arma pidar ir arnas Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.

In animals, a gland is a group of cells in an animal's body that synthesizes substances for release into the bloodstream or into cavities inside the body or its outer surface.

Exocrine glands are glands that secrete substances on to an epithelial surface by way of a duct. Examples of exocrine glands include sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, sebaceous, prostate and mucous. Exocrine glands are one of two types of glands in the human body, the other being endocrine glands, which secrete their products directly into the bloodstream. The liver and pancreas are both exocrine and endocrine glands; they are exocrine glands because they secrete products—bile and pancreatic juice—into the gastrointestinal tract through a series of ducts, and endocrine because they secrete other substances directly into the bloodstream. Exocrine sweat glands are part of the integumentary system; they have eccrine and apocrine types.

In biology, tissue is a historically derived biological organizational level between cells and a complete organ. A tissue is therefore often thought of as assembly of similar cells and their extracellular matrix from the same origin that together carry out a specific function. Organs are then formed by the functional grouping together of multiple tissues.

Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin.

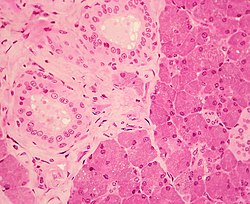
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word mamma, "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates, the udder in ruminants, and the dugs of other animals. Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances.

The parotid gland is a major salivary gland in many animals. In humans, the two parotid glands are present on either side of the mouth and in front of both ears. They are the largest of the salivary glands. Each parotid is wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secretes serous saliva through the parotid duct into the mouth, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches. There are also two other types of salivary glands; they are submandibular and sublingual glands. Sometimes accessory parotid glands are found close to the main parotid glands.

Transitional epithelium is a type of stratified epithelium. Transitional epithelium is a type of tissue that changes shape in response to stretching. The transitional epithelium usually appears cuboidal when relaxed and squamous when stretched. This tissue consists of multiple layers of epithelial cells which can contract and expand in order to adapt to the degree of distension needed. Transitional epithelium lines the organs of the urinary system and is known here as urothelium. The bladder for example has a need for great distension.
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed lamina propria. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved.

Sialadenitis (sialoadenitis) is inflammation of salivary glands, usually the major ones, the most common being the parotid gland, followed by submandibular and sublingual glands. It should not be confused with sialadenosis (sialosis) which is a non-inflammatory enlargement of the major salivary glands.

Stratified columnar epithelium is a rare type of epithelial tissue composed of column-shaped cells arranged in multiple layers. It is found in the conjunctiva, pharynx, anus, and male urethra. It also occurs in embryo.

A pseudostratified epithelium is a type of epithelium that, though comprising only a single layer of cells, has its cell nuclei positioned in a manner suggestive of stratified epithelia. As it rarely occurs as squamous or cuboidal epithelia, it is usually considered synonymous with the term pseudostratified columnar epithelium.

A stratified squamous epithelium consists of squamous (flattened) epithelial cells arranged in layers upon a basal membrane. Only one layer is in contact with the basement membrane; the other layers adhere to one another to maintain structural integrity. Although this epithelium is referred to as squamous, many cells within the layers may not be flattened; this is due to the convention of naming epithelia according to the cell type at the surface. In the deeper layers, the cells may be columnar or cuboidal. There are no intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is well suited to areas in the body subject to constant abrasion, as the thickest layers can be sequentially sloughed off and replaced before the basement membrane is exposed. It forms the outermost layer of the skin and the inner lining of the mouth, esophagus and vagina.

Myoepithelial cells are cells usually found in glandular epithelium as a thin layer above the basement membrane but generally beneath the luminal cells. These may be positive for alpha smooth muscle actin and can contract and expel the secretions of exocrine glands. They are found in the sweat glands, mammary glands, lacrimal glands, and salivary glands. Myoepithelial cells in these cases constitute the basal cell layer of an epithelium that harbors the epithelial progenitor. In the case of wound healing, myoepithelial cells reactively proliferate. Presence of myoepithelial cells in a hyperplastic tissue proves the benignity of the gland and, when absent, indicates cancer. Only rare cancers like adenoid cystic carcinomas contains myoepithelial cells as one of the malignant components.

In anatomy and physiology, a duct is a circumscribed channel leading from an exocrine gland or organ.

Simple cuboidal epithelium is a type of epithelium that consists of a single layer of cuboidal (cube-like) cells which have large, spherical and central nuclei.

Eccrine sweat glands are the major sweat glands of the human body, found in virtually all skin, with the highest density in palm and soles, then on the head, but much less on the torso and the extremities. In other mammals, they are relatively sparse, being found mainly on hairless areas such as foot pads. They reach their peak of development in humans, where they may number 200–400/cm2 of skin surface. They produce a clear, odorless substance, sweat, consisting primarily of water. These are present from birth. Their secretory part is present deep inside the dermis.

The gastrointestinal wall of the gastrointestinal tract is made up of four layers of specialised tissue. From the inner cavity of the gut outwards, these are:
- Mucosa
- Submucosa
- Muscular layer
- Serosa or adventitia

Anatomical terminology is used to describe microanatomical structures. This helps describe precisely the structure, layout and position of an object, and minimises ambiguity. An internationally accepted lexicon is Terminologia Histologica.
The monotremes represent the order of extant mammals most distantly related to humans. The platypus is indigenous to eastern Australia; the short-beaked echidna is indigenous to Australia and Papua New Guinea; whereas the long-beaked echidna is restricted to Papua New Guinea and Irian Jaya. Since monotremes exhibit characteristics common with both reptiles and therian mammals, they are of great interest for the study of mammalian evolution.