Related Research Articles
E2F is a group of genes that encodes a family of transcription factors (TF) in higher eukaryotes. Three of them are activators: E2F1, 2 and E2F3a. Six others act as suppressors: E2F3b, E2F4-8. All of them are involved in the cell cycle regulation and synthesis of DNA in mammalian cells. E2Fs as TFs bind to the TTTCCCGC consensus binding site in the target promoter sequence.

The progesterone receptor (PR), also known as NR3C3 or nuclear receptor subfamily 3, group C, member 3, is a protein found inside cells. It is activated by the steroid hormone progesterone.
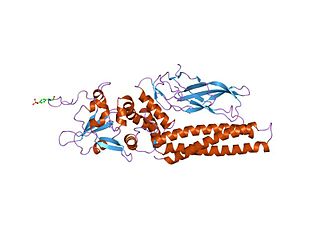
Members of the signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) protein family are intracellular transcription factors that mediate many aspects of cellular immunity, proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. They are primarily activated by membrane receptor-associated Janus kinases (JAK). Dysregulation of this pathway is frequently observed in primary tumors and leads to increased angiogenesis which enhances the survival of tumors and immunosuppression. Gene knockout studies have provided evidence that STAT proteins are involved in the development and function of the immune system and play a role in maintaining immune tolerance and tumor surveillance.
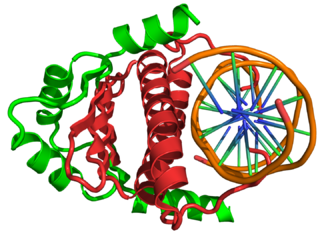
In the field of molecular biology, myocyte enhancer factor-2 (Mef2) proteins are a family of transcription factors which through control of gene expression are important regulators of cellular differentiation and consequently play a critical role in embryonic development. In adult organisms, Mef2 proteins mediate the stress response in some tissues. Mef2 proteins contain both MADS-box and Mef2 DNA-binding domains.
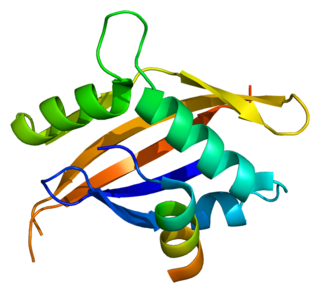
The nuclear receptor coactivator 1 (NCOA1) is a transcriptional coregulatory protein that contains several nuclear receptor interacting domains and an intrinsic histone acetyltransferase activity. NCOA1 is recruited to DNA promotion sites by ligand-activated nuclear receptors. NCOA1, in turn, acylates histones, which makes downstream DNA more accessible to transcription. Hence, NCOA1 assists nuclear receptors in the upregulation of DNA expression.

The Rev-Erb proteins are members of the nuclear receptor (NR) superfamily of intracellular transcription factors and key regulatory components of the circadian clock. There are two forms of the receptor, Rev-Erb alpha and Rev-Erb beta, which are each encoded by a separate gene .
The testicular receptor proteins are members of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. There are two forms of the receptor, TR2 and TR4, each encode by a separate gene.

V-erbA-related protein 2 (EAR-2) also known as NR2F6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F6 gene. V-erbA-related protein 2 is a member of the nuclear receptor family of intracellular transcription factors. It is named after its similarity to v-erbA, a helper of an oncoprotein called v-erbB in avian erythroblastosis virus.
The EGF module-containing Mucin-like hormone Receptors (EMRs) are closely related subgroup of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). These receptors have a unique hybrid structure in which an extracellular epidermal growth factor (EGF)-like domain is fused to a GPCR domain through a mucin-like stalk. There are four variants of EMR labeled 1-4, each encoded by a separate gene. These receptors are predominantly expressed in cells of the immune system and bind ligands such as CD55.

Krueppel-like factor 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF6 gene.

Retinoid X receptor beta (RXR-beta), also known as NR2B2 is a nuclear receptor that in humans is encoded by the RXRB gene.

COUP-TF1 also known as NR2F1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F1 gene. This protein is a member of nuclear hormone receptor family of steroid hormone receptors.

COUP-TFII, also known as NR2F2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NR2F2 gene. The COUP acronym stands for chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter.
Response elements are short sequences of DNA within a gene promoter or enhancer region that are able to bind specific transcription factors and regulate transcription of genes.

Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2D is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MEF2D gene.

Transcription factor NF-E2 45 kDa subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NFE2 gene.

B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL11A gene.

B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL11B gene.

Krueppel-like factor 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KLF9 gene. Previously known as Basic Transcription Element Binding Protein 1, Klf9 is part of the Sp1 C2H2-type zinc finger family of transcription factors. Several previous studies showed Klf9-related regulation of animal development, including cell differentiation of B cells, keratinocytes, and neurons. Klf9 is also a key transcriptional regulator for uterine endometrial cell proliferation, adhesion, and differentiation, all factors that are essential during the process of pregnancy and are turned off during tumorigenesis.

Transcription factor AP-4 , also known as TFAP4, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the TFAP4 gene.
References
- ↑ Qiu Y, Krishnan V, Zeng Z, Gilbert DJ, Copeland NG, Gibson L, Yang-Feng T, Jenkins NA, Tsai MJ, Tsai SY (1995). "Isolation, characterization, and chromosomal localization of mouse and human COUP-TF I and II genes". Genomics. 29 (1): 240–6. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1237. PMID 8530078.
- ↑ Park JI, Tsai SY, Tsai MJ (2003). "Molecular mechanism of chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter-transcription factor (COUP-TF) actions" (PDF). The Keio Journal of Medicine. 52 (3): 174–81. doi: 10.2302/kjm.52.174 . PMID 14529150.