External links
- Winged-Helix+Transcription+Factors at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consisting of about 110 amino acids, the domain in winged-helix transcription factors (see Regulation of gene expression) has four helices and a two-strand beta-sheet.
These proteins are classified into 19 families called FoxA-FoxS.
Mutations in FoxP proteins are implicated in human autoimmune diseases.
FOXproteins are a family of transcription factors that play important roles in regulating the expression of genes involved in cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, and longevity. Many FOX proteins are important to embryonic development. FOX proteins also have pioneering transcription activity by being able to bind condensed chromatin during cell differentiation processes.
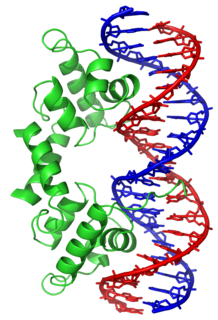
In proteins, the helix-turn-helix (HTH) is a major structural motif capable of binding DNA. Each monomer incorporates two α helices, joined by a short strand of amino acids, that bind to the major groove of DNA. The HTH motif occurs in many proteins that regulate gene expression. It should not be confused with the helix–loop–helix motif.

A basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) is a protein structural motif that characterizes one of the largest families of dimerizing transcription factors. The word "basic" does not refer to complexity but to the chemistry of the motif because transcription factors in general contain basic amino acid residues in order to facilitate DNA binding.
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure.
Basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factors are, as their name indicates, transcription factors containing both Basic helix-loop-helix and leucine zipper motifs.

Transcription factor 3, also known as TCF3, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCF3 gene. TCF3 has been shown to directly enhance Hes1 expression.

DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ID2 gene.

Forkhead box C1, also known as FOXC1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the FOXC1 gene.

DNA-binding protein inhibitor ID-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ID3 gene.

Forkhead box protein H1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXH1 gene.

Transcription factor RFX4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RFX4 gene.

Forkhead box protein P4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXP4 gene.

Forkhead box protein N1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXN1 gene.

Pho4 is a protein with a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor. It is found in S. cerevisiae and other yeasts. It functions as a transcription factor to regulate phosphate responsive genes located in yeast cells. The Pho4 protein homodimer is able to do this by binding to DNA sequences containing the bHLH binding site 5'-CACGTG-3'. This sequence is found in the promoters of genes up-regulated in response to phosphate availability such as the PHO5 gene.
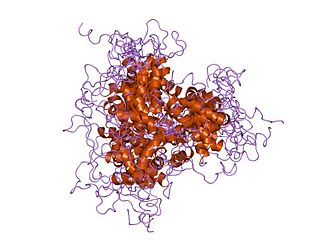
The fork head domain is a type of protein domain that is often found in transcription factors and whose purpose is to bind DNA.

Forkhead box protein A2 (FOXA2), also known as hepatocyte nuclear factor 3-beta (HNF-3B), is a transcription factor that plays an important role during development, in mature tissues and, when dysregulated or mutated, also in cancer.

Forkhead box protein J1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXJ1 gene. It is a member of the Forkhead/winged helix (FOX) family of transcription factors that is involved in ciliogenesis. FOXJ1 is expressed in ciliated cells of the lung, choroid plexus, reproductive tract, embryonic kidney and pre-somite embryo stage.

Forkhead box D1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXD1 gene. Forkhead d1 is a kidney expressed transcription factor maps at the chromosome 5 at position 5q12—q13, identified in Drosophila forkhead protein and mammalian HNF3 transcription factor. The name of was derived from two spiked head structures in the embryos of Drosophila forkhead mutant. It belong to transcription factor family that displays remarkable functional diversity and involved in a wide variety of biological processes. The most commonly used synonyms for Forkhead D1 are, FOX D1, FREAC-4 and BF2.

Transcription factor 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCF15 gene.

Forkhead box S1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FOXS1 gene.