 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | TamoGel |
| Other names | 4-Hydroxytamoxifen; 4-OHT; 4-HT; OHTAM; TamoGel |
| Routes of administration | Topical (gel) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.163.120 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
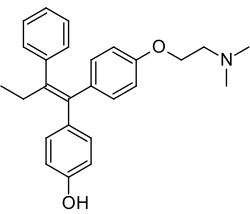
| Formula | C26H29NO2 |
| Molar mass | 387.523 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Afimoxifene, also known as 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4-OHT) and by its tentative brand name TamoGel, is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) of the triphenylethylene group and an active metabolite of tamoxifen. [1] [2] [3] The drug is under development under the tentative brand name TamoGel as a topical gel for the treatment of hyperplasia of the breast. [1] [4] It has completed a phase II clinical trial for cyclical mastalgia, [5] but further studies are required before afimoxifene can be approved for this indication and marketed. [4]
Contents
Afimoxifene is a SERM and hence acts as a tissue-selective agonist–antagonist of the estrogen receptors ERα and ERβ with mixed estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity depending on the tissue. It is also an agonist of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER) with relatively low affinity (100–1,000 nM, relative to 3–6 nM for estradiol). [6] In addition to its estrogenic and antiestrogenic activity, afimoxifene has been found to act as an antagonist of the estrogen-related receptors (ERRs) ERRβ and ERRγ. [7] [8] [9]