The nuclear receptor coactivator 2 also known as NCoA-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA2 gene. NCoA-2 is also frequently called glucocorticoid receptor-interacting protein 1 (GRIP1), steroid receptor coactivator-2 (SRC-2), or transcriptional mediators/intermediary factor 2 (TIF2).

Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1-alpha (PGC-1α) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPARGC1A gene. PPARGC1A is also known as human accelerated region 20 (HAR20). It may, therefore, have played a key role in differentiating humans from apes.

Cyclic AMP-dependent transcription factor ATF-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATF1 gene.
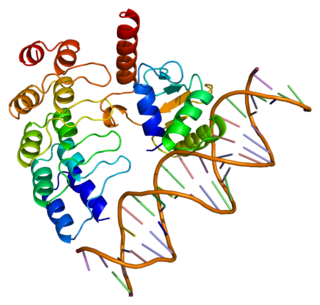
GA-binding protein alpha chain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABPA gene.

COUP-TFII, also known as NR2F2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F2 gene. The COUP acronym stands for chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter.

DNA damage-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DDB1 gene.

Nuclear inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP1R8 gene.

Nuclear receptor coactivator 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NCOA6 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing 24 (TRIM24) also known as transcriptional intermediary factor 1α (TIF1α) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the TRIM24 gene.

Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 21 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MED21 gene.

Nuclear transcription factor Y subunit gamma is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFYC gene.

GA-binding protein subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GABPB1 gene.

Mediator of RNA polymerase II transcription subunit 17 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MED17 gene.

Cbp/p300-interacting transactivator 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CITED1 gene.

Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPRC1 gene.

Dimethyladenosine transferase 2; transcription factor B2, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TFB2M gene.

Biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex 1 subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BLOC1S1 gene.
Mitochondrial biogenesis is the process by which cells increase mitochondrial numbers. It was first described by John Holloszy in the 1960s, when it was discovered that physical endurance training induced higher mitochondrial content levels, leading to greater glucose uptake by muscles. Mitochondrial biogenesis is activated by numerous different signals during times of cellular stress or in response to environmental stimuli, such as aerobic exercise.
Small Maf proteins are basic region leucine zipper-type transcription factors that can bind to DNA and regulate gene regulation. There are three small Maf (sMaf) proteins, namely MafF, MafG, and MafK, in vertebrates. HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC)-approved gene names of MAFF, MAFG and MAFK are “v-maf avian musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog F, G, and K”, respectively.

PPARG coactivator 1 alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPARGC1A gene.