CAMP responsive element binding protein-like 1, also known as CREBL1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CREBL1 gene. [5] [6]
CAMP responsive element binding protein-like 1, also known as CREBL1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CREBL1 gene. [5] [6]
The protein encoded by this gene bears sequence similarity with the Creb/ATF subfamily of the bZip superfamily of transcription factors. It localizes to both the cytoplasm and the nucleus. The gene localizes to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class III region on chromosome 6. [5]

CREB-TF is a cellular transcription factor. It binds to certain DNA sequences called cAMP response elements (CRE), thereby increasing or decreasing the transcription of the genes. CREB was first described in 1987 as a cAMP-responsive transcription factor regulating the somatostatin gene.

CAMP responsive element binding protein 1, also known as CREB-1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREB1 gene. This protein binds the cAMP response element, a DNA nucleotide sequence present in many viral and cellular promoters. The binding of CREB1 stimulates transcription.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-3 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ATF3 gene.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF1 gene.

Activating transcription factor 4 , also known as ATF4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF4 gene.

Activating transcription factor 6, also known as ATF6, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ATF6 gene and is involved in the unfolded protein response.
Serum response factor, also known as SRF, is a transcription factor protein.

Activating transcription factor 2, also known as ATF2, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ATF2 gene.

Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2A gene. MEF2A is a transcription factor in the Mef2 family. In humans it is located on chromosome 15q26. Certain mutations in MEF2A cause an autosomal dominant form of coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction.
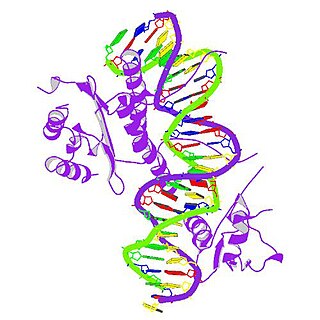
cAMP responsive element modulator is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREM gene, and it belongs to the cAMP-responsive element binding protein family. It has multiple isoforms, which act either as repressors or activators. CREB family is important for in regulating transcription in response to various stresses, metabolic and developmental signals. CREM transcription factors also play an important role in many physiological systems, such as cardiac function, circadian rhythms, locomotion and spermatogenesis.

Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-5 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPS6KA5 gene. This kinase, together with RPS6KA4, are thought to mediate the phosphorylation of histone H3, linked to the expression of immediate early genes.

Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPS6KA2 gene.

MHC class II regulatory factor RFX1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the RFX1 gene located on the short arm of chromosome 19.

Cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREB3 gene.

Activating transcription factor 5, also known as ATF5, is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ATF5 gene.

Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPS6KA4 gene.

CREB regulated transcription coactivator 2, also known as CRTC2, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CRTC2 gene.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF7 gene.

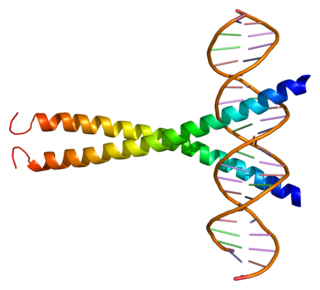
The Basic Leucine Zipper Domain is found in many DNA binding eukaryotic proteins. One part of the domain contains a region that mediates sequence specific DNA binding properties and the leucine zipper that is required to hold together (dimerize) two DNA binding regions. The DNA binding region comprises a number of basic amino acids such as arginine and lysine. Proteins containing this domain are transcription factors.

CREB/ATF bZIP transcription factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CREBZF gene.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.