
A basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) is a protein structural motif that characterizes one of the largest families of dimerizing transcription factors. The word "basic" does not refer to complexity but to the chemistry of the motif because transcription factors in general contain basic amino acid residues in order to facilitate DNA binding.

INT-2 proto-oncogene protein also known as FGF-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FGF3 gene.

Agouti-signaling protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ASIP gene. It is responsible for the distribution of melanin pigment in mammals. Agouti interacts with the melanocortin 1 receptor to determine whether the melanocyte produces phaeomelanin, or eumelanin. This interaction is responsible for making distinct light and dark bands in the hairs of animals such as the agouti, which the gene is named after. In other species such as horses, agouti signalling is responsible for determining which parts of the body will be red or black. Mice with wildtype agouti will be grey-brown, with each hair being partly yellow and partly black. Loss of function mutations in mice and other species cause black fur coloration, while mutations causing expression throughout the whole body in mice cause yellow fur and obesity.
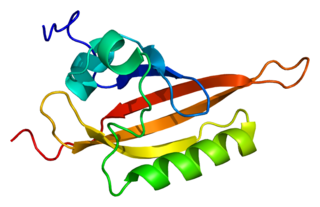
The ARNT gene encodes the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator protein that forms a complex with ligand-bound aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), and is required for receptor function. The encoded protein has also been identified as the beta subunit of a heterodimeric transcription factor, hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF1). A t(1;12)(q21;p13) translocation, which results in a TEL–ARNT fusion protein, is associated with acute myeloblastic leukemia. Three alternatively spliced variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene.

Pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PBX1 gene. The homologous protein in Drosophila is known as extradenticle, and causes changes in embryonic development.
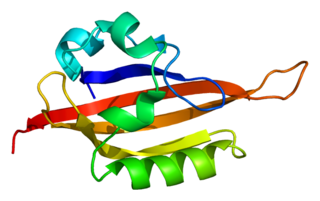
Endothelial PAS domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that is encoded by the EPAS1 gene in mammals. It is a type of hypoxia-inducible factor, a group of transcription factors involved in the physiological response to oxygen concentration. The gene is active under hypoxic conditions. It is also important in the development of the heart, and for maintaining the catecholamine balance required for protection of the heart. Mutation often leads to neuroendocrine tumors.

Single-minded homolog 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SIM2 gene. It plays a major role in the development of the central nervous system midline as well as the construction of the face and head.

40S ribosomal protein S4, X isoform is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPS4X gene.

Polyhomeotic-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PHC1 gene.

Protein atonal homolog 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ATOH1 gene.

Protein deltex-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DTX1 gene.

Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ARNT2 gene.
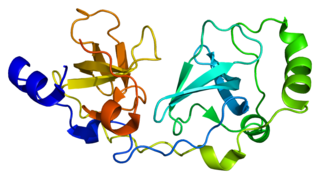
Polycomb protein SCMH1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCMH1 gene.

Disco-interacting protein 2 homolog A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIP2A gene.

A Per-Arnt-Sim (PAS) domain is a protein domain found in all kingdoms of life. Generally, the PAS domain acts as a molecular sensor, whereby small molecules and other proteins associate via binding of the PAS domain. Due to this sensing capability, the PAS domain has been shown as the key structural motif involved in protein-protein interactions of the circadian clock, and it is also a common motif found in signaling proteins, where it functions as a signaling sensor.
Single-minded may refer to:
The achaete-scute complex (AS-C) is a group of four genes in the fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster. These genes encode basic helix-loop-helix transcription factors that have been best studied in their regulation of nervous system development. Because of their role in specifying neuroblast fate, the genes of the AS-C are called proneural genes. However, the AS-C has non-proneural functions, such as specifying muscle and gut progenitors. Homologues of AS-C in other animals, including humans and other vertebrates, have similar functions.

Dachshund homolog 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DACH2 gene.

Disco interacting protein 2 homolog C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DIP2C gene.
dClock (clk) is a gene located on the 3L chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mapping and cloning of the gene indicates that it is the Drosophila homolog of the mouse gene CLOCK (mClock). The Jrk mutation disrupts the transcription cycling of per and tim and manifests dominant effects.


















