| Exocrine gland | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | glandula exocrina |
| MeSH | D005088 |
| TH | H2.00.02.0.03014 |
| FMA | 9596 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
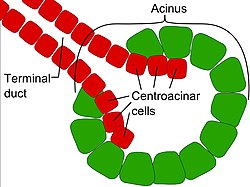
Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances onto an epithelial surface by way of a duct. [1] Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous glands. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have merocrine and apocrine types.




