Related Research Articles

Transcription is the process of copying a segment of DNA into RNA. The segments of DNA transcribed into RNA molecules that can encode proteins produce messenger RNA (mRNA). Other segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules called non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs).

The preinitiation complex is a complex of approximately 100 proteins that is necessary for the transcription of protein-coding genes in eukaryotes and archaea. The preinitiation complex positions RNA polymerase II at gene transcription start sites, denatures the DNA, and positions the DNA in the RNA polymerase II active site for transcription.

RNA polymerase II is a multiprotein complex that transcribes DNA into precursors of messenger RNA (mRNA) and most small nuclear RNA (snRNA) and microRNA. It is one of the three RNAP enzymes found in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. A 550 kDa complex of 12 subunits, RNAP II is the most studied type of RNA polymerase. A wide range of transcription factors are required for it to bind to upstream gene promoters and begin transcription.

General transcription factors (GTFs), also known as basal transcriptional factors, are a class of protein transcription factors that bind to specific sites (promoter) on DNA to activate transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA. GTFs, RNA polymerase, and the mediator constitute the basic transcriptional apparatus that first bind to the promoter, then start transcription. GTFs are also intimately involved in the process of gene regulation, and most are required for life.

The TATA-binding protein (TBP) is a general transcription factor that binds to a DNA sequence called the TATA box. This DNA sequence is found about 30 base pairs upstream of the transcription start site in some eukaryotic gene promoters.
Transcription factor II D (TFIID) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a form of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II that is recruited to the promoters of protein-coding genes in living cells. It consists of RNA polymerase II, a subset of general transcription factors, and regulatory proteins known as SRB proteins. Before the start of transcription, the transcription Factor II D (TFIID) complex binds to the core promoter DNA of the gene through specific recognition of promoter sequence motifs, including the TATA box, Initiator, Downstream Promoter, Motif Ten, or Downstream Regulatory elements.

Eukaryotic transcription is the elaborate process that eukaryotic cells use to copy genetic information stored in DNA into units of transportable complementary RNA replica. Gene transcription occurs in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Unlike prokaryotic RNA polymerase that initiates the transcription of all different types of RNA, RNA polymerase in eukaryotes comes in three variations, each translating a different type of gene. A eukaryotic cell has a nucleus that separates the processes of transcription and translation. Eukaryotic transcription occurs within the nucleus where DNA is packaged into nucleosomes and higher order chromatin structures. The complexity of the eukaryotic genome necessitates a great variety and complexity of gene expression control.
Transcription factor TFIIA is a nuclear protein involved in the RNA polymerase II-dependent transcription of DNA. TFIIA is one of several general (basal) transcription factors (GTFs) that are required for all transcription events that use RNA polymerase II. Other GTFs include TFIID, a complex composed of the TATA binding protein TBP and TBP-associated factors (TAFs), as well as the factors TFIIB, TFIIE, TFIIF, and TFIIH. Together, these factors are responsible for promoter recognition and the formation of a transcription preinitiation complex (PIC) capable of initiating RNA synthesis from a DNA template.
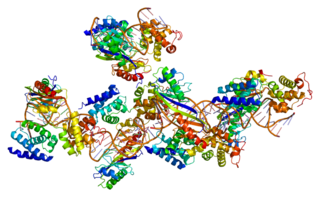
Transcription factor II B (TFIIB) is a general transcription factor that is involved in the formation of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex (PIC) and aids in stimulating transcription initiation. TFIIB is localised to the nucleus and provides a platform for PIC formation by binding and stabilising the DNA-TBP complex and by recruiting RNA polymerase II and other transcription factors. It is encoded by the TFIIB gene, and is homologous to archaeal transcription factor B and analogous to bacterial sigma factors.
Transcription factor II E (TFIIE) is one of several general transcription factors that make up the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. It is a tetramer of two alpha and two beta chains and interacts with TAF6/TAFII80, ATF7IP, and varicella-zoster virus IE63 protein.

General transcription factor IIH subunit 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2H4 gene.
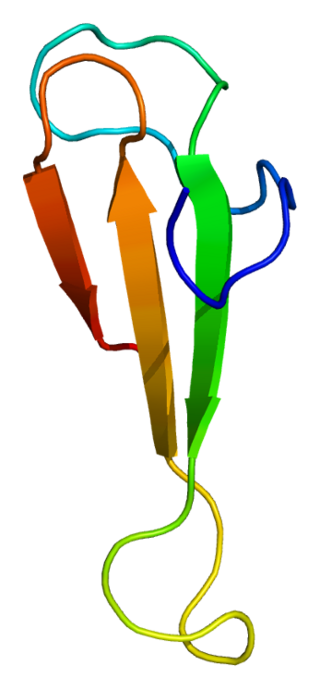
Transcription elongation factor A protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TCEA1 gene.

RNA polymerase II subunit A C-terminal domain phosphatase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CTDP1 gene.

General transcription factor IIH subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2H2 gene.

General transcription factor IIF subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2F1 gene.
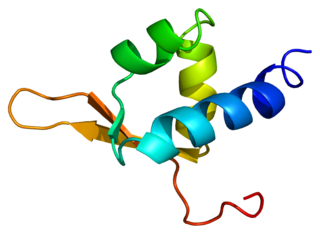
General transcription factor IIF subunit 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GTF2F2 gene.

DNA-directed RNA polymerase, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the POLRMT gene.
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme is a form of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II that is recruited to the promoters of protein-coding genes in living cells. It consists of RNA polymerase II, a subset of general transcription factors, and regulatory proteins known as SRB proteins.

The B recognition element (BRE) is a DNA sequence found in the promoter region of most genes in eukaryotes and Archaea. The BRE is a cis-regulatory element that is found immediately near TATA box, and consists of 7 nucleotides. There are two sets of BREs: one (BREu) found immediately upstream of the TATA box, with the consensus SSRCGCC; the other (BREd) found around 7 nucleotides downstream, with the consensus RTDKKKK.

Archaeal transcription factor B is a protein family of extrinsic transcription factors that guide the initiation of RNA transcription in organisms that fall under the domain of Archaea. It is homologous to eukaryotic TFIIB and, more distantly, to bacterial sigma factor. Like these proteins, it is involved in forming transcription preinitiation complexes. Its structure includes several conserved motifs which interact with DNA and other transcription factors, notably the single type of RNA polymerase that performs transcription in Archaea.
References
- ↑ Lewin, Benjamin (2004). Genes VIII. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Prentice Hall. pp. 636–637. ISBN 0-13-144946-X.
- ↑ Lee TI, Young RA (2000). "Transcription of eukaryotic protein-coding genes". Annu. Rev. Genet. 34: 77–137. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.34.1.77. PMID 11092823.
- ↑ Kim TK, Lagrange T, Wang YH, Griffith JD, Reinberg D, Ebright RH (1997). "Trajectory of DNA in the RNA polymerase II transcription preinitiation complex". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94 (23): 12268–73. Bibcode:1997PNAS...9412268K. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.23.12268 . PMC 24903 . PMID 9356438.
- ↑ Finkelstein A, Kostrub CF, Li J, Chavez DP, Wang BQ, Fang SM, Greenblatt J, Burton ZF (1992). "A cDNA encoding RAP74, a general initiation factor for transcription by RNA polymerase II". Nature. 355 (6359): 464–7. Bibcode:1992Natur.355..464F. doi:10.1038/355464a0. PMID 1734284. S2CID 1241044.
- ↑ Heng HH, Xiao H, Shi XM, Greenblatt J, Tsui LC (1994). "Genes encoding general initiation factors for RNA polymerase II transcription are dispersed in the human genome". Hum. Mol. Genet. 3 (1): 61–4. doi:10.1093/hmg/3.1.61. PMID 8162052.
- ↑ Purrello M, Di Pietro C, Rapisarda A, Mirabile E, Motta S, Sichel G, Grzeschik KH (1995). "Genetic characterization of general transcription factors TFIIF and TFIIB of Homo sapiens sapiens". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 69 (1–2): 75–80. doi:10.1159/000133942. PMID 7835093.