It is a genetic disorder that follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. It is a rare autosomal recessive disorder resulting from accumulation of free cystine in lysosomes, eventually leading to intracellular crystal formation throughout the body. Cystinosis is the most common cause of Fanconi syndrome in the pediatric age group. Fanconi syndrome occurs when the function of cells in renal tubules is impaired, leading to abnormal amounts of carbohydrates and amino acids in the urine, excessive urination, and low blood levels of potassium and phosphates.

Citrullinemia is an autosomal recessive urea cycle disorder that causes ammonia and other toxic substances to accumulate in the blood.
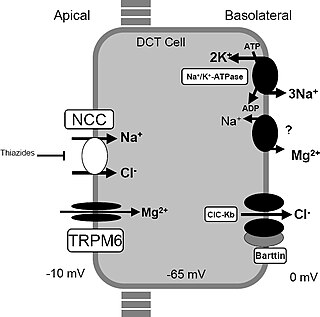
Gitelman syndrome (GS) is an autosomal recessive kidney tubule disorder characterized by low blood levels of potassium and magnesium, decreased excretion of calcium in the urine, and elevated blood pH. It is the most frequent hereditary salt-losing tubulopathy. Gitelman syndrome is caused by disease-causing variants on both alleles of the SLC12A3 gene. The SLC12A3 gene encodes the thiazide-sensitive sodium-chloride cotransporter, which can be found in the distal convoluted tubule of the kidney.
Severe congenital neutropenia (SCN), also often known as Kostmann syndrome or disease, is a group of rare disorders that affect myelopoiesis, causing a congenital form of neutropenia, usually without other physical malformations. SCN manifests in infancy with life-threatening bacterial infections. It causes severe pyogenic infections. It can be caused by autosomal dominant inheritance of the ELANE gene, autosomal recessive inheritance of the HAX1 gene. There is an increased risk of leukemia and myelodysplastic cancers.

Mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency is an autosomal recessive fatty acid oxidation disorder that prevents the body from converting certain fats to energy, particularly during periods without food. People with this disorder have inadequate levels of an enzyme that breaks down a certain group of fats called long-chain fatty acids.

Chromosome 19 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 19 spans more than 61.7 million base pairs, the building material of DNA. It is considered the most gene-rich chromosome containing roughly 1,500 genes, despite accounting for only 2 percent of the human genome.

Apparent mineralocorticoid excess is an autosomal recessive disorder causing hypertension, hypernatremia and hypokalemia. It results from mutations in the HSD11B2 gene, which encodes the kidney isozyme of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2. In an unaffected individual, this isozyme inactivates circulating cortisol to the less active metabolite cortisone. The inactivating mutation leads to elevated local concentrations of cortisol in the aldosterone sensitive tissues like the kidney. Cortisol at high concentrations can cross-react and activate the mineralocorticoid receptor due to the non-selectivity of the receptor, leading to aldosterone-like effects in the kidney. This is what causes the hypokalemia, hypertension, and hypernatremia associated with the syndrome. Patients often present with severe hypertension and end-organ changes associated with it like left ventricular hypertrophy, retinal, renal and neurological vascular changes along with growth retardation and failure to thrive. In serum both aldosterone and renin levels are low.

Alström syndrome (AS), also called Alström–Hallgren syndrome, is a very rare autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterised by childhood obesity and multiple organ dysfunction. Symptoms include early-onset type 2 diabetes, cone-rod dystrophy resulting in blindness, sensorineural hearing loss and dilated cardiomyopathy. Endocrine disorders typically also occur, such as hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism and hypothyroidism, as well as acanthosis nigricans resulting from hyperinsulinemia. Developmental delay is seen in almost half of people with Alström syndrome.
Pseudohypoaldosteronism (PHA) is a condition that mimics hypoaldosteronism. However, the condition is due to a failure of response to aldosterone, and levels of aldosterone are actually elevated, due to a lack of feedback inhibition.
XX gonadal dysgenesis is a type of female hypogonadism in which the ovaries do not function to induce puberty in an otherwise normal girl whose karyotype is found to be 46,XX. With nonfunctional streak ovaries, she is low in estrogen levels (hypoestrogenic) and has high levels of FSH and LH. Estrogen and progesterone therapy is usually then commenced. Some cases are considered a severe version of premature ovarian failure where the ovaries fail before puberty.
Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I deficiency is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that causes ammonia to accumulate in the blood due to a lack of the enzyme carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. Ammonia, which is formed when proteins are broken down in the body, is toxic if the levels become too high. The nervous system is especially sensitive to the effects of excess ammonia.
Vici syndrome, also called immunodeficiency with cleft lip/palate, cataract, hypopigmentation and absent corpus callosum, is a rare autosomal recessive congenital disorder characterized by albinism, agenesis of the corpus callosum, cataracts, cardiomyopathy, severe psychomotor retardation, seizures, immunodeficiency and recurrent severe infections. To date, about 50 cases have been reported.

Spondylocostal dysostosis, also known as Jarcho-Levin syndrome (JLS), is a rare, heritable axial skeleton growth disorder. It is characterized by widespread and sometimes severe malformations of the vertebral column and ribs, shortened thorax, and moderate to severe scoliosis and kyphosis. Individuals with Jarcho-Levin typically appear to have a short trunk and neck, with arms appearing relatively long in comparison, and a slightly protuberant abdomen. Severely affected individuals may have life-threatening pulmonary complications due to deformities of the thorax. The syndrome was first described by Saul Jarcho and Paul M. Levin at Johns Hopkins University in 1938.

SARS and cytoplasmic seryl-tRNA synthetase are a human gene and its encoded enzyme product, respectively. SARS belongs to the class II amino-acyl tRNA family and is found in all humans; its encoded enzyme, seryl-tRNA synthetase, is involved in protein translation and is related to several bacterial and yeast counterparts.
Phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial (FARS2) is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FARS2 gene. This protein encoded by FARS2 localizes to the mitochondrion and plays a role in mitochondrial protein translation. Mutations in this gene have been associated with combined oxidative phosphorylation deficiency 14, also known as Alpers encephalopathy, as well as spastic paraplegia 77 and infantile-onset epilepsy and cytochrome c oxidase deficiency.

Seryl-tRNA synthetase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SARS2 gene.
Björnstad syndrome is an autosomal recessive congenital condition involving pili torti, sensorineural deafness, and hair abnormalities. It was first characterized in 1965, in Oslo, by prof. Roar Theodor Bjørnstad after he observed an association between pili torti and hearing loss. The condition is extremely rare, with less than 50 cases documented in medical literature worldwide.

Pontocerebellar hypoplasia (PCH) is a heterogeneous group of rare neurodegenerative disorders caused by genetic mutations and characterised by progressive atrophy of various parts of the brain such as the cerebellum or brainstem. Where known, these disorders are inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. There is no known cure for PCH.














